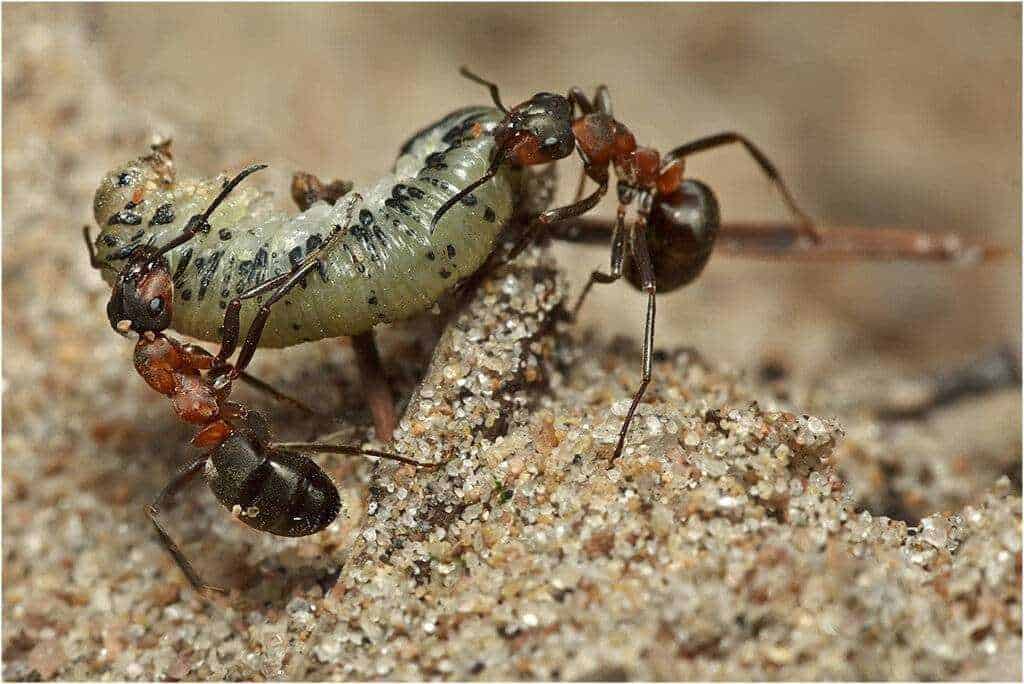
Butterflies are among the most beautiful creatures in nature. These delicate and graceful insects attract attention with their bright colors and graceful flights. However, there is a certain group of caterpillars that pose a threat to butterflies and their habitat. These are parasitic caterpillars.
Parasitic caterpillars are caterpillars that feed on the tissues of other butterflies. They use their hosts as a source of food and protection from predators. Parasitic caterpillars can be very diverse: from small and inconspicuous to large and colorful. They can live inside or outside the host's body and feed on its food resources.
Parasitic caterpillars are a serious threat to butterflies and their habitats. They can destroy the larvae and pupae of butterflies, which leads to a decrease in the size and diversity of populations. In addition, parasitic caterpillars can alter the behavior and physiology of their hosts, which can affect their ability to reproduce and survive.
What are parasitic caterpillars?
Parasitic caterpillars are species of caterpillars that live on or inside other organisms, causing harm to them. They are parasites, using their hosts for food and reproduction. Parasitic caterpillars can be found in a variety of habitats, including forests, fields, gardens, and farmland.
Parasitic caterpillars have different ways of attacking their hosts. Some caterpillars feed on the plant tissues of their hosts, reducing their nutritional strength and weakening them. Other caterpillars can enter the body of their host and feed on its tissues, which can lead to its death.
Parasitic caterpillars can be dangerous to butterflies and their habitats. They can destroy plants that provide food for butterflies, thereby reducing their food resources. In addition, they can also carry various diseases that can affect the health and survival of the butterflies.
How do parasitic caterpillars affect butterflies?
Parasitic caterpillars are a major threat to butterflies and their habitats. They feed on the tissues of butterflies, which leads to harm to them and a decrease in their numbers. When caterpillars parasitize butterflies, they can cause serious consequences, such as weakening the butterflies and possibly killing them.
Parasitic caterpillars can also affect butterfly reproduction. They may feed on butterfly eggs or young caterpillars, which reduces their survival rate and reduces their numbers. This can lead to a decline in butterfly populations and disruption of the ecosystem in which they exist.
Parasitic caterpillars can also influence the behavior and physiology of butterflies. They can cause butterflies stress and illness, which can lead to changes in their behavior and a decrease in their ability to reproduce. In addition, parasitic caterpillars can carry various infectious diseases, which can cause further harm to butterflies and their habitat.
Overall, parasitic caterpillars pose a serious threat to butterflies and their habitats. Their impact can be varied, but is mainly associated with harming butterflies, reducing their numbers and disrupting the ecosystem. Therefore, it is necessary to take measures to protect butterflies from parasitic caterpillars and preserve their habitats.
How do parasitic caterpillars affect butterfly habitats?
Parasitic caterpillars can have serious impacts on butterfly habitats and butterfly populations. They are pests that feed on butterfly tissue and can cause significant damage to them.
First, parasitic caterpillars feed on leaves and other plants, which are a food source for butterflies. Increased plant consumption by parasitic caterpillars can deplete food resources for butterflies, reducing their survival and population.
Secondly, parasitic caterpillars can be carriers and transmit various diseases to butterflies. This can lead to widespread illness and death of butterflies, affecting biodiversity and the ecosystem in which they live.
In addition, parasitic caterpillars can directly affect the reproduction process of butterflies. They can parasitize butterfly eggs or caterpillars, destroying them or weakening their health. This can lead to a decrease in butterfly populations and disruption of their natural reproduction.
Overall, parasitic caterpillars pose a serious threat to butterfly habitats. Their impact can be negative both on individuals and on the entire butterfly population, which requires measures to be taken to control and prevent the spread of these pests.
Which butterfly species are at risk from parasitic caterpillars?

Parasitic caterpillars pose a threat to various species of butterflies. One of these types is blue bush butterfly (Celastrina argiolus). Its caterpillars parasitize a variety of shrubs, including those that are food plants for other butterfly species. This can lead to competition for food and a decline in the numbers of other species.
Another threatened species is cabbage whites (Pieris brassicae). Its caterpillars feed on plants from the cabbage family, as well as many other cultivated plants. When caterpillars of this species reproduce massively, they can cause significant damage to agriculture and horticulture.
Also, birch sawfly (Zeuzera pyrina) is a parasite of several species of butterflies, including birch poplar (Limenitis populi), which is a well-known and beautiful species of butterfly. Birch sawfly caterpillars penetrate the trunks and branches of trees, which can cause their death.
Thus, parasitic caterpillars pose a threat to a variety of butterfly species, including the blue bush butterfly, cabbage butterfly and birch cottonwood. Their presence can negatively affect the numbers and diversity of butterflies, as well as their habitat.
What plants are the main hosts of parasitic caterpillars?

Parasitic caterpillars are dangerous pests for many plants. They feed on the juices and leaves of various plants, which leads to their damage and even death. Some plants are the main hosts for parasitic caterpillars, on which they reproduce and develop. Here are some of them:
1. Euphorbia
Milkweed is one of the most popular plants for parasitic caterpillars. They feed on its leaves and stems, which leads to the exhaustion of the plant and its death. Milkweed contains substances that can be toxic to caterpillars, but some species have adapted to these conditions and successfully reproduce on it.
2. Oak
Oak trees are also primary hosts for several species of parasitic caterpillars. These caterpillars feed on oak leaves and can cause significant damage to its crown. This can cause the plant to weaken and become more vulnerable to other pests and diseases.
3. Cabbage

Cabbage and other members of the cabbage family are also susceptible to attacks by parasitic caterpillars. These caterpillars feed on cabbage leaves and can severely damage the plant, especially during its active growth period. They can cause deformation of leaves and stems, as well as destroy flower buds and fruits.
Thus, parasitic caterpillars can be harmful to a variety of plants, including milkweed, oak and cabbage. The spread and control of these pests are important for the conservation of biodiversity and the conservation of habitats for many species of plants and animals.
What are the consequences for the ecosystem when the number of parasitic caterpillars increases?
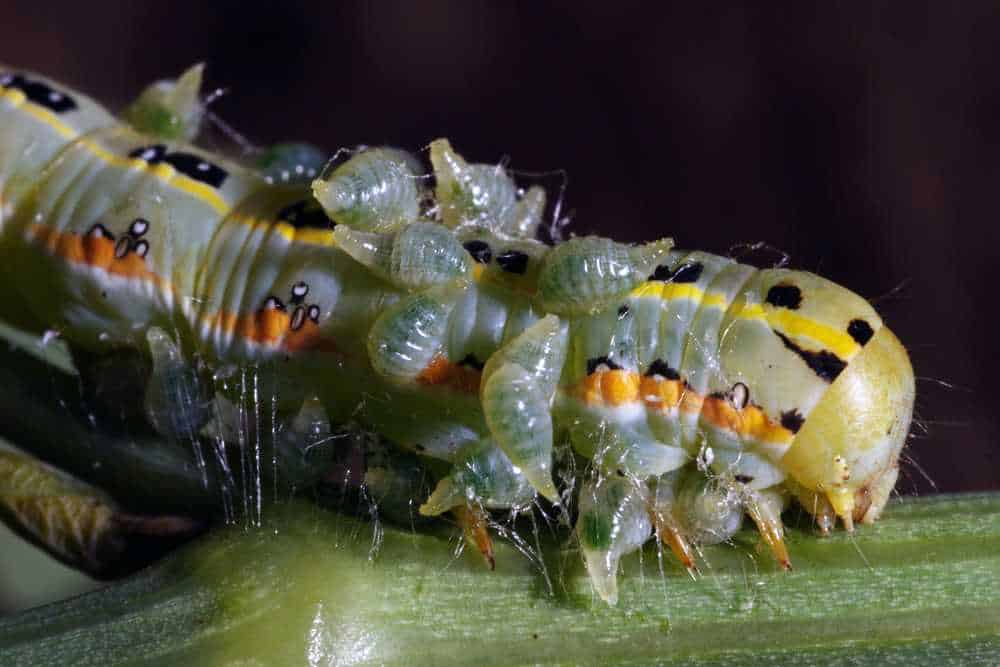

An increase in the number of parasitic caterpillars can have serious consequences for the ecosystem. Firstly, this can lead to a decline in the butterfly population, as the caterpillars feed on their eggs, larvae and pupae. A decline in butterfly numbers can affect plant pollination, as they are important pollinators.
Secondly, an increase in the number of parasitic caterpillars can lead to defoliation of plants. Caterpillars feed on plant leaves, which can lead to defoliation. This can affect plant growth and development, as well as their ability to carry out photosynthesis.
In addition, an increase in the number of parasitic caterpillars can cause an imbalance in the ecosystem. If caterpillars become too numerous, they can consume all the available resources in their habitat, which can lead to the extinction of not only the butterflies, but also other organisms that depend on these resources.
It is also worth noting that an increase in the number of parasitic caterpillars can lead to changes in the composition of vegetation in the ecosystem. If caterpillars prefer certain plant species, they may become dominant while other plant species may be suppressed. This can lead to changes in food chains and a decrease in biodiversity in the ecosystem.
In general, an increase in the number of parasitic caterpillars can have negative consequences on the ecosystem, including a decrease in butterfly populations, defoliation of plants, imbalance and changes in vegetation composition. Therefore, it is necessary to monitor and control the numbers of these caterpillars to maintain balance in natural communities.
How to protect butterflies and their habitats from parasitic caterpillars?

Parasitic caterpillars can pose a serious threat to butterflies and their habitats. However, there are certain measures that can be taken to protect butterflies and preserve their habitat.
1. Maintain a variety of vegetation
Butterflies are pollinators and depend on a variety of vegetation for nutrition and reproduction. Providing a rich variety of vegetation in your garden or property can help butterflies survive and reduce the risk of attack by parasitic caterpillars.
2. Kill parasitic caterpillars early

If you notice parasitic caterpillars on plants, begin eliminating them immediately. The sooner you find and destroy the caterpillars, the less impact they will have on the butterflies and their habitat.
3. Use biological control methods
Biological control methods, such as the use of natural enemies of parasitic caterpillars, can be effective in controlling this threat. For example, you may attract predators such as birds, frogs and insects that feed on the caterpillars.
4. Avoid using pesticides

The use of pesticides can have a negative impact on butterflies and their habitats. When using pesticides is necessary, choose environmentally friendly alternatives and apply them with caution to minimize exposure to butterflies and other beneficial insects.
Following these measures will help protect butterflies and their habitats from parasitic caterpillars and preserve their beauty and diversity.