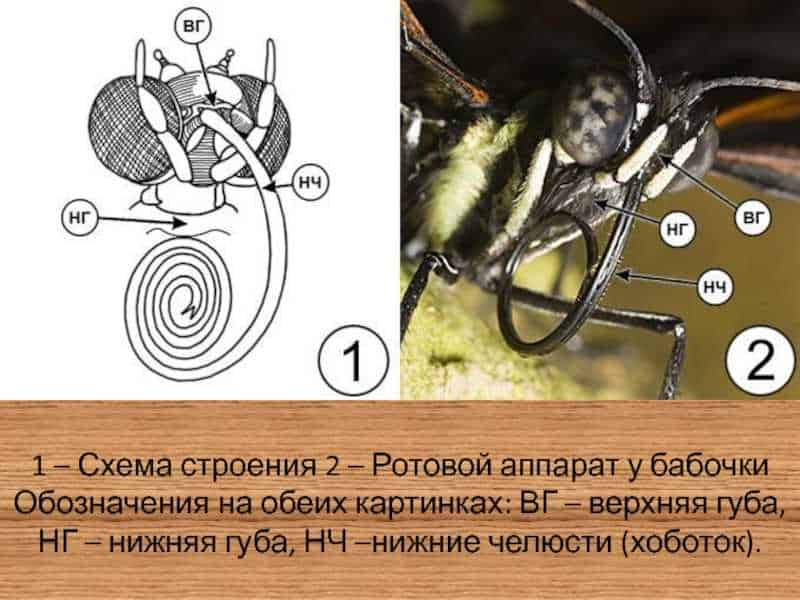
The butterfly has a mouthpart, which is a complex structure specially adapted for feeding. This apparatus consists of several parts, each of which performs its own unique function.
One of the features of the butterfly's mouth apparatus is its flexibility and mobility. It consists of two jaws that can move independently of each other. This allows the butterfly to accurately point its mouthparts towards the flower or other food source.
The main function of the butterfly's mouth apparatus is to suck nectar from flowers. To do this, the butterfly uses its jaws, which are able to compress and decompress, forming a vacuum. Thanks to this, the butterfly can easily and efficiently extract nectar from flowers and move from flower to flower.
In addition, the butterfly's mouthparts can also perform other functions. Some species of butterflies can use their mouthparts to ingest food in the form of pollen or fruit juice. Also, some species of butterflies can use their mouthparts to protect themselves from predators by releasing toxic substances.
The structure of the mouth apparatus of a butterfly:
The butterfly has a mouth apparatus, which is its main organ for nutrition. The mouth apparatus of a butterfly differs from the mouth apparatus of other insects and has a number of features.
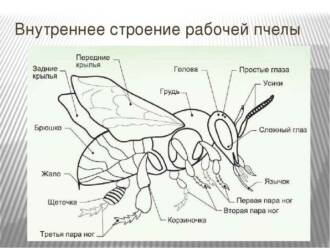
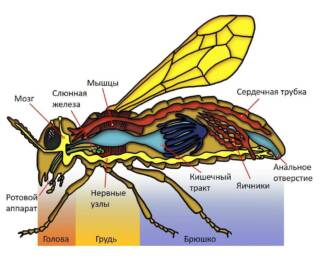
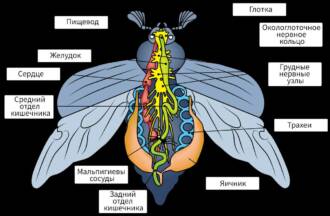
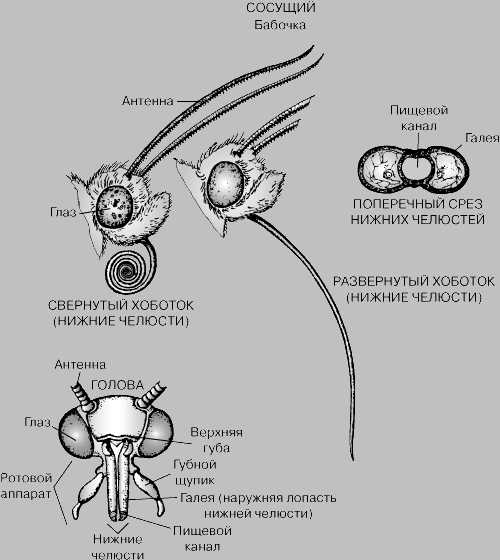
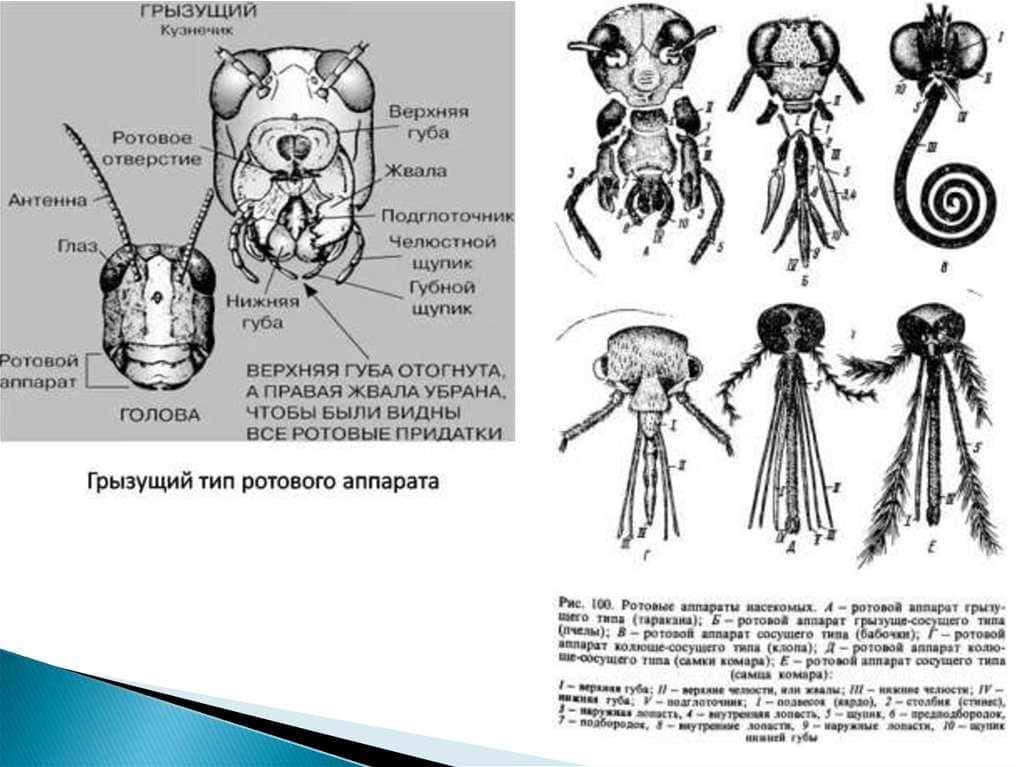
The main parts of the mouth apparatus of a butterfly are the lips, mandibles and pharynx. Lips are thick plates that serve to capture and hold food. The mandibles are two pairs of pointed tentacles that are used to soften food. The pharynx serves to transport food into the butterfly's body.
The mouth apparatus of a butterfly has a specialization depending on the type of food. In nectar-eaters, the oral apparatus is represented by a long and thin proboscis, which is used to suck nectar from flowers. In predatory butterflies, the oral apparatus is in the form of a thin tube, which is used to suck juices from fruits and other food sources.
The structure and functions of the butterfly's mouth apparatus are closely related to its ability to feed and survive. A variety of forms and functions of the mouth apparatus allows butterflies to adapt to various environmental conditions and find the food necessary for growth and development.
Features and functions

Butterflies have mouthparts that are different from those of other insects. It is adapted to feed on butterflies and provides several functions.
1. Nutrition
The butterfly's mouth apparatus allows it to eat various types of food. In most butterflies, the mouth is a tube called a sponge. It serves to absorb nectar from the flowers, which is the main source of nutrition for butterflies.
However, in some species of butterflies, the mouthparts can be adapted for other types of food. For example, in some predatory butterflies, the mouth turns into a sharp proboscis, which is used to absorb fruit juice or juice from the body of other insects.
2. Pollinization

Butterflies also play an important role in the process of plant pollination. When a butterfly feeds on the nectar of a flower, the pollen grains stick to its body. Moving from flower to flower, the butterfly carries pollen and contributes to the pollination of plants. This allows plants to reproduce and ensures diversity in the plant kingdom.
Thus, the butterfly's mouth apparatus has features and functions that allow them to feed and play an important role in nature.
The atomic structure of the oral apparatus
The butterfly has a mouthpart, which is a complex structure specialized for feeding. The mouth apparatus of a butterfly consists of several elements, each of which performs a specific function.
1. Lips
Butterfly lips are the outer part of the mouth apparatus and perform a protective function. They cover the internal elements of the oral apparatus and prevent harmful substances or particles from entering inside.
2. Mandibles
The mandibles of a butterfly are a pair of jointed structures that serve to soften and absorb food. They are located inside the mouth and can move back and forth to help the butterfly capture and process food.
3. Language
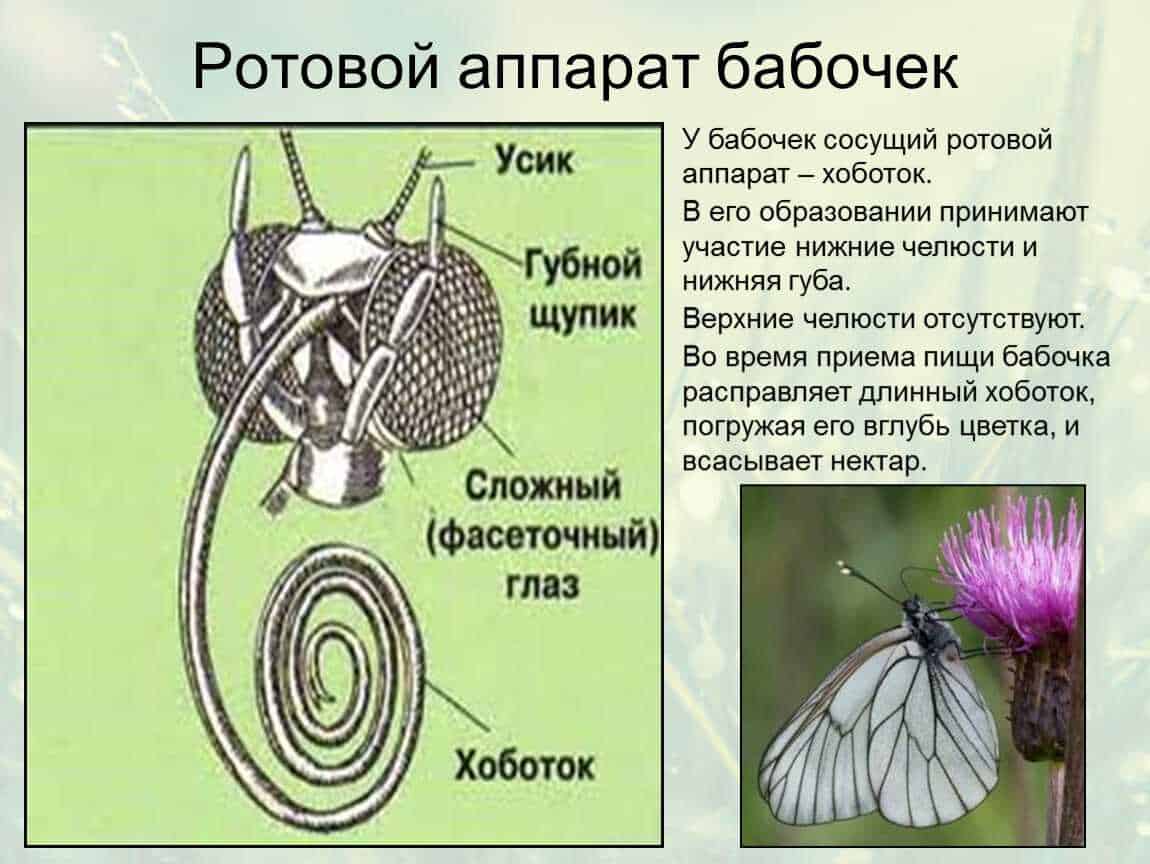
Butterfly tongue is the main tool for feeding. It is a long, thin, and coiled organ that the butterfly can extend from its mouth to reach flowers or other food sources. The tongue is usually covered with microscopic hairs called papillae that help hold food in place and deliver it to the mouth.
In general, the atomic structure of the butterfly's mouthparts is a complex and unique adaptive mechanism that allows them to feed and survive in various conditions. Each element of the mouth apparatus performs its function, providing the butterfly with the necessary efficiency in finding food and obtaining nutrients.
Butterfly oral organs
Butterflies have mouthparts that allow them to eat and get the necessary nutrients. The mouth apparatus of a butterfly consists of several organs, each of which performs its own function.
Lips
Butterfly lips are the main digestive organ. They serve to capture food and move it into the oral cavity. The lips have sensitive hairs that help the butterfly determine the quality of food.
Labial palps

The labial palps of the butterfly are located at the end of the lips and are the organs of smell and taste. They help the butterfly determine the aroma and taste of food. The palps are also used for taking liquid food, as they are capable of absorbing and retaining liquid.
papillae
Papillae are organs located on the lips of a butterfly that serve to absorb food. The papillae have many microscopic openings through which the butterfly can draw food and take it into the oral cavity.
Pharynx
The pharynx is a cavity in the throat of a butterfly that serves to temporarily store food. In the pharynx, further processing and digestion of food takes place before it enters the butterfly's stomach.
All these organs of the butterfly's mouth apparatus work together to ensure that it is able to feed and survive. The butterfly's oral apparatus is adapted to the type of nutrition of this insect species and allows it to receive the necessary nutrients for its development and reproduction.
Functions of the oral apparatus in nutrition
Butterflies have mouthparts that perform several important feeding functions. It is designed to eat food and get the necessary nutrients.
- Absorption of liquid food: The butterfly's mouth apparatus allows it to absorb liquid food, such as the nectar of flowers. It consists of special adaptations, such as a long proboscis or mouth bristles, which help the butterfly to absorb liquid from the flowers.
- Chewing solid food: Unlike nectar, some species of butterflies feed on solid food such as leaves or fruits. The butterfly's mouth apparatus allows it to chew and chew solid food to improve its absorption. Some species of butterflies have tiny teeth that help them crush and chew their food before swallowing it.
- Food Filtration: The mouthparts of a butterfly can also serve as a food filter. Some species of butterflies have special structures called filterophores that help them separate unwanted food particles such as dust or dirt. This allows the butterfly to receive only clean and nutritious food.
Thus, the butterfly's mouthparts play a key role in nutrition, allowing it to obtain the necessary nutrients from various food sources.
Diversity of mouthparts in different types of butterflies
Like other insects, butterflies have mouthparts that are used for feeding. However, in different species of butterflies, this apparatus may have a different structure and function.
Some butterflies have simple mouthparts made up of small sponges or setae called labial rods. These sticks serve to absorb liquid nutrients such as flower nectar or fruit juices. This type of mouth apparatus is found in many species of butterflies, especially those that feed on nectar.
Other butterflies have more complex mouthparts, such as a papillary-suction apparatus. It consists of two long tubes called papillae that can be coiled. With the help of this apparatus, butterflies can reach nectar in the depths of a flower or draw juices from fruits. This type of mouth apparatus is common in butterflies of the scoop family.
Another type of mouthparts in butterflies is the gnawing apparatus. These butterflies have a pair of powerful jaws that can gnaw and chew food. This type of mouthparts is common in butterflies that feed on leaves and other plant material.
Thus, the variety of mouthparts in different species of butterflies allows them to adapt to different food sources and allows them to efficiently obtain nutrients for survival and reproduction.
Mouth adaptations to different types of food

Butterflies have mouthparts, which are the key tool for feeding. Butterfly mouthparts have an amazing ability to adapt to different types of food, which allows them to survive and reproduce in a variety of environments.
One of the adaptations of the mouth apparatus of butterflies is the presence of sponges. Butterfly sponges are specialized organs that serve to absorb liquid nutrition, such as nectar from flowers or plant juices. Sponges are usually made up of many filaments that allow the butterfly to reach and absorb food efficiently.
Another adaptation of the mouthparts of butterflies is the presence of bristles. The bristles on the mouthparts are designed to filter food and remove excess particles. Because of this, butterflies can separate nutrients from inedible parts of food and absorb them efficiently.
In addition, the mouthparts of butterflies can be adapted for feeding with the help of blinds. The louvered mouthparts allow the butterfly to absorb food by penetrating inside fruits or other hard objects. This is especially useful for butterflies that prefer to feed on fruit juices or aged food.
Thus, the butterfly's mouth apparatus is an excellent example of adaptation to various types of food. It allows butterflies to survive and thrive in a variety of environments by providing them with the nutrients they need to survive and reproduce.
Coevolution of mouthparts and plants
The butterfly's mouth apparatus has a special structure that allows it to feed on the nectar of flowers. However, this structure did not appear on its own, but developed as a result of co-evolution with plants.
Butterflies and plants have evolved in parallel over millions of years, and as a result of this process, the mouthparts of butterflies have become ideally adapted to feed on plant nectar. The plants, in turn, developed complex and unique flowers to attract pollinators, including butterflies.
The butterfly's mouthparts consist of two main parts: the lips and the thoracic palps. The lips are used to absorb nectar from a flower, and the palps help the butterfly locate flowers and determine their contents. Over millions of years of coevolution, the butterfly's mouthparts have become increasingly specialized and efficient at extracting food from flowers.
Thus, the co-evolution of the oral apparatus and plants is an example of the interaction of two species that formed and adapted to each other in the process of evolution. Thanks to this interaction, butterflies and plants have found the best way to provide food and reproduction, which has made their existence mutually beneficial.
Interaction of the mouth apparatus of a butterfly with the environment

The butterfly has mouthparts that play an important role in its interaction with the environment. The butterfly's mouth apparatus is a complex organ system that allows it to eat and receive the necessary nutrients.
The main functions of the butterfly's mouth apparatus are sucking nectar from flowers and absorbing plant juices. To do this, the butterfly has a long nectar sucker, which it introduces into a flower or plant and uses to pump out food.
In addition, the butterfly can also use its mouthparts to obtain moisture. She is able to drink water from the surface of leaves, drops from rain, or even drinking water from a puddle. This allows the butterfly to maintain its water balance and survive in dry conditions.
Butterfly mouthparts can also perform a protective function. Some species of butterflies have sharp stingers or spikes on their mouthparts, which they use to protect themselves from predators. These spikes can be poisonous and can cause serious damage to the enemy.
Influence of the structure of the oral apparatus on the evolution of butterflies
Butterflies have mouthparts that play a key role in their evolution. The mouthparts of butterflies have unique features that allow them to obtain food and survive in various conditions.
One of the important features of the mouth apparatus of butterflies is its flexibility. It consists of two tentacles called galleys that help butterflies find and make their way to a food source. The galleys can bend and turn in different directions, which allows the butterflies to reach the flowers and other plants on which they feed.
Another important feature of the mouth apparatus of butterflies is its adaptability. In different species of butterflies, the mouth apparatus can have a different shape and structure, which allows them to eat a variety of types of food. Some butterflies have long and thin galleys that allow them to reach nectar in deep flowers, while other species have short and wide galleys for feeding from fruit or leaf surfaces.
The structure of the mouth apparatus of butterflies also affects their interaction with other organisms. For example, some species of butterflies have specialized mouthparts that allow them to feed on the nectar of certain types of flowers. This promotes mutual pollination of plants and the spread of pollen, which is an important factor in the evolution of butterflies and plants.
Thus, the structure of the mouth apparatus of butterflies plays a decisive role in their evolution. It provides butterflies with access to food and allows them to adapt to different environmental conditions, as well as interact with other organisms in their ecosystem.
The role of the mouth apparatus in the reproduction of butterflies
The butterfly has a mouth apparatus, which plays an important role in its reproduction. The mouth apparatus is a specialized organ that allows the butterfly to receive nutrients.
During the reproduction of a butterfly, the mouthparts are used to feed the female and maintain her energy balance. The female butterfly produces eggs, and in order to successfully bear offspring, she needs sufficient food supplies. The mouth apparatus allows it to feed on various types of plants, flowers and juices, providing the necessary nutrients.
In addition, the oral apparatus plays an important role in attracting a partner for reproduction. Some species of butterflies can eat not only plant foods, but also juices containing aromatic and attractive substances. These substances are secreted from the mouthparts and attract male moths that may be interested in breeding with the female.
Thus, the butterfly's mouth apparatus plays an important role in its reproduction, providing food for the female and attracting partners for successful reproduction. This organ allows the butterfly to maintain its energy and ensures the transfer of genetic material to the next generation.