Moths are one of the most beautiful and diverse groups of insects. Their structure is superbly adapted to their lifestyle and the role they play in the ecosystem. They belong to the Lepidoptera order, and their main difference from other insects is the presence of scales on their wings and body, which give them a unique beauty and reflect light in different colors.
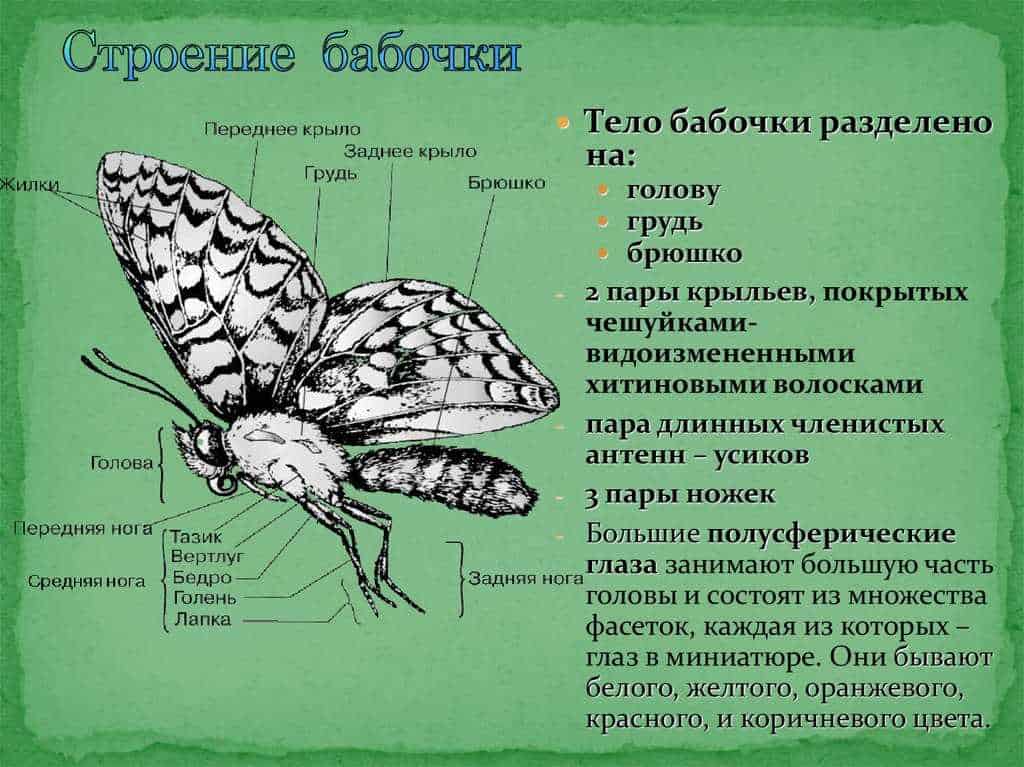
The structure of the moth includes not only wings, but also the body, head, legs and antennae. The wings of a moth consist of two pairs, anterior and posterior. They are covered with scales that serve as protection and help the moths to fly. Their wings are strong and flexible, which allows them to maneuver in the air. The body of a moth consists of a head, thorax and abdomen. The head contains the eyes, antennae and mouthparts. The eyes of a moth are made up of many small eyes that allow them to see in all directions.
Moth antennae perform many functions: they help to navigate in space, find food, determine the temperature and humidity of the air, and communicate with other individuals of their species.
The legs of a moth are six limbs that allow them to move on different surfaces. At the ends of the legs, moths have claws that help them hold on to flowers or leaves. Each leg of a moth has its own purpose: the front legs are used for feeding, the middle legs are used for movement, and the back legs are used for holding and protection.
The structure of the moth is the result of millions of years of evolution and adaptation to various environmental conditions. They are not only an object of study for scientists, but also an inspiration for artists and poets who have found a source of inspiration in their beauty and grace.
Moths: winged creatures
Moth structure
Moths are winged insects that belong to the order Lepidoptera. They have a unique wing structure consisting of thin plates covered with scales. This feature gives moths a distinctive appearance and allows them to move easily in the air.
Moth adaptations
The structure of the moth is the result of its evolutionary adaptations to various environmental conditions. For example, moths that live in environments with high humidity have thick scales on their wings that help them retain moisture and protect their wings from damage. In addition, some species of moths have bright colors that serve to deceive predators or attract mates.
Moths also have a highly developed sensory system that helps them navigate in space and find food. They have compound eyes on their heads that allow them to see in a wide range. In addition, they have tactile organs on their legs that help them locate food and navigate surfaces.
variety of moths
Moths are represented by a variety of species with unique features and adaptations. Some moth species can migrate long distances across oceans and mountain ranges. Other types of moths have specialized wings that allow them to camouflage themselves as leaves or flowers.
All in all, moths are amazing creatures of nature that continue to amaze us with their build and adaptations. Studying their diversity and biology allows you to better understand the world of living organisms and their amazing ability to adapt.
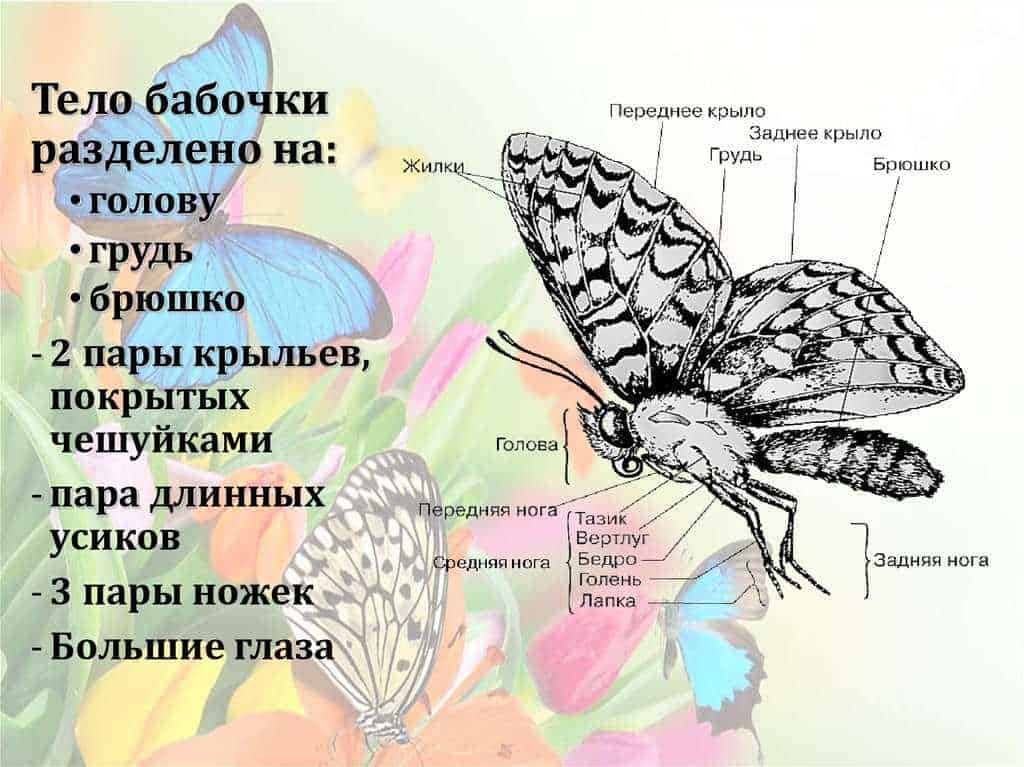
The structure of the moth: the main features

The structure of the moth is a complex and unique system that allows this insect to perform its basic functions. It includes many adaptations that allow the moth to survive in various conditions.
Wings
One of the main structural features of a moth is its wings. They are covered with tiny scales, which give them special strength and flexibility. Moth wings can be of various shapes and colors, which allows them to hide from predators or attract the attention of breeding partners.
Mandibles
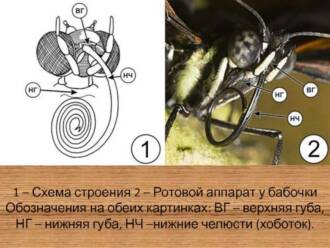
The moth has a proboscis and mandibles that allow it to eat and drink nectar from flowers. The mandibles of the moth are long and curved, which allows it to reach the most inaccessible places of the flower and extract food from them.
sensory organs

The structure of the moth also includes various sensory organs that help it navigate in space and detect danger. Moths have well-developed antennae that serve them to detect smells and perceive sounds. Thanks to these organs, moths can find food, breeding partners and avoid danger.
Thus, the structure of the moth is a complex system that allows this insect to adapt to various environments and perform its main functions.
Moths their head: unique features

The structure of the moth is distinguished by its uniqueness and adaptability to various environmental conditions. The head of a moth plays an important role in its life and performance of various functions.
Antennas

On the head of the moth are antennae, which are an important organ of touch and smell. The moth's antennae allow it to smell and warn of possible danger. They also help the moth find food and a breeding partner.
Mandible
Moths have special mandibles on their heads, which are used for eating. The moth's mandibles enable it to feed on flower nectar, plant sap, or pollen. They also have the ability to coil and unfold, which helps the moth to feed and move around in a variety of environments.
Eyes
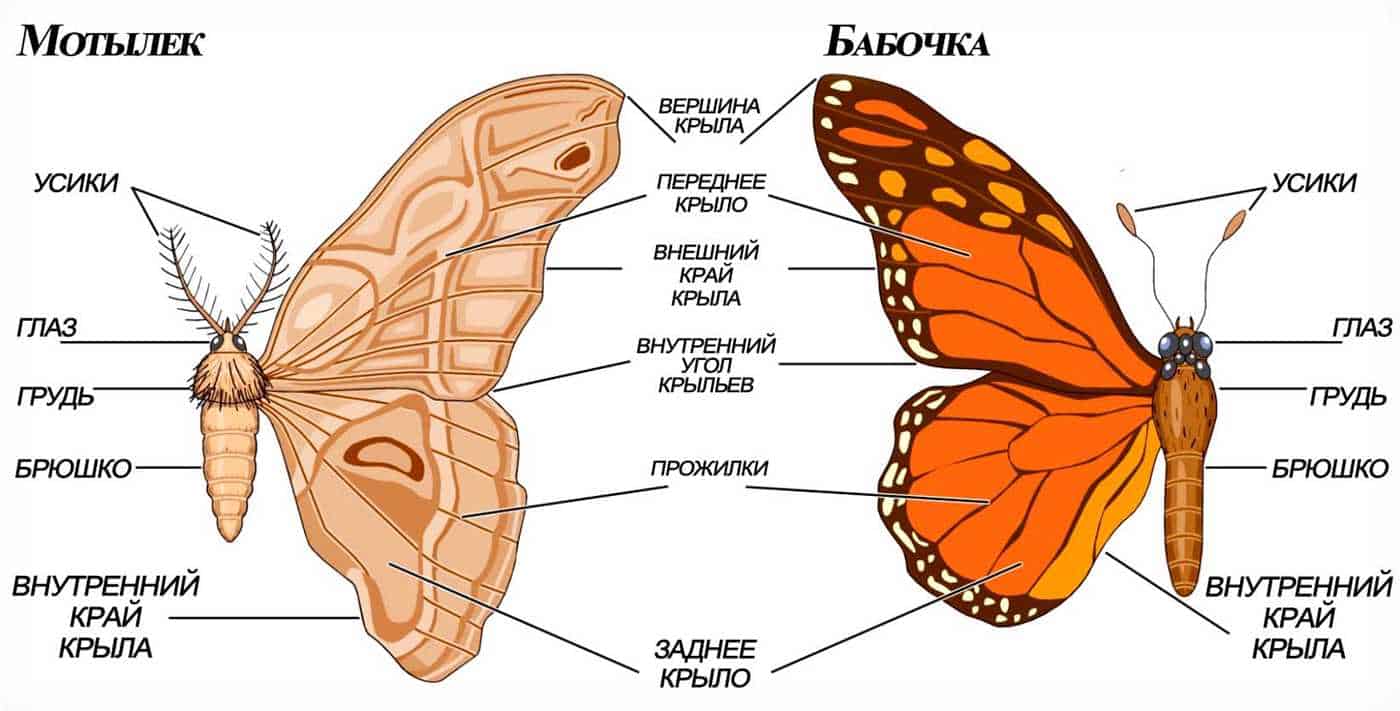
Moths usually have two compound eyes, consisting of many small facets. These eyes allow moths to see the world around them. They have good eyesight and can distinguish colors, shapes and movements. The eyes of a moth help him navigate in space, find food and avoid danger.
Thus, the structure of the moth's head is a complex system of organs that help it survive and successfully adapt to the environment.
Moth eyes: role and structure
The structure of the moth includes unique eyes that play an important role in its life. The eyes of a moth have a complex structure that allows them to perceive light and provide vision.
In moths, the eyes are represented by many small ocelli called compound ocelli. They are located on the eye sockets that form on the moth's head. Each compound eye consists of one or more cells called ommatidia.
The structure of the ommatidia includes a lens, light-sensitive cells and nerve fibers. The lens performs the function of focusing light on light-sensitive cells that respond to light stimuli. The received information is transmitted along the nerve fibers to the moth's brain, where the processing and analysis of the received data takes place.
The moth's eyes play an important role in its behavior and survival. They allow the moth to navigate its environment, determine the direction of light, and recognize objects. With their eyes, moths can detect food, avoid danger, and find breeding partners.
Moth body: anatomy features
The structure of the moth has a number of features that allow this insect to survive and successfully reproduce. One of the main elements of the anatomy of a moth is its wings. They are covered with tiny scales that give them beauty and a variety of colors. Moth wings also have a complex vein system that provides strength and flexibility. Thanks to this structure, moths can easily and quickly fly, maneuver and even swim.
Another important feature of the moth's anatomy is its head. On the head of the moth are two antennae, which act as organs of touch and smell. The antennae help moths find food and breeding partners. In addition, compound eyes are located on the head of the moth, consisting of many small torches. These eyes allow moths to see in a wide range of angles and detect danger at great distances.
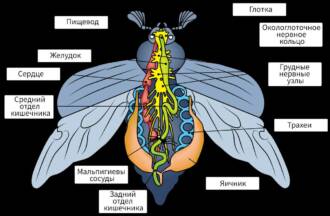
The body of the moth also consists of three segments: the chest, abdomen and head. The breast of the moth is the largest and strongest segment. It contains the muscles that provide the movement of the wings and legs. The abdomen of the moth serves for digestion, reproduction and storage of energy reserves. The moth's head contains its sense organs and brain, which governs all bodily functions.
In general, the structure of the moth is complex and adapted to its lifestyle. It allows this insect to successfully exist in various conditions and perform all the necessary functions for survival and reproduction.
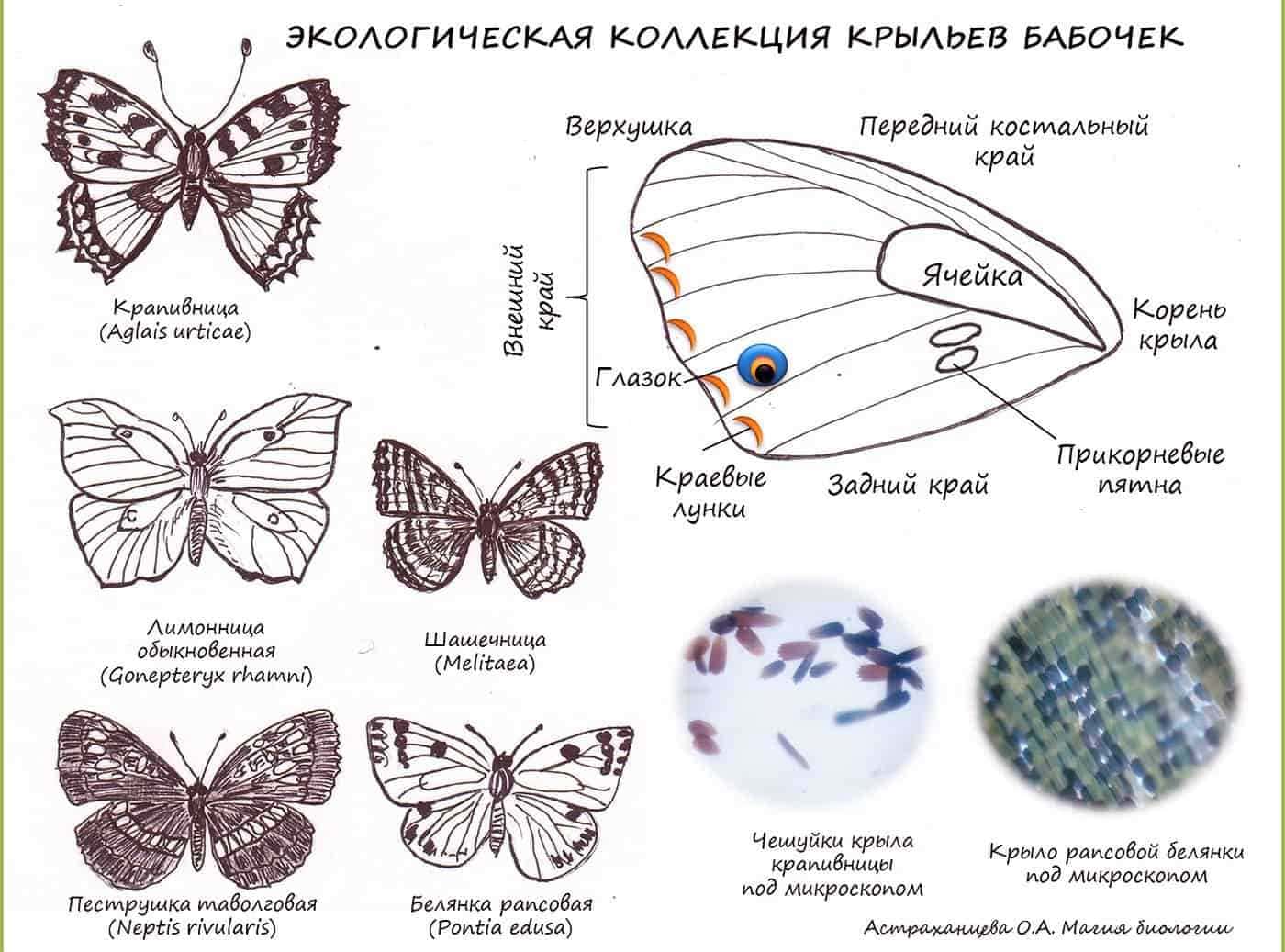
Moth wings: device and functions
The structure of the moth has a special adaptation, which is manifested in its wings. The wings of a moth are light and durable organs that play an important role in its life.
The wings of a moth are made up of tiny scaly structures called lepidoptera. These scales cover the entire top of the wing and give it a special coloration and patterns that help the moth to hide from the background and avoid danger.
The wings of a moth also play an important role in its movement. They allow the moth to fly with great agility and speed. Moth wings have a complex structure of mesh veins that give them strength and elasticity. Thanks to this, moths can fly long distances and conquer even significant heights.
The functions of the moth's wings are also related to its reproduction. Males have pheromones on their wings that serve as an attractive signal to females. Moth wings play a role not only in attracting a partner, but also in protecting against competitors. They can be used to scare away other males and defend their territory.
As a result, the wings of a moth are not just organs for flight, but also an indispensable part of its life cycle. They provide the moth with survival, reproduction and successful adaptation to the environment.
How Moths Fly: The Mechanism of Flight

The structure of the moth provides its amazing flight abilities. The moth's wings consist of many tiny scales, which give them not only a beautiful appearance, but also an important function - they provide the aerodynamic structure of the wing. Each scale on the moth's wing is attached to a special frame of rigid and flexible elements, which allows the wings to move in the desired direction and create lift.
A feature of the structure of the moth is the presence of special muscles that control the movement of the wings. These muscles allow the moth to change the speed and direction of flight, as well as to maneuver in the air. Moth wings can move with a large amplitude and very quickly, which allows them to fly maneuverably and move efficiently in space.
Moths also have a mechanism for air resistance. Their wings have a special structure that allows you to create and control air resistance. This allows the moths to hover slowly in the air or maneuver quickly in search of food and a breeding partner. The ability of moths to maneuver and hover in the air is one of the key adaptations that ensure their survival and reproduction in natural conditions.
Moths and their food plants: how nutrition occurs
The structure of the moth is a complex system that allows it to obtain food and survive in its environment. The main organs of nutrition in moths are the lips and lip cheeks. The lips help the moth to get inside the flower or fruit, where its host plant is located.
One of the features of moths is their ability to choose certain food plants. Each species of moth has its own eating habits and the ability to recognize certain smells and tastes. This allows the moths to find their food plants and get the nutrients they need.
Moths feed on nectar, which is secreted by host plants. Nectar serves as a source of energy and nutrients for moths. Moths use their long stigma to reach for nectar that is found deep within the flower or fruit.
Some types of moths can also feed on pollen, which also contains important nutrients. They use their lips and lip cheeks to pick up pollen from the flower and move it to the stigma where it will be transferred to other flowers.
Moths and their habitat adaptations
The structure of the moth has a number of features that allow them to successfully adapt to their habitat. One of the most important adaptations is the ability of moths to metamorphosis. They go through several stages of development, starting with an egg, then turning into a caterpillar, a chrysalis, and finally an adult moth. This sequence of stages allows moths to adapt to different environmental conditions, such as food and habitat.
Another important structural feature of the moth is their wings. They are covered with tiny scales, which give them a special structure and color. This allows moths to be invisible to predators or, conversely, to attract attention with their bright colors. In addition, moth wings are used for flight and locomotion, allowing them to maneuver through the air and find food or a breeding mate.
One of the most interesting adaptations of moths is their ability to navigate in space using antennae. Moth antennas contain receptors that allow them to sense smells and pheromones, as well as navigate in space. Through this adaptation, moths are able to find food, avoid danger, and find breeding partners.
In general, the structure of the moth has a number of features that allow them to successfully adapt to their habitat. They can change depending on the environment and the needs of the moth, making them one of the most successful and adaptable creatures on the planet.
Moths and their structure: adaptations and protection

The moth's structure has many adaptations that help them survive in various conditions and defend themselves from enemies. One of their main adaptations is their winged form, which allows them to move easily and avoid danger. Moth wings have a complex structure, consisting of many tiny scales, which give them a beautiful and bright appearance.
In addition, the moth's structure also includes special organs that allow them to locate a breeding partner. The sense organs of insects are located on the antennae and legs, and they play an important role in the process of finding a partner. Some types of moths can also emit special pheromones that attract members of the opposite sex.
Defense mechanisms are also part of the moth's structure. Some species of moths have special colorations that help them camouflage themselves in their environment and avoid predators. Some species have luminous spots on their wings, which distract the attention of predators and allow the moths to escape. Other species have a venomous coloration that warns predators of their poisonousness and repels them.
In general, the structure of the moth and its adaptations allow them to successfully exist in various conditions and effectively protect themselves from dangers. The study of these adaptations allows you to better understand the world of insects and their amazing abilities.