butterflies - these are beautiful and amazing insects that are very interesting for children in grade 1. They have a unique body structure that allows them to fly, find food and defend themselves from enemies.
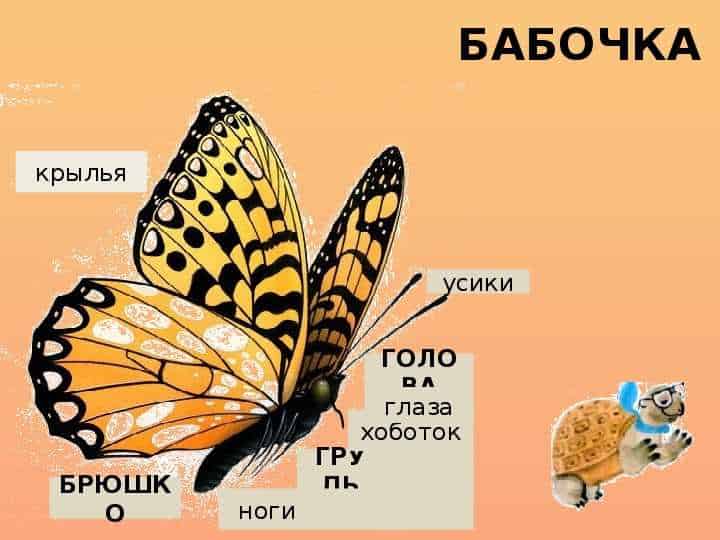
The body of a butterfly consists of several main parts:
- Head - this is the part of the body where the eyes, antennae and proboscis are located. A butterfly's eyes are made up of many small eyes that allow it to see in all directions. The antennae serve as organs of smell and help the butterfly find food. The proboscis is the main feeding organ of the butterfly - with its help, it sucks nectar from flowers.
- Breast - This is a strong and powerful part of the body of a butterfly, which serves for movement and flight. The chest contains muscles that allow the butterfly to flap its wings and fly long distances. The wings of a butterfly are covered with fine pollen, which helps it in flight.
- Abdomen - This is the back of the butterfly's body, where the digestive and reproductive organs are located. The butterfly's abdomen consists of several segments that allow it to move flexibly and perform different functions.
Each part of the butterfly's body performs its own function and helps it survive in the environment. Knowing about the structure of a butterfly, children in grade 1 will be able to better understand and study these amazing insects.
Butterfly head: structure and function

The head is one of the main parts of the body structure of a class 1 butterfly. It is located in front of the torso and performs several important functions.
The structure of the head
The head of a butterfly consists of several parts, each of which has its own specific structure and function. These include:
- Eyes: Butterflies have compound eyes made up of many small eyes called ommatidia. The eyes allow butterflies to see the world around them and navigate in space.
- Mandibles: This is a pair of strong and spiky organs that serve for eating. Butterflies use their mandibles to suck nectar from flowers.
- Frontal palps: they are located above the eyes and help the butterfly navigate in space, as well as find food and breeding partners.
- Mouth palps: are located below the mandibles and are also used for eating. They have taste buds that help butterflies determine the quality and composition of their food.
Head functions

The head of a butterfly performs several important functions that ensure its survival and successful reproduction:
- Orientation and foraging: thanks to the eyes and palps, butterflies can navigate in space, find flowers with nectar and determine the quality of food.
- meal: Mandibles and mouth palps allow butterflies to suck nectar from flowers, which is the main food source for most species.
- Identification of breeding partners: thanks to the frontal palpi, butterflies can detect pheromones secreted by other individuals of their species, and thus find breeding partners.
Thus, the head of a butterfly plays an important role in its life, providing it with the ability to navigate the world around it, find food and partners for reproduction.
Butterfly breast: structure and function

The butterfly's thorax is one of the main parts of this beautiful insect's body. It is located between the head and abdomen and consists of several segments.
The main function of the butterfly's chest is to support and control the movement of the wings. The chest contains powerful muscles that are responsible for bending and unbending the wings. Thanks to this, butterflies can fly and move in space.
Each segment of the chest has its own role. The first segment is called the prothorax and contains the muscles responsible for moving the front legs and head. The second segment is called the mesothorax and contains the muscles responsible for the movement of the middle legs and forewings. The third segment is called the metathorax and contains the muscles responsible for the movement of the hind legs and hind wings.
The butterfly's chest also serves as protection for the internal organs. It forms a kind of shell that protects delicate organs from damage.
So, the butterfly's chest is an important part of its body, which provides movement of the wings and protects the internal organs. Now you know a little more about butterflies for children of the 1st grade!
Butterfly abdomen: structure and functions
The abdomen is one of the main parts of the body structure of class 1 butterflies. It represents the back of the body, which is located behind the chest and head of the butterfly. The abdomen has an oval or cylindrical shape and consists of several segments, which are interconnected by flexible membranes.
The main function of the butterfly's abdomen is to store and digest food. Inside the abdomen is the digestive system, which consists of various organs such as the stomach, intestines, and omentum. The abdomen also plays an important role in the reproduction process. Female butterflies have organs on their abdomens for laying eggs, while males have organs for fertilization.
In addition, the butterfly's abdomen performs the function of temperature regulation. Some species of butterflies have special organs in their abdomen called "heat spots." They allow the butterfly to regulate its temperature by warming up in the sun or cooling down in the shade.
Thus, the butterfly's abdomen is an important part of its structure and performs several functions related to digestion, reproduction and temperature regulation. It allows the butterfly to survive and adapt to different environmental conditions.
Butterfly wings: structure and function
Butterfly wings are one of the most amazing and important parts of its body. They have a special structure that allows the butterfly to fly and perform its functions.
Butterfly wings are made up of transparent plates called scales. Each butterfly can have from several thousand to several million scales on its wings. They come in a variety of shapes and colors, which is what makes butterfly wings so beautiful and varied.
The function of a butterfly's wings is to fly. Thanks to its wings, a butterfly can move through the air and search for food, a partner for reproduction, and a place to rest. Wings also help the butterfly protect itself from predators and attract the attention of other butterflies.
Butterfly wings are very sensitive. They allow the butterfly to sense temperature, humidity, and wind, which helps it navigate its environment. The wings also serve to signal other butterflies, such as when looking for a mate or danger.
So, the butterfly's wings are a unique and important part of its body. They help the butterfly fly, protect itself, and communicate with other butterflies. Studying the wings of butterflies allows us to better understand their lives and admire their beauty and amazing nature.
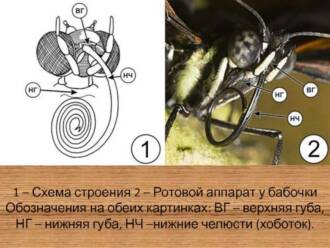
Butterfly proboscis: structure and function

The proboscis is a special part of the butterfly's body that performs important functions. About butterflies for grade 1 children, it will be interesting to know that the proboscis is a thin and flexible tube that is located on the front of the butterfly's body.
The main function of the proboscis is food. Thanks to the proboscis, the butterfly can drink nectar from flowers. The proboscis has very small holes through which the butterfly sucks nectar. Butterflies can eat not only nectar, but also juices from fruits, trees, or the juice of rotten fruits.
The butterfly's proboscis has a special structure that allows it to reach the nectar inside the flower. It can be long, short, straight or curved, depending on the type of butterfly and its adaptation to a particular type of flower.
Butterfly proboscis is one of the amazing and important body parts of these beautiful insects. About butterflies for grade 1 children, it will be interesting to learn how the proboscis helps the butterfly get food and how it is specially adapted for nutrition from flowers and other sources.
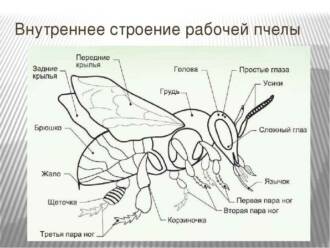
Butterfly legs: structure and function
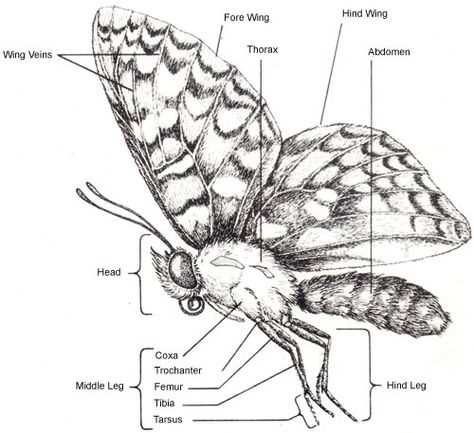
Butterfly legs play a very important role. They help them move around and look for food. Butterflies have six legs, each of which consists of several segments. Each segment can move independently of the others, allowing the butterfly to be very flexible and agile.
Butterfly legs are covered with small hairs called setae. These hairs help the butterfly to stick to various surfaces such as flowers or leaves. They also help the butterfly feel the world around it. The bristles on the legs contain many nerve endings that allow the butterfly to sense touch and vibration.
Each leg of a butterfly ends in tiny claws. They help the butterfly to cling to surfaces and stick to them. The claws can be sharp and strong so that the butterfly can hang from a flower or branch, or they can be blunt and flexible so that the butterfly can walk on a smooth surface.
Butterfly legs are very comfortable for her lifestyle. They allow her to fly, feed and breed. When a butterfly sits on a flower, it uses its legs to crouch and drink the nectar. When a butterfly flies, it spreads its legs to the sides to stay in the air. And when a butterfly wants to lay eggs, it uses its legs to attach them to a leaf or stem.
Butterfly antennas: structure and functions

Antennae are an important part of the butterfly's body. They are located on the head and consist of several segments. Butterfly antennae are thin and flexible organs that help the butterfly navigate the world around it.
The main function of antennae is to sense and perceive the environment. Thanks to antennae, a butterfly can sense smells, tastes, and even sounds. A butterfly's antennae are a kind of sensory organs that help it find food, avoid danger, and find a partner for reproduction.
Butterfly antennae have another important function - communication. Butterflies use antennae to communicate with each other. They can transmit signals and information to each other using the movements of the antennae. For example, butterflies can use antennae to determine the sex and age of another butterfly, as well as to transmit signals about territory or threat.
Thus, the butterfly's antennae play a very important role in its life. They help the butterfly to sense and perceive the world around it, as well as communicate with other butterflies. Studying the butterfly's antennae will help 1st grade children better understand and learn about amazing creatures - butterflies.
Butterfly eyes: structure and function
The butterfly's eyes are an important part of its body, helping it to navigate and survive. Butterflies usually have two compound eyes, which are made up of many small eyes called ommatidia. These ommatidia provide the butterfly with a wide field of view and help it spot danger or find food.
Butterfly eyes have the ability to see colors and shapes. They are able to perceive both visible and ultraviolet light, which makes them sensitive to many shades and details of the world around them. Thanks to this, the butterfly can find not only flowers, but also its mate for breeding.
Butterfly eyes also help her avoid danger. Thanks to their wide field of view, they can spot an incoming predator and quickly fly away to escape an attack. The butterfly can see moving objects, which allows it to react to danger and take action to protect itself.
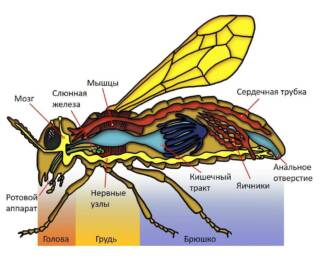
Butterfly heart: structure and function

The heart of a butterfly is an important organ that circulates blood and nourishes its entire body. It is a small pouch located in the lower part of the chest. The heart of a butterfly consists of several departments, each of which performs its own function.
The main function of a butterfly's heart is to pump blood throughout its body. Parts of the heart contract and relax, creating the so-called cardiac contractions. During the contraction of the heart, blood is pushed out of it and sent through the blood vessels to organs and tissues. During the relaxation of the heart, the blood returns to it again.
The blood circulating in the body of a butterfly carries oxygen and nutrients necessary for the vital activity of all its cells. It also removes waste products of metabolism and carbon dioxide, which is formed in the process of breathing. Thus, the heart of a butterfly plays an important role in ensuring its life.
Butterfly stomach: structure and functions
The stomach is one of the main body parts of a butterfly. It is located in the lower part of the body and has important functions in the digestive system of these insects.
The structure of the butterfly's stomach is a flexible tube, which consists of several sections. One of them is the front stomach, which serves to receive food. The second section is the middle stomach, where food is digested. And finally, the back stomach, in which food is further digested and prepared for waste excretion.
The function of the butterfly's stomach is to digest food. When a butterfly feeds, it uses its long proboscis to extract nectar from a flower. The nectar then enters the stomach, where it is digested with the help of enzymes and gastric juice. After that, the nutrients from the food are absorbed into the blood of the butterfly and distributed throughout the body to support life and growth.
From the stomach of a butterfly, digestive waste is carried, which is excreted through the hind stomach and enters through the anus. This process is an integral part of the butterfly's digestive system.