Butterflies are amazing insects that attract attention with their beautiful colors and delicate wings. But in addition to external beauty, the structural features of butterflies are also of interest. The internal structure of a butterfly is a complex system of organs that allows them to perform various functions.
One of the features of the anatomy of butterflies is their antennae. The antennae of a butterfly act as an organ of smell and touch. They consist of a number of articular segments, at the ends of which are sensitive hairs. Thanks to the antennae, butterflies can sense various smells and vibrations, which helps them find food and find breeding partners.
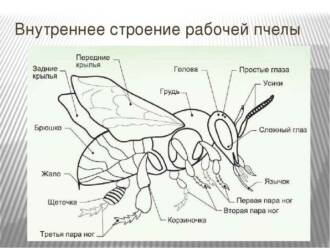
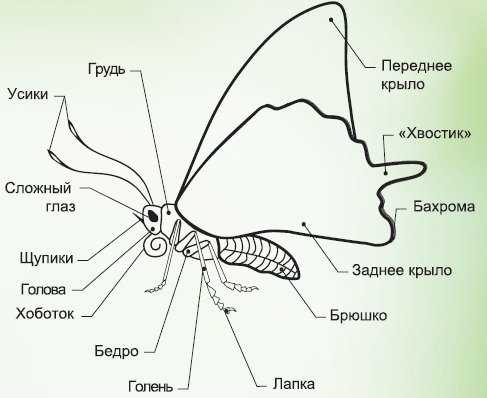
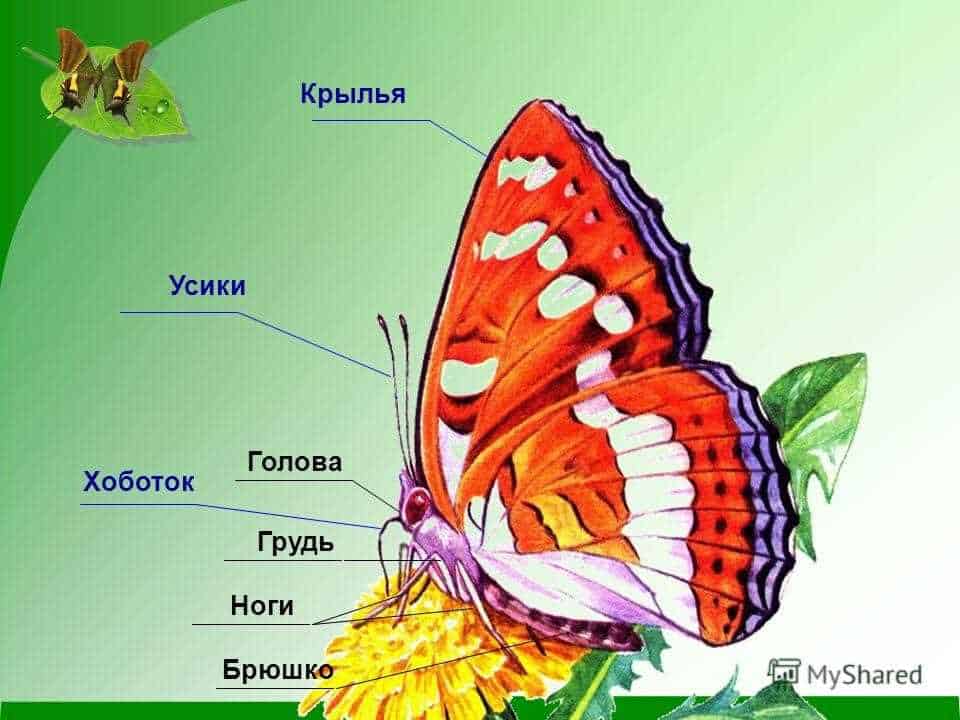
The body structure of a butterfly consists of several main parts. The head of a butterfly contains eyes, consisting of many small facets, which provide good vision. Also on the head are the antennae, which have already been mentioned. The torso of a butterfly consists of three segments: the chest, on which the wings are located, and the abdomen. Butterfly wings are covered with tiny scales, which give them a beautiful pattern and are necessary for flight.
Thus, the structure of butterflies is a complex and unique system that provides them with the ability to reproduce, find food and navigate in the world around them. The variety of shapes and colors of butterflies makes them interesting objects of study for children and adults.
The external structure of butterflies
The structure of butterflies is very interesting and unique. By studying the anatomy of butterflies, we can learn a lot of interesting things about their features and ways of survival.
The body structure of a butterfly consists of several parts. The main part of the body is the chest, which contains the organs for flight and the digestive system. On the chest are two pairs of wings that allow butterflies to fly. The wings are covered with thin scales, which give them brightness and beauty.
The antennae of a butterfly are another feature of their structure. The antennae serve as organs of smell and touch. They allow butterflies to find food, find breeding partners, and navigate in space.
Studying the structure of butterflies in pictures for children helps to understand how their body works and how they have adapted to their environment. Butterflies have amazing abilities and their body structure plays an important role in their life cycle and behavior.
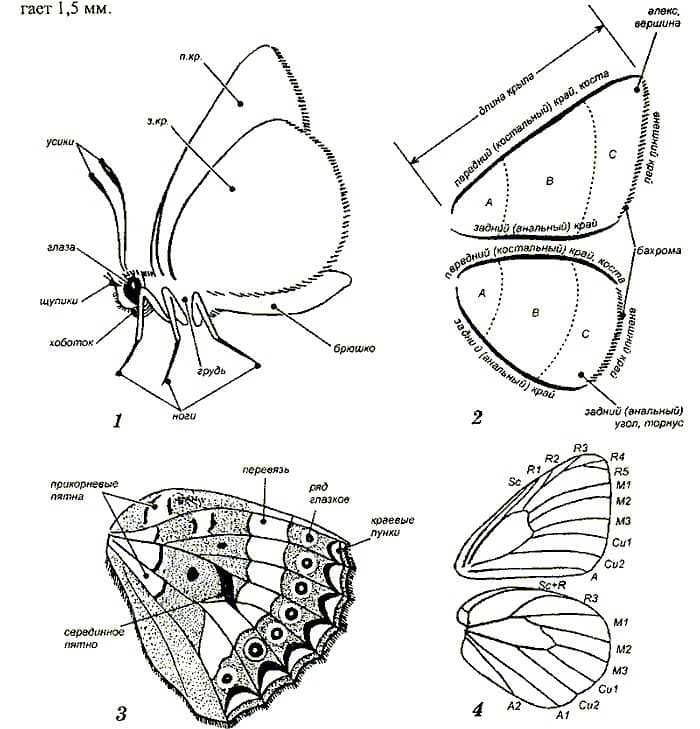
The structure of the wings and their functions

Butterflies are incredibly beautiful and amazing creatures that attract attention with their wings. What is a butterfly made of? Butterfly wings are the main and most characteristic organ. They are flat and transparent structures, consisting of tiny scales, which give them brightness and beauty.
The structure of a butterfly in pictures for children makes it easy to understand how its wings are arranged. Each wing consists of several parts: a pterygoid vein, a transverse vein, a longitudinal vein, and a lobule. The pterygoid vein is the main vein that runs through the wing from base to edge. The transverse vein connects the pterygoid vein with the longitudinal vein, and the longitudinal vein runs in the middle of the wing and connects all the lobules.
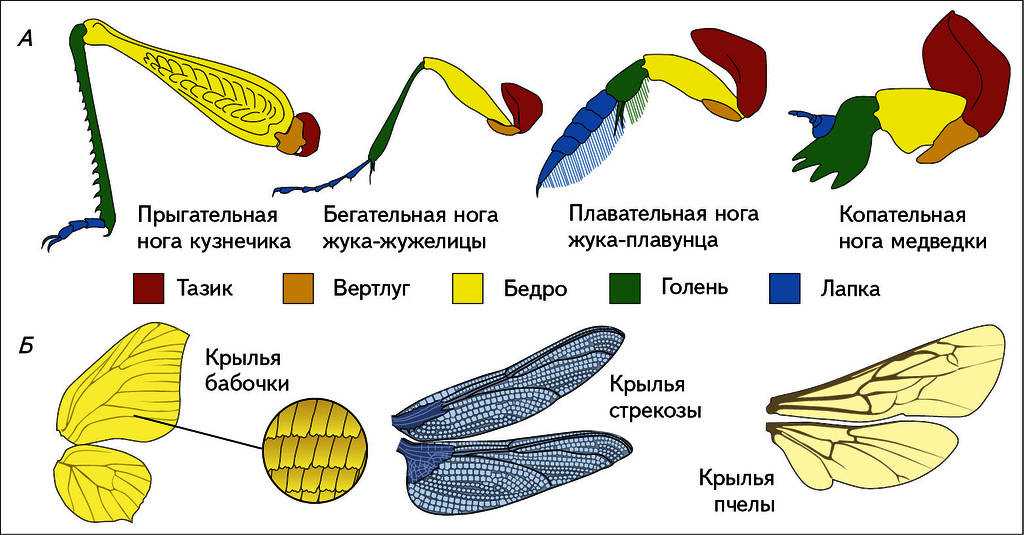
Butterflies internal structure of the wings allows them to perform not only an aesthetic function, but also the function of flight. Wings are used for movement and maneuvering in the air. They are lightweight and flexible structures that allow butterflies to fly at high speed and maneuver in tight spaces.
The structural features of butterflies determine their ability to fly. Butterfly wings are covered with microscopic scales that help them fly. The scales on the wings create a vortex of air that helps the butterfly to rise into the air and maneuver in it. In addition, butterfly wings have special muscles that allow them to move in the air.
Butterfly anatomy also includes antennae. The antennae of a butterfly are a pair of organs that are located on the head. They are thin and flexible antennae that serve to orientate themselves in space and detect food and a breeding partner.
Butterfly's sense organs
Butterflies, like other insects, have developed sensory organs that help them navigate the world around them and perform their vital functions. The structural features of butterflies determine the specialization and effectiveness of their sense organs.
Antennae are one of the main sense organs in butterflies. They are paired organs located on the head of a butterfly. The antennae consist of segments covered with numerous fine hairs. Thanks to these hairs, butterflies can sense smells, tastes, and even small changes in their environment.
The body structure of butterflies also includes the eyes, which are another important sensory organ. Butterfly eyes are made up of many small eyes called facets. Each facet contains its own set of photoreceptor cells that allow butterflies to perceive light and form an image of the world around them.
In addition, butterflies have sensitive bristles located on the surface of their bodies. These bristles help butterflies sense the touch and vibration of their environment, allowing them to avoid danger and find food.
The structure and function of the butterfly head
The butterfly's head is one of the key parts of its anatomy. It plays an important role in providing the basic functions of this beautiful insect. Let's take a closer look at the structure and features of the butterfly's head.
The structure of the head
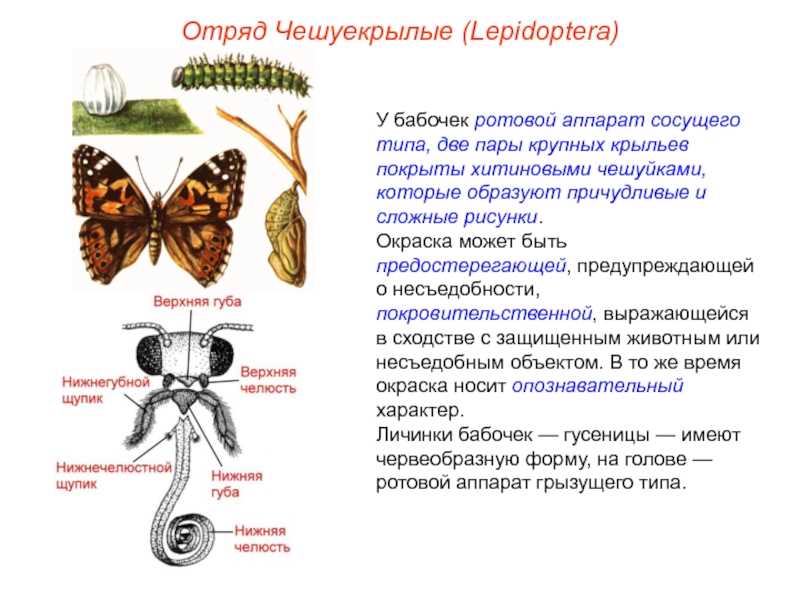
The head of a butterfly has a complex internal structure. It consists of various organs, each of which performs its own function. On the head of a butterfly, the following main parts can be distinguished:
- tendrils - This is a pair of long, thread-like outgrowths located on the front of the head. The antennae serve as an organ of touch and smell, allowing the butterfly to find food and avoid danger.
- Eyes - Butterflies have complex eyes, consisting of many facicles. This allows them to perceive their environment and detect danger or a breeding partner.
- Mouth organs - the head of a butterfly contains mouthparts that allow it to feed. They can be of various shapes and structures, depending on the type of butterfly and its preferred food.
Head functions

The head of a butterfly performs several important functions necessary for its survival and reproduction:
- Touch and smell - antennae allow the butterfly to find food, detect danger and find a partner for reproduction.
- Vision Compound eyes allow butterflies to perceive their environment and detect danger or a breeding partner.
- Nutrition - the mouth organs of the butterfly's head allow it to eat plant or animal food, depending on the species.
Thus, the butterfly's head is an important organ that ensures its survival and successful reproduction. Its complex structure and specialized organs allow the butterfly to interact with the environment and perform the necessary vital functions.
Butterfly oral apparatus
Butterfly features include unique mouthparts that allow them to obtain nutrients from flowers and other plants. The oral apparatus of a butterfly consists of several parts, each of which performs a specific function.
The main part of the butterfly's oral apparatus is the lips, which are used for eating. The lips form two halves that can open and close. When a butterfly wants to feed, it opens its lips and applies them to a flower or other food source.
To hold food and suck nectar from flowers, butterflies have a proboscis. The proboscis is a long tube that is formed by the fusion of the lower lip and the maxilla, and is the main feeding organ in butterflies. The proboscis can be of various lengths and shapes, depending on the type of butterfly.
Butterfly antennae also play an important role in the feeding process. The antennae serve as organs of touch, they help butterflies find food and determine its quality. Butterfly antennae are usually covered with many small sensory hairs that help them sense smells and tastes.
The structure of the body of a butterfly and its mouthparts allow them to be effective pollinators of flowers, as well as to receive the necessary nutrients for their development and survival. Due to their internal structure, butterflies can adapt to different types of food and use the available resources in the environment.
The structure and function of the butterfly breast

A butterfly is an insect belonging to the class of insects. The structural features of butterflies are due to their way of life and the functions of organs. What is a butterfly made of? A butterfly consists of a head, thorax and abdomen. The breast of a butterfly plays an important role in its life.
Butterfly anatomy suggests the presence of three sections of the chest: anterior, middle and posterior. Each section of the chest performs its own functions. The forechest is responsible for the movement of the front legs and the front pair of wings. The middle chest controls the movement of the middle legs and the middle pair of wings. The hind thorax is responsible for the movement of the hind legs and the rear pair of wings.
The structure of the body of a butterfly also provides for the presence of antennae. The antennae of a butterfly are organs of touch and smell. They help the butterfly navigate in space and find food. Butterfly antennae are made up of segments that can be of different shapes and sizes depending on the type of butterfly.
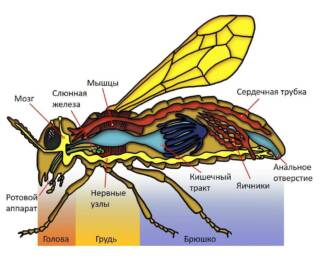
The internal structure of the butterfly is also of interest. Inside the chest are the muscles that provide the movement of the legs and wings. Also in the chest are respiratory organs that allow the butterfly to receive oxygen and release carbon dioxide. The butterfly breathes with the help of trachea - tubular organs that permeate the entire body and deliver oxygen to the cells.
The structure and functions of the butterfly's abdomen
The structure of a butterfly includes various organs and systems that perform a variety of functions. One of the important components of the butterfly's body is its abdomen.
The abdomen of a butterfly consists of several segments, which are interconnected by flexible membranes. This allows the butterfly to move freely and adjust the shape of its body to different conditions.
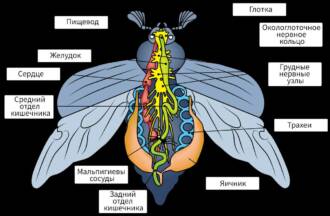
Inside the butterfly's abdomen are various organs and systems that perform important functions. For example, the digestive and waste systems are located here. The butterfly feeds on the nectar of flowers, which enters its stomach, where the process of digestion begins. Waste is expelled through special openings called anus.
In addition, the butterfly's abdomen contains respiratory organs. Butterflies breathe through small holes called stigmas, which are located on the sides of the body. Through the stigmas, air enters the trachea - thin tubes that spread throughout the butterfly's body and deliver oxygen to the body's cells.
The abdomen of the butterfly also plays an important role in reproduction. In females, the abdomen contains the ovaries, in which eggs are formed. After fertilization, the female lays her eggs on plants, where they mature and turn into caterpillars.
Thus, the butterfly's abdomen is an important and multifunctional organ that performs a number of important functions related to digestion, respiration, and reproduction.
Respiratory organs in butterflies

The body structure of butterflies includes various organs, one of which is the respiratory organs. Thanks to these organs, butterflies can receive the oxygen they need for life.
Butterfly anatomy provides for the presence of special respiratory organs that are located on their abdomen. These organs are called tracheae. Tracheas are thin tubes that penetrate all organs and tissues of the butterfly's body.
Butterfly antennae also play a role in the breathing process. The antennae are a pair of antennae, at the ends of which are numerous sensors. These sensors help butterflies locate food sources and dangers, and also play a role in spatial orientation.
The structural features of butterflies are associated with their ability to fly. Butterflies can maneuver in the air thanks to their wings, which are made up of numerous transparent scales. These scales allow butterfly wings to be light and strong at the same time.
Thus, the respiratory organs of butterflies play an important role in their life, providing them with the necessary oxygen for flight and other activities. The structure of butterflies and their internal structure allow them to be adapted to their environment and successfully exist in various conditions.
Butterfly circulatory system
Butterflies internal structure differs from other insects in its uniqueness and complexity. The cardiovascular system plays an important role in the body of a butterfly, providing oxygen and nutrients to all organs and tissues.
Butterfly body structure includes an open vascular system, consisting of blood vessels and a heart. The blood in a butterfly does not circulate in a closed circle, as in a person, but moves freely throughout the body.
Structural features of butterflies are also manifested in the cardiovascular system. In butterflies, the heart is a long tubular organ located in the chest. It consists of segmented sections that contract and expand, pumping blood through the vessels.
The structure of the body of a butterfly also includes antennae, which act as sensory organs. Butterfly antennae are a pair of long and thin outgrowths on the head. They contain many nerve endings that allow the butterfly to smell and navigate in space.
Butterfly anatomy is of interest to many, especially children. The structure of a butterfly in pictures helps to visualize how its body works and how various organs function. Various illustrations and diagrams help children easily absorb information about the structure of a butterfly and its features.
Butterfly reproductive system
Butterfly anatomy includes various organs and systems, including the reproductive system. The structure of butterflies in pictures for children allows you to clearly see the features of their structure.
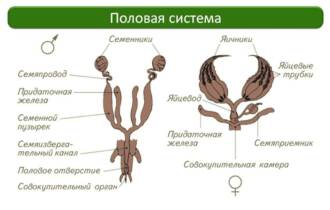
The butterfly's reproductive system consists of several main parts. One of them is the ovaries, which are located at the bottom of the female's abdomen. The ovaries form eggs that will be laid on a suitable surface.
The male butterfly has a special organ called genitals. They are a pair of small protrusions at the end of the abdomen. The male genitals serve to transfer spermatozoa to the female's organs.
Butterfly antennae also play an important role in the reproductive process. They are sensory organs and help butterflies find breeding partners. The antennae are equipped with many microscopic receptors that are able to detect pheromones released by other butterflies.
The structure of the body of a butterfly and the structural features of butterflies allow them to successfully reproduce and continue their appearance. The variety of shapes and colors of butterflies makes them one of the most attractive creatures on the planet.