Butterflies are one of the most colorful and amazing creatures on our planet. They attract attention not only with their bright colors, but also with their complex behavior. However, like any other living organisms, butterflies are susceptible to parasites.
Parasites can cause serious damage to a butterfly population, and in some cases even threaten its survival. They can attack butterflies at different stages of their life cycle, from eggs to larvae to adults. Parasites can feed on the tissues of butterflies or use them as hosts for their own breeding stages.
However, butterflies have evolved various adaptive strategies to protect themselves from parasites. They may have bright colors that serve as a signal to predators that they are poisonous or unsuitable for food. Butterflies may also have various defense mechanisms such as thorns or a foul odor that repels parasites.
The protection of butterflies from parasites is of great importance for their evolution and migration. Parasites can put pressure on butterfly populations, leading to selection in favor of individuals with more effective defense mechanisms. This may lead to the emergence of new species or subspecies of butterflies that are more successfully adapted to their environment.
Also protecting butterflies from parasites can be important for their migration. Parasites can weaken butterflies, making them less capable of long flights. This may lead to changes in migration routes and the distribution of butterfly populations. Studying the interactions between butterflies and their parasites helps us better understand the processes of evolution and migration in nature.
Importance of Butterfly Conservation
Butterfly conservation is essential for biodiversity conservation and ecosystem sustainability. Butterflies are important plant pollinators, so conserving them helps maintain soil fertility and crop yields.
Butterfly conservation also plays an important role in maintaining food chains and biological balance. Butterflies are a food source for many species of birds, mammals, and other predators. If the butterflies disappear, it could disrupt food chains and worsen conditions for other animals.
Butterfly conservation also contributes to the conservation of their unique evolutionary adaptations and migration routes. Many species of butterflies have complex life cycles, including long distance migrations and interactions with different ecosystems. The loss of butterfly species can lead to a violation of the ecological integrity and a decrease in the resilience of ecosystems.
Butterfly protection is also important from an aesthetic point of view. Butterflies are one of the most beautiful and amazing creatures of nature. Their bright colors and graceful movements attract the attention and admiration of people. Butterfly protection allows you to preserve this beauty for future generations and enjoy it in the present.
Types of parasites that harm butterflies

Butterflies are the object of attention of many types of parasites, which can cause them significant harm. One of the most common parasites that attack butterflies are caterpillar parasites. These parasites lay their eggs on leaves, which are then ingested by butterfly caterpillars along with their food. Caterpillar parasites feed on the tissue of the caterpillars, which can cause them to die or weaken to the point where they cannot go through the process of metamorphosis and turn into an adult butterfly.
Another type of parasites that cause harm to butterflies are riders. These parasites lay their eggs on butterflies or their caterpillars. After hatching, the ichneumon larvae enter the body of the butterflies and feed on their blood or tissue. This can lead to the weakening and death of butterflies, as well as limit their ability to reproduce and migrate.
There are also parasites that attack butterfly eggs. They lay their eggs in butterfly eggs, and parasitic larvae feed on the contents of these eggs. This can lead to the death of a large number of butterfly eggs and reduce their number in the population.
In general, parasites are a serious threat to butterflies, weakening them, reducing their numbers and limiting their ability to migrate and reproduce. This may have a long-term impact on the evolution and diversity of butterflies, as well as the ecosystem in which they play an important role.
Butterfly adaptations to protect against parasites
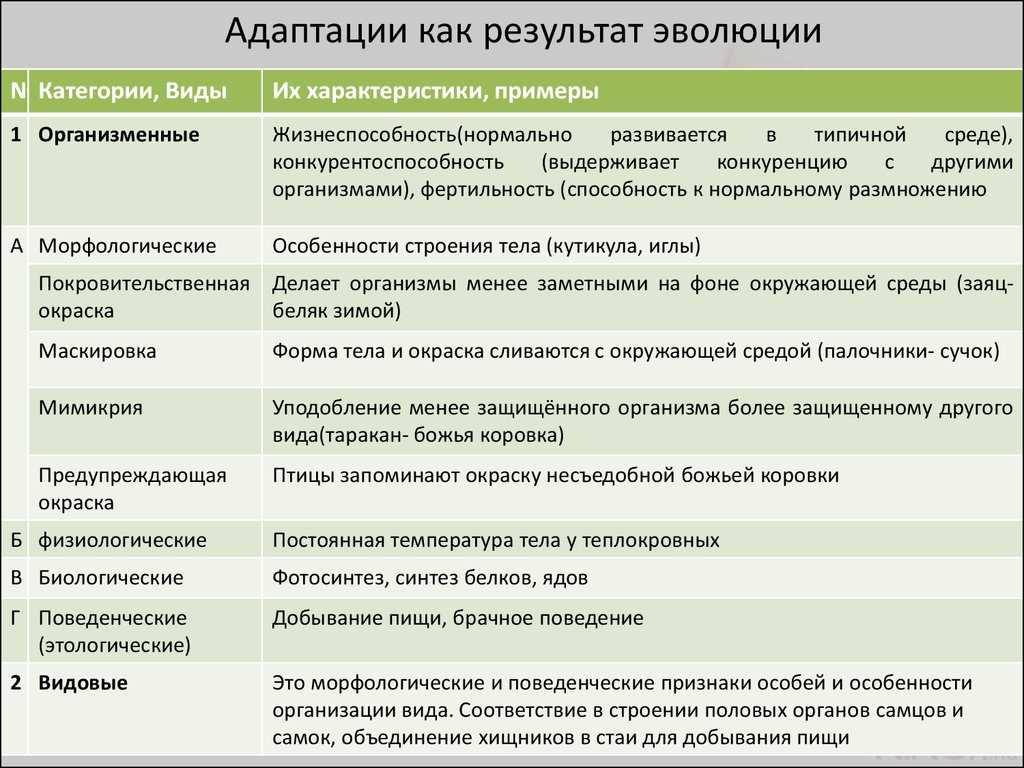
Butterflies have developed various adaptations to protect themselves from parasites such as parasitoid insects and fungi. One of the most effective adaptations is the evolutionary diversity of wing coloration, which can serve as both a camouflage and a signal to potential parasites.
Disguise — This is one of the most common adaptations in butterflies to protect themselves from parasites. They can imitate the environment to blend into the background and avoid detection by parasites. Some butterflies have coloring that imitates leaves or tree bark, thereby deceiving parasites and preventing their attack.
Aposematic coloration — This is another adaptation that butterflies use to protect themselves from parasites. They have bright and contrasting coloration that warns parasites that they are toxic or unpleasant. This strategy gives parasites a clear signal that the butterflies are dangerous and should not be attacked.
Physical adaptations also play an important role in protecting butterflies from parasites. For example, some species of butterflies have spikes or hairs on their bodies that act as a defense against parasites. These spines and hairs may be venomous or simply present a physical barrier to parasites, making them difficult or dangerous to attack.
Cryptosymbiosis — This is another interesting adaptation that some butterflies use to protect themselves from parasites. They can interact with microorganisms, such as fungi, and develop a symbiotic relationship within themselves. This allows them to protect their bodies from parasitic fungi and increase their survival.
Interactions between parasites and butterflies
Butterflies are the object of interaction with various types of parasites. Parasites can be internal or external, and their presence can have a significant impact on the life and evolution of butterflies. One of the most well-known forms of interaction is the parasitism of butterfly larvae. Some types of parasites lay their eggs on butterfly larvae, and when the eggs develop, they feed on the tissues and organs of the butterfly.
External parasites, such as parasitoid insects, can have a direct impact on the lives of butterflies. Parasitoid larvae feed on the tissues and fluids of butterflies, leading to their death. In response to such exposure, butterflies can develop defense mechanisms, such as evolving the ability to lay eggs in places inaccessible to parasitoids, or developing the ability to quickly hide from them.
internal parasites also play an important role in interacting with butterflies. They can affect the physiological processes of butterflies, change their behavior and even lead to their death. Some internal parasites may use butterflies as an intermediate or definitive host for their development. This can lead to a change in the butterflies' migratory patterns as they become vulnerable to parasites in certain areas and must seek new places to breed and feed.
Thus, the interaction between parasites and butterflies is a complex and dynamic process that can have a strong influence on the evolution and migration of butterflies. The study of this interaction allows a better understanding of the mechanisms of evolution and adaptation in nature.
The evolutionary influence of parasites on butterflies
Parasites play an important role in the evolution of butterflies, affecting their morphology, behavior, and even genetic makeup. They can cause the death of butterflies or exert pressure on selection in a population, which leads to changes in the genetic material and, ultimately, to evolution.
Change in morphology
Parasites can affect the morphology of butterflies, causing changes in their appearance. For example, some parasites can infect caterpillars and change their shape or color. This may cause butterflies with altered morphology to become more resistant to parasites, as they may be less conspicuous or have defense mechanisms against parasites.
Behavior change
Some parasites can influence the behavior of butterflies, causing them to change their habits or coping strategies. For example, parasitic ichneumons may cause butterflies to change egg laying sites or periods of activity to reduce the chance of infection. This may lead to changes in migratory routes or habitual habitats, which may affect the evolution and migration of butterflies.
genetic changes
Parasites can exert selection pressure in butterfly populations, which can lead to changes in their genetic makeup. Butterflies that have a genetic predisposition for stronger immune systems or other defense mechanisms against parasites will be more likely to survive and pass on their genes to the next generation. This can lead to a change in the frequency of certain genes in a population and, ultimately, to the evolution of butterflies.
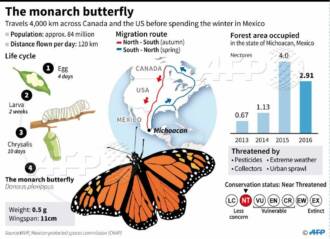
The role of parasites in butterfly migration

Butterfly migration is an amazing phenomenon that allows them to travel vast distances in search of food, a mate, or a suitable place to live. However, on this long and dangerous journey, butterflies face various threats, including parasites.
Parasites such as wasps and helminths play an important role in the life cycle of butterflies. They can affect the behavior and physiology of butterflies, which can significantly affect their ability to migrate. For example, parasites can cause a change in appetite or weaken butterflies, making it difficult for them to store enough energy to migrate.
In addition, parasites can have a direct effect on the reproduction of butterflies. For example, some parasites can infect caterpillars and affect their ability to pupa or their survival after transformation. This can lead to a decline in butterfly populations and limit their ability to migrate in large numbers.
At the same time, parasites can also have a negative effect on the organisms that parasitize them. For example, butterflies can develop defense mechanisms against parasites, such as immunity or behavioral strategies to reduce the risk of infection. This can lead to evolutionary changes in the parasitic population and influence the dynamics of butterfly migration.
Thus, parasites play a complex role in butterfly migration. They can have a negative impact on the ability of butterflies to migrate, but they can also stimulate evolutionary changes in butterfly populations and their parasites. Understanding this role is an important aspect in studying the influence of parasites on the evolution and migration of butterflies, as well as in developing strategies to protect them from parasitic infections.
Butterfly strategies to prevent parasitic attacks
Butterflies have evolved various strategies to protect themselves from parasitic attacks that help them survive and continue their reproductive cycles. One of these strategies is mimicry, when butterflies take on the appearance of other species that are dangerous or unpleasant for parasites. For example, some butterflies have coloration similar to bright and poisonous species to scare off parasites and warn of danger.
Another strategy is an evolutionary race against parasites. Butterflies constantly change their defense mechanisms and body structure to evade parasites, and parasites in turn adapt to new conditions and develop new methods of attack. This constant confrontation leads to evolutionary change and species diversity.
Some butterflies also use pheromones to trick parasites. They release chemicals that can attract or repel parasites and thus control their interactions with them. This allows the butterflies to avoid attacks and maintain their vitality.
However, not all butterflies have effective defense strategies. Some species are unable to resist parasites and become their victims. This can lead to population decline and even extinction of certain species of butterflies. Therefore, studying the strategies of butterflies to prevent parasitic attacks is an important task for the conservation of biodiversity and understanding the evolution of living organisms.
Influence of climatic conditions on the population of butterflies and their parasites

Climatic conditions have a significant impact on the population of butterflies and their parasites. Changes in temperature, precipitation, and seasonality can lead to shifts in the distribution and behavior of these organisms. For example, an increase in temperature can speed up the development of butterflies, which can lead to an increase in population size.
However, climate change can also have a negative impact on butterflies and their parasites. Dry periods and lack of food can reduce the survival and reproduction of butterflies, as well as reduce the availability and availability of food for parasites.
In addition, climate change can lead to changes in seasonality and migration of butterflies and their parasites. Shifts in seasonality can lead to mismatch between the timing of butterfly development and the availability and availability of food, which can adversely affect the population. Also, climate change may cause changes in migratory routes and patterns of movement of parasites, which can alienate them from their hosts.
In general, climatic conditions have an important influence on the population of butterflies and their parasites. Understanding these relationships is important for protecting biodiversity and ecosystem resilience, as well as for predicting and adapting to climate change.
The impact of anthropogenic activities on the protection of butterflies from parasites
Anthropogenic activities have a significant impact on the protection of butterflies from parasites. One of the most serious consequences is the destruction of the natural habitats of butterflies under the influence of various types of buildings and industrial facilities.
The destruction of natural habitats leads to a decrease in the number of butterfly populations and the deterioration of their living conditions. Butterflies lose the opportunity to find suitable plants for laying eggs and feeding caterpillars, which reduces their survival and ability to reproduce.
In addition, anthropogenic activities can lead to changes in climatic conditions, which also negatively affects butterflies. Changes in temperature and rainfall can disrupt the seasonal developmental cycles of butterflies, reducing their survival and resulting in population declines.
The protection of butterflies from parasites also suffers from environmental pollution. Emissions of harmful substances and the use of pesticides contribute to an increase in the number of parasites that can harm butterflies. They can infect eggs, caterpillars and pupae, reducing populations and threatening their survival.
To save butterflies from parasites, it is necessary to take measures to protect and restore their natural habitats, as well as to reduce environmental pollution. It is also important to conduct research on the interaction of butterflies with parasites and to develop methods of protection against them.
Butterfly pest control methods
Butterflies are objects of parasitic attack by various types of insects and microorganisms. They are attacked by parasites both during their development and in adulthood. There are several methods of pest control that allow you to protect butterflies from unwanted influences.
1. Use of chemicals

One of the methods of controlling parasites in butterflies is the use of chemicals. These preparations may be intended for the treatment of plants on which the butterflies feed, or directly for the treatment of the butterfly itself. Chemicals can kill parasites or prevent them from reproducing, helping to keep the butterfly population alive.
2. Biological control
Biological control is one of the effective methods of controlling parasites in butterflies. It is based on the use of natural enemies of parasites, such as predatory insects or parasitic organisms. These organisms can be released into the butterfly's natural habitat, where they begin to actively reproduce and reduce the parasite population. Biological control is a safer and more environmentally friendly method of pest control.
3. Genetic selection
Genetic selection is an important method for controlling parasites in butterflies. With this method it is possible to create genetically stable lines of butterflies that will be resistant to parasites. Genetic selection allows you to save valuable genetic resources of butterflies and prevent the evolution of parasites.
The value of butterfly conservation for the ecosystem
Butterflies play an important role in the ecosystem, serving as pollinators and food objects for other organisms. They are one of the main pollinators of plants, carrying pollen from one flower to another and promoting plant reproduction. Without the participation of butterflies, many plant species will not be able to pollinate and produce seeds, which will lead to their extinction.
In addition, butterflies are an important food base for many animals, including birds, frogs, lizards, and mammals. Their caterpillars serve as a source of food for many species of birds, and adult butterflies are a tasty morsel for predatory insects and birds. Therefore, the conservation of butterfly populations is important to maintain biodiversity in the ecosystem.
Protecting butterflies from parasites is also essential to maintaining their populations. Parasitic insects such as ichneumons and caterpillar gadflies can cause significant damage to butterflies by feeding on their eggs and caterpillars. If butterfly populations are reduced due to parasites, this can lead to an imbalance in the ecosystem and negative consequences for other organisms that depend on butterflies for food or pollinators.
Thus, the protection of butterflies is an important task for the conservation of the ecosystem as a whole. This allows you to maintain biodiversity, provide pollination of plants and maintain a food base for other organisms. In addition, the protection of butterflies from parasites helps to prevent disruption of the ecosystem balance and preserve the functioning of natural communities.
Prospects for research in the field of protection of butterflies from parasites
The protection of butterflies from parasites is an urgent problem that requires further research. After all, parasites can cause significant harm to the butterfly population, which leads to its reduction and even extinction. Therefore, it is important to conduct research aimed at developing effective methods for protecting butterflies from parasites.
One of the promising areas of research is the study of the natural mechanisms of protection of butterflies from parasites. Some species of butterflies have special structures and behavioral adaptations that help them avoid attacks from parasites. Research in this area will reveal these mechanisms and apply them to develop new methods of protection.
Another promising direction of research is the study of the interaction of butterflies with natural enemies of parasites. Some species of butterflies enter into symbiosis with other organisms that help them fight parasites. Research in this area can help identify these interactions and use them as a basis for developing new methods of protecting butterflies.
Also, it is important to conduct research on the development of new biological preparations to combat butterfly parasites. Natural preparations based on bacteria, fungi and other microorganisms can be effective in controlling parasites without harming the environment. Research in this area will help identify new potential control agents and develop methods for their application.