Butterflies are one of the most beautiful and amazing creatures of nature. They play an important role in the ecosystem, participating in pollination of plants and serving as food for other animals. However, like other organisms, butterflies can fall prey to various diseases and viruses that can seriously affect their abundance and diversity.
One of the most common diseases affecting butterflies is poisonous pollen. This virus is transmitted from one organism to another through the pollen of plants that serve as food for butterflies. Poisonous pollen causes a sharp weakening of the immune system of butterflies, which makes them more vulnerable to other diseases and infections.
Another dangerous virus that affects butterflies is the coccidia virus. This virus attacks the digestive system of butterflies, which leads to indigestion and a deterioration in the general condition of the body. Butterflies infected with the coccidia virus often become easy prey for predators, as they lose the ability to actively fly and evade danger.
Diseases and viruses affecting butterflies can have a major impact on the ecosystem as a whole. A decrease in the number of butterflies can lead to a violation of pollination of plants, which will lead to a deterioration in the yield and a decrease in soil fertility. In addition, butterflies are an important food source for many animals and their extinction could disrupt the food chain and lead to further changes in the ecosystem.
To conserve butterflies and prevent the spread of diseases and viruses, systematic research and monitoring of their populations is necessary. It is also important to conserve and restore their natural habitats by providing enough plants to serve as a food source for the butterflies. This is the only way to preserve the beauty and uniqueness of these amazing creatures and support the ecosystem as a whole.
Diseases and viruses that have infected butterflies: impact on the ecosystem

Butterflies are an important part of the ecosystem, playing the role of pollinators and being food for other animals. However, there are various diseases and viruses that can infect butterflies and have a negative impact on the ecosystem.
1. Viral infections

One of the most common diseases that can infect butterflies are viral infections. These viruses are transmitted through contact with infected individuals or through food. Viral infections can cause a variety of symptoms in butterflies, such as wing deformities, developmental delay, and death. This can lead to a decrease in the butterfly population and affect the biodiversity in the ecosystem.
2. Diseases of fungal origin

One of the main enemies of butterflies are diseases of fungal origin. Fungi can infect butterflies through contact with infected surfaces or through eating contaminated food. Diseases of fungal origin can lead to the death of butterflies, a weakening of their immune system, and a deterioration in their quality of life. As a result, the butterfly population may decline, which will affect the ecosystem and biodiversity.
3. Parasitic insects
Parasitic insects can also cause diseases in butterflies and affect the ecosystem. Some species of parasites lay their eggs on caterpillars or pupae, which later develop into adult parasites. This can lead to the death of butterflies or the weakening of their vitality. An increase in the number of parasites can lead to a decrease in the population of butterflies and changes in the ecosystem.
In general, diseases and viruses that infect butterflies have a significant impact on the ecosystem. They can lead to reduced butterfly populations, altered biodiversity and disrupted food chains. Therefore, it is important to study these diseases and develop measures for their prevention and control in order to maintain a balance in the ecosystem.
Viral infections and their consequences
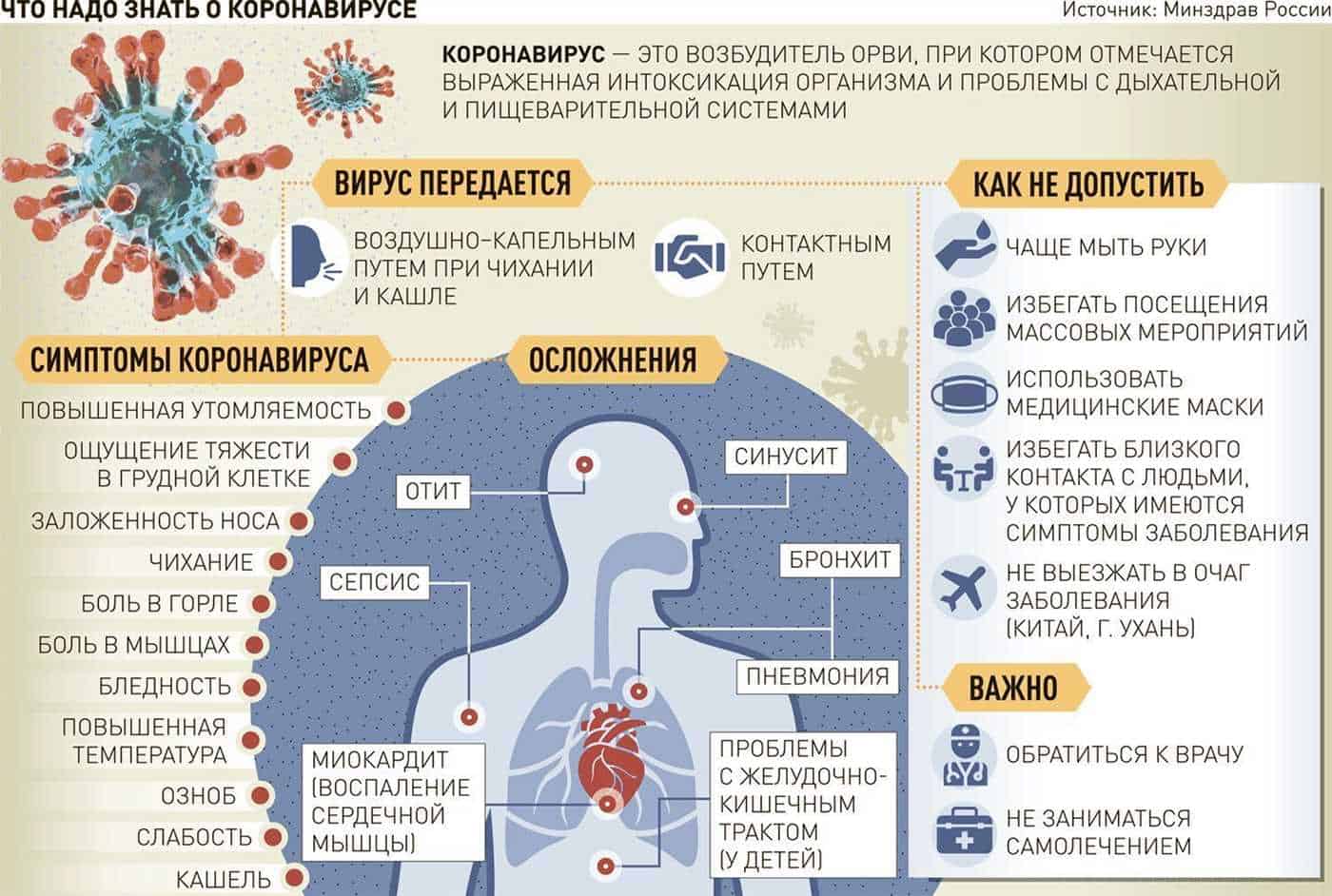
Viral infections pose a serious threat to butterflies and the ecosystem as a whole. These microscopic organisms are able to infect butterflies and cause various diseases that can have negative consequences.
One example of a viral infection that can affect butterflies is the poison ass virus. This virus infects butterflies and changes their appearance. Infected butterflies lose their brightness and beauty, which affects their ability to attract mates and reproduce.
Viral infections can also have a negative impact on the butterfly population as a whole. When a large number of butterflies are infected with a virus, this can lead to a significant reduction in their numbers. Butterfly population declines can have serious consequences for the ecosystem, as they are important plant pollinators.
Another consequence of viral infections may be disruption of the migratory routes of butterflies. Infected butterflies may lose their ability to navigate and be unable to find their way back to their breeding grounds. This can disrupt natural breeding cycles and affect biodiversity in the region.
Infection control measures must be taken to prevent the spread of viral infections among butterflies. This may include the use of biological drugs that can destroy viruses and the creation of conditions to strengthen the immune system of butterflies.
In general, viral infections are a major problem for butterflies and the ecosystem as a whole. Understanding and preventing these infections are essential steps to conserve the biodiversity and health of butterflies.
Parasitic diseases and their impact
Butterflies, like other organisms, are susceptible to various parasitic diseases that can seriously affect their life and impact on the ecosystem. One of the most well-known diseases affecting butterflies is the butterfly fungus. This fungus attacks insects, causing fungal infections in them and often leading to their death.
butterfly mushroom spreads through spores that fall on the body of a butterfly during its larval stage. The spores then enter the body of the butterfly, causing it to become sick. A butterfly affected by a fungus becomes weak and incapable of normal life. It may have delayed development, altered wing color and shape, and a weakened immune system.
The influence of the butterfly fungus on the ecosystem can be significant. Butterflies are important plant pollinators and also provide food for many predators. If the butterfly population is reduced due to fungal infections, this can lead to an imbalance in the ecosystem.
In addition to the butterfly fungus, there are other parasitic diseases that affect butterflies. For example, butterflies can be infested with parasitic ichneumons such as insect parasitic gadflies and parasitic gadflies. These parasites lay their eggs on the butterfly's body, and the larvae develop inside its body, feeding on its tissues and organs.
Parasitic diseases have a negative impact on butterflies and their ecosystem. Therefore, it is important to study and control the spread of these diseases in order to maintain biodiversity and ecosystem stability.
Bacterial infections and their effect on butterflies
Butterflies, like other organisms, are susceptible to various bacterial infections that can have a significant impact on their health and population. The bacteria can infect butterflies through a variety of routes, including contact with infected surfaces or through food.
One important bacterial infection that can affect butterflies is a disease called butterfly polyhedrosis. This infection is caused by a bacterium called Baculovirus, which attacks butterfly caterpillars. The bacterium multiplies inside the caterpillar, causing it to become sick and eventually die. This can significantly reduce the butterfly population and have a negative impact on the ecosystem.
Bacterial infections can also affect the reproduction and development of butterflies. For example, the bacteria Pseudomonas aeruginosa can infect caterpillars and cause them to die before they can pupa. This can lead to a decrease in the number of butterflies and disruption of their life cycle.
It is important to note that bacterial infections can be dangerous not only for butterflies, but also for other organisms in the ecosystem. For example, some bacteria can be transferred from butterflies to other insects or animals, which can cause disease and death. Therefore, the study of bacterial infections in butterflies is an important task for the conservation of biodiversity and ecological balance.
Fungal diseases and their impact on the ecosystem
Fungal diseases are one of the main threats to butterflies and their ecosystem. These diseases are caused by various types of fungi that can infect butterflies at different stages of their life cycle. Fungi can infect larvae, pupae and adults, causing various symptoms and death.
The impact of fungal diseases on the butterfly ecosystem can be significant. First, fungi can destroy a significant number of individuals, which leads to a decrease in the population. This can have negative consequences for other organisms that depend on butterflies for food or pollinators.
Secondly, fungal diseases can change the balance in an ecosystem, as some fungi can only be pathogenic for certain species of butterflies. If the population of one species of butterfly is reduced due to a fungal disease, this can lead to an increase in the abundance of other species, which can affect vegetation and other organisms in the ecosystem.
Also, fungal diseases can affect the migration of butterflies. Some fungi can infect butterflies along their migration routes, which can lead to a decrease in the number of butterflies in certain areas and upset the balance between species in different regions.
In general, fungal diseases are a major problem for butterflies and their ecosystem. To preserve the diversity and stability in nature, it is necessary to conduct research and develop measures to prevent the spread of fungal infections and protect the butterfly population.
Spread of disease through contact with other butterflies
Butterflies, like other animals, can be susceptible to various infectious diseases that can be spread through contact with other butterflies. This can occur during wing contact or interaction on forage plants.
One of the most common diseases among butterflies is the nuclear glacier virus. It can be transmitted from a sick butterfly to a healthy one through contact or by eating infected plants. As a result, the disease can enter the body of a healthy butterfly and cause various symptoms in it, such as deformation of the wings or a weakened immune system.
There are also other diseases that can be transmitted through contact with other butterflies. For example, fungal infections can be transmitted by wing contact or contact with contaminated surfaces. These infections can cause moths to blotch their wings or even kill them.
The spread of diseases through contact with other butterflies can have a major impact on an ecosystem. Infected butterflies can become a source of infection for other individuals, which can lead to a decrease in population and imbalance in the ecosystem. Therefore, it is important to take precautions to prevent the spread of disease among butterflies and to keep their populations healthy.
The influence of diseases and viruses on the reproduction of butterflies
Diseases and viruses can have a serious impact on butterfly reproduction, which can lead to disruption of the ecosystem and a decline in their numbers. One of the most common diseases that can affect butterflies is poisonous fungi. These fungi can enter the butterflies’ bodies through the food supply or through damaged areas on the wings and body. Poisonous fungi can cause a variety of symptoms, including wing deformities, loss of color, and weakness, making it difficult for butterflies to reproduce and survive.
Viruses can also be dangerous to butterflies. Some viruses can be passed from infected butterflies to healthy ones through contact or food. This can lead to massive infection and death of the butterfly population. Viruses can cause a variety of symptoms, including discoloration of the wings, deformation and weakening of the body. Diseases and viruses can also affect the ability of butterflies to fly, making it difficult for them to move around and find food, as well as find a breeding partner.
Diseases and viruses can have long-term effects on the butterfly population and the ecosystem as a whole. Butterfly decline can lead to disruption of the food chain and interactions with other organisms. Butterflies play an important role in the pollination of plants, so their reduction can lead to a deterioration in the conditions for plant growth and reproduction. In addition, butterflies are food for many animals, so their absence can affect the food chain and biodiversity in an ecosystem.
Consequences of infecting butterflies with their appetite and nutrient cycles
Infecting butterflies with certain diseases and viruses can have serious consequences for the ecosystem. When butterflies become infected, their appetite and feeding cycles can change dramatically, which can lead to imbalances in natural communities.
Changing eating habits
Viruses and diseases can cause changes in appetite in infected butterflies. They may begin to consume more food or, conversely, stop eating. This can lead to resource scarcity and competition with other species that feed on the same plants. Uncontrolled breeding of butterflies due to increased appetite can also lead to overpopulation and depletion of food resources.
The spread of disease
Infected butterflies can become carriers of diseases and viruses that can infect other individuals and plant species. When visiting different plants and flowers, infected butterflies can transmit infections and spread them throughout the ecosystem. This can lead to mass wilt of plants and a decrease in biodiversity in the area.
Impact on populations
Infection of butterflies with diseases can have a negative impact on the populations of these insects. If the disease is highly prevalent and causes high mortality, the butterfly population may be greatly reduced. This can lead to an imbalance in the ecosystem, as butterflies play an important role in plant pollination and are a food source for other animals.
In general, infecting butterflies with their appetite and nutrient cycles can have serious consequences for the ecosystem. Therefore, it is important to study and control the spread of diseases among butterflies in order to maintain biodiversity and ecosystem stability.
Influence of diseases on migration and life cycle of butterflies
Butterflies are an important part of the ecosystem, performing a number of functions, including pollinating flowers and serving as food for other animals. However, they are also susceptible to various diseases that can significantly affect their life cycle and migration.
Viral infections
One of the most common diseases affecting butterflies are viral infections. These infections are transmitted through contact between butterflies or through baits such as flowers. The virus can cause a variety of symptoms, including wing deformity, muscle weakness, and even butterfly death.
Viral infections can seriously affect butterfly migration. An infected butterfly may lose its ability to fly or disrupt its navigation, hindering its ability to migrate long distances. This can lead to a change in the distribution of butterflies and disruption of the ecosystem in which they play an important role.
parasites
In addition to viruses, butterflies are also susceptible to attacks by various parasites. Some parasites can infect butterflies in their larval stage by entering the body and feeding on their tissues. This can lead to weakness and death of the butterfly before it is fully developed.
Parasites can also influence the migration of butterflies, causing them to change their routes or stay in one place to avoid infection. This can lead to a decrease in the number of butterflies in certain regions and affect the interaction between butterflies and other organisms in the ecosystem.
Immunity and adaptation
Some butterflies may develop immunity to certain diseases or be more resistant to their effects. This is due to genetic adaptations that allow them to survive and reproduce even in the presence of disease.
However, as climate and environmental conditions change, butterflies may encounter new types of diseases for which they have no immunity. This can lead to the deterioration of their life cycle and migration, and ultimately to the disruption of the ecosystem in which they play an important role.
The importance of studying diseases and viruses in butterflies for the conservation of the ecosystem
Butterflies are an important part of the ecosystem, performing a number of functions in nature. The study of diseases and the viruses that they can infect is of great importance for the conservation of biodiversity and balance in natural communities.
The impact of diseases and viruses on butterflies:
Diseases and viruses can seriously affect the life of butterflies. They can cause a decrease in population, slow down the growth and development, and in some cases even lead to the complete extinction of certain species. Some diseases and viruses can be fatal to butterflies, especially their larvae and pupae.
Impact on the ecosystem:
The disappearance or decline of certain species of butterflies can have negative consequences for the ecosystem as a whole. Butterflies play an important role in the pollination of plants, which contributes to their reproduction and conservation. They are also food for many other animals, including birds, insects, and spiders. Therefore, a decline in butterfly populations can disrupt food chains and cause imbalances in natural communities.
Research Significance:
Studying diseases and viruses in butterflies allows us to understand what factors can contribute to their spread and what measures can be taken to prevent epidemics and save populations. This allows the development of strategies for the protection and restoration of biodiversity. Research is also helping to identify new types of diseases and viruses that could threaten butterflies and other organisms in the future.