Butterfly migrations are one of the most amazing phenomena in the world of wildlife. These delicate and colorful insects are capable of covering vast distances, moving from one area to another. Butterfly migrations occur throughout the world and are of great interest to scientists and nature observers.
One of the main reasons for butterfly migrations is climate change. Butterflies migrate in search of more favorable conditions for reproduction and survival. Some butterfly species migrate from tropical areas to cold northern regions to escape extreme temperatures and food shortages. Other species migrate in search of suitable places to lay eggs and to obtain food for their caterpillars.
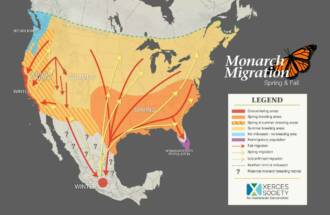
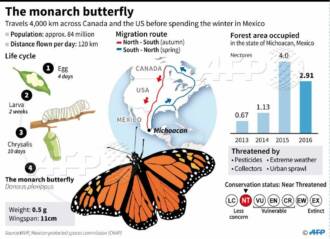
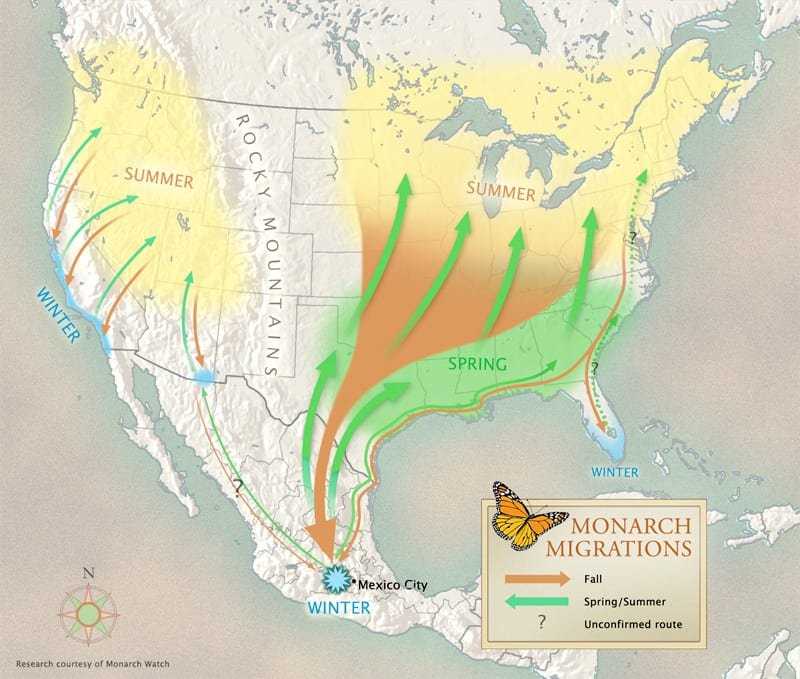
The migration routes of butterflies can be quite diverse. Some species of butterflies fly thousands of kilometers, crossing oceans and mountains. For example, monarch butterflies migrate from North America to Mexico every year, covering a distance of up to 4,000 kilometers. Other butterflies migrate shorter distances, moving from one area to another within their region.
Butterfly migrations have their own characteristics. For example, butterflies may use different methods of orientation and navigation during migration. They can use the sun, stars, Earth's magnetic field and smells to determine their direction. Butterflies can also fly in groups, which helps them reduce energy loss and increase their chances of survival during migration.
Reasons for butterfly migrations
Butterfly migration is a phenomenon that is caused by various reasons and has its own characteristics. One of the main reasons for migration is the search for food. Butterflies migrate from one place to another to find suitable plants on which they can feed and reproduce. Due to changes in the environment and seasonal fluctuations, some plants may become inaccessible to butterflies for a period of time, forcing them to seek new habitats.
Another reason for migration is the need to exclude competition. Butterflies may migrate due to decreased resource availability and increased population density in a particular area. In such cases, they look for new territories where they can find more food and space to survive and reproduce. Migrations also help avoid competition with other butterfly species or with other animals that may be competing for the same resources.
The third reason for butterfly migrations is changes in climatic conditions. Butterflies are very sensitive to environmental temperature and humidity. If climatic conditions become unsuitable for their survival, they can migrate to more suitable places. For example, some species of butterflies migrate south before winter to escape the cold and lack of food. Other species may migrate north during warmer months to avoid heat and overheating.
The influence of climatic conditions on migration
Climatic conditions are one of the main factors influencing butterfly migrations. Changes in temperature, precipitation and seasonality can significantly influence the behavior of butterflies during their migrations.
Temperature is an important factor determining the beginning and duration of butterfly migrations. Changes in temperature can prevent or delay the onset of migration and also affect the speed and direction of butterfly flight. For example, low temperatures may delay migration until more favorable conditions occur.
Precipitation also play an important role in butterfly migration. Excess or lack of precipitation can change the natural conditions necessary for butterflies to reproduce and feed. For example, a prolonged period of drought can reduce the amount of food available to butterflies and cause them to migrate in search of new food sources.
Changes in seasonality can also influence butterfly migrations. Changes in the length and intensity of seasons can alter food availability and breeding conditions, which can affect butterfly migration. For example, shorter summers can lead to more migration as butterflies must move faster to find food and breeding sites.
Thus, climatic conditions play an important role in butterfly migrations. Changes in temperature, precipitation and seasonality can affect the onset, duration and direction of butterfly migrations, as well as food availability and breeding conditions. Understanding these influences allows us to better understand and predict butterfly migration patterns and their adaptation to changing climate conditions.
Butterfly migration routes
Butterfly migrations are an amazing phenomenon that happens every year. Butterflies migrate in search of better conditions for life and reproduction. Depending on the species and habitat, migration routes can vary significantly.
Some butterfly species migrate short distances, moving from one area to another. They follow flower fields and food sources. For example, moth butterflies migrate along the coast, moving from one region to another in search of places with an abundance of nectar and suitable conditions for reproduction.
Other species of butterflies migrate over considerable distances, covering hundreds and even thousands of kilometers. The most famous migrations are those of monarch butterflies. They cross North America every year, flying from their wintering grounds in Mexico to their breeding grounds in Canada and back. This incredible journey takes several generations of butterflies, who pass on information about the route to the next generation.
In some cases, butterfly migrations may be related to changes in climate or the availability of food resources. For example, if the area where butterflies lived becomes uninhabitable due to drought or other factors, they may begin to migrate in search of more favorable conditions. This happens, for example, with cabbage butterflies.
Butterfly migration routes can be studied using a variety of methods, including field observations and the use of radio tags or tracking devices. These studies help scientists better understand the causes and characteristics of butterfly migrations, as well as develop measures for their conservation and protection.
The role of geographical barriers in migrations

Geographical barriers play an important role in butterfly migrations, determining their routes and influencing their characteristics. One of the main obstacles is the mountains, which often prove to be insurmountable obstacles for migrating butterflies. Mountain ranges create barriers that prevent butterflies from moving in certain directions, forcing them to find a way around or through the mountains.
Some species of butterflies are able to overcome mountain obstacles by taking advantage of thermal currents or high-altitude winds. They rise to heights and use atmospheric conditions to fly over mountains. Such species can overcome mountain ranges, which are insurmountable obstacles for other butterflies.
Water barriers such as rivers and oceans also influence butterfly migrations. They can become serious obstacles to migrating butterflies, forcing them to find their way around or over water obstacles. Some species of butterflies are able to overcome water obstacles by swimming or flying above them at a considerable height.
Thus, geographical barriers have a significant impact on butterfly migrations. They determine migration routes and can influence their characteristics. Butterflies are forced to overcome mountains and water obstacles, looking for a way around or through them. Some species are able to overcome these obstacles using atmospheric conditions or swimming abilities. Studying the role of geographic barriers in butterfly migrations helps to better understand their behavior and adaptations to the environment.
Features of migrations of different species of butterflies
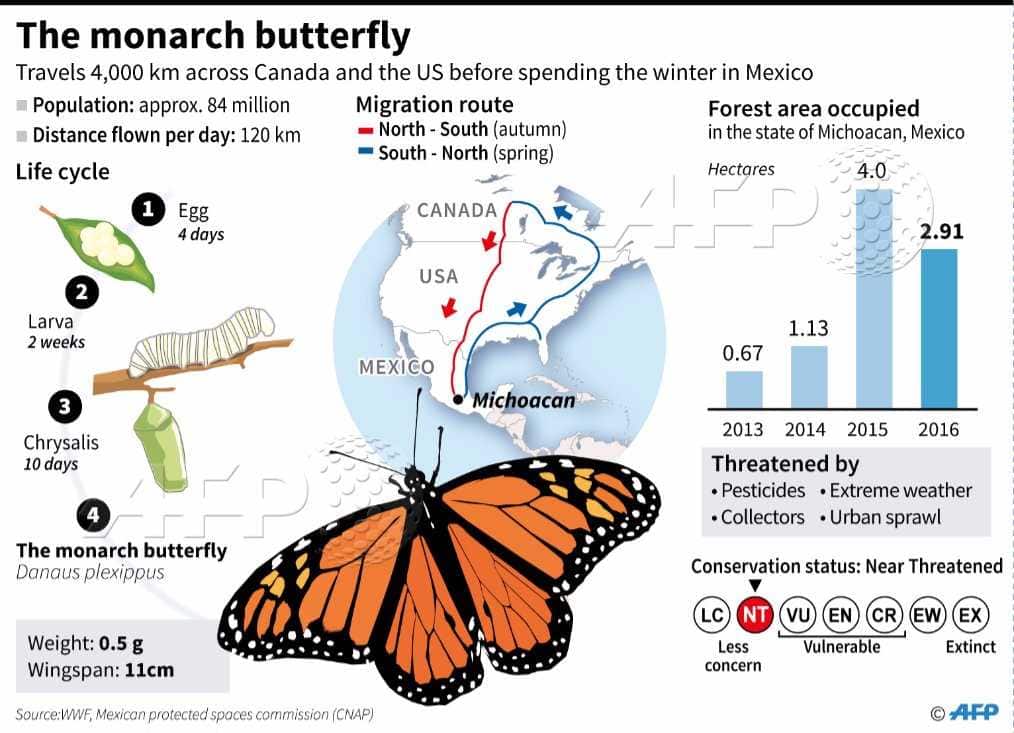
Migrations of different species of butterflies have their own characteristics, which are determined by many factors. One of the main factors influencing the migration of butterflies is seasonality. Some butterfly species migrate only at certain times of the year, such as spring or autumn, when conditions are favorable for their life cycle to continue.
Another feature of butterfly migration is the route. Some species of butterflies migrate very long distances, covering hundreds and even thousands of kilometers. They follow certain routes, which are often repeated from year to year. Such migrations may be associated with the search for food, reproduction, or avoidance of unfavorable conditions.
When migrating, butterflies can use various methods of movement. Some species of butterflies prefer to travel in large groups, forming so-called flocks, which provide them with protection and help them find their way to their destination. Other species can migrate alone or in small groups, flying over fairly long distances.
It is also worth noting that butterfly migrations can have a significant impact on ecosystems. The movement of butterflies can help spread pollen, which is important for plant pollination. In addition, butterfly migration can be an important factor in the balance of populations, as it allows different species to live in different places at different times of the year, which contributes to the stability of the ecosystem.
Impact of migration on butterfly populations
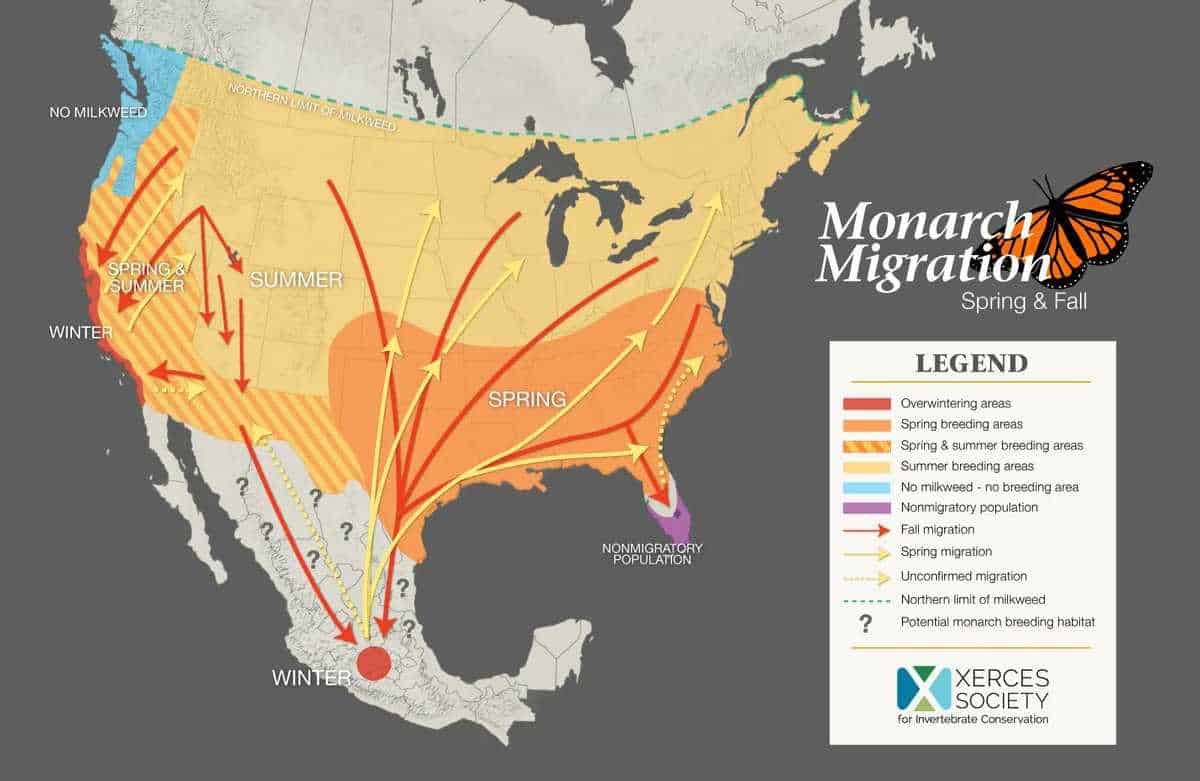
Butterfly migrations have a significant impact on the populations of these insects. They can lead to changes in population size and structure, as well as genetic flow between different populations. Migrations are an important factor in the dynamics of butterfly populations.
Moving butterflies over long distances allows them to colonize new territories and find new food sources. However, migrations can also pose a threat to butterfly populations. For example, butterflies may encounter unfavorable conditions during their migrations, such as extreme weather or loss of larval habitat. This can lead to population decline and extinction.
Migrations can also influence the genetic diversity of butterfly populations. When butterflies move between different populations, they can increase genetic flow, which promotes the exchange of genetic materials and increases genetic diversity within populations. This, in turn, can increase the adaptive capabilities of the population and contribute to its survival in changing conditions.
Overall, butterfly migrations have complex effects on these insect populations. They can be either beneficial or dangerous for the population, depending on the specific conditions and factors affecting the movement of butterflies. Understanding these influences is an important aspect in studying butterfly migrations and developing strategies for their conservation and sustainable development.
The role of humans in changing butterfly migrations

Butterfly migrations are a complex and unique phenomenon that is influenced by various factors, including human activities. Human activities can have both positive and negative impacts on butterfly migrations.
Habitat loss and destruction
One of the main negative impacts of humans on butterfly migration is the loss and destruction of their habitats. Agricultural expansion, deforestation, coastal development, and other forms of anthropogenic activity are leading to the loss of natural habitats necessary for butterflies to breed and overwinter. As a result, many butterfly populations are forced to find new places to migrate or are threatened with extinction.
Changing of the climate
Human activity is also significantly influencing climate change, which has a negative impact on butterfly migrations. Global warming, caused by greenhouse gas emissions, is changing temperature conditions in different regions of the world. This can lead to shifts in butterfly distribution boundaries, changes in the timing and direction of migrations, and a decrease in the availability of food resources. As a result, these changes may negatively impact butterfly survival and population dynamics.
However, humans can also play a positive role in conserving and supporting butterfly migrations. The creation and protection of reserves, parks and other natural areas where butterflies can find shelter and resources helps preserve their populations. It is also important to limit the use of pesticides and other chemicals that can negatively impact butterflies and their habitats.
Defense mechanisms of butterflies during migrations
Butterfly migrations are long and dangerous journeys during which they cover vast distances. Due to this, butterflies have evolved a number of defense mechanisms that allow them to survive and successfully reach their destination.
Cryptic coloration and mimicry
One of the main defense mechanisms of butterflies during migration is cryptic coloration and mimicry. Many species of butterflies have colors that allow them to blend into their environment and be virtually invisible to predators. They can imitate leaves, tree bark or flowers, making them invisible to their enemies. Moreover, some species of butterflies mimic other dangerous or unpalatable insects, such as wasps or bees, in order to intimidate their enemies and avoid attack.
Rejection and toxicity
Another defense mechanism of butterflies is rejection and toxicity. Some species of butterflies have bright colors, which serve as a signal to predators that they are poisonous or a nuisance. They may contain toxic substances in their bodies that can repel or even poison predators. Butterflies that have such protection can be calm and confidently continue on their way without fear of being eaten.
Using wind and thermal currents
During migration, butterflies can use wind and thermal air currents to their advantage. They are able to fly for long periods of time, using the support of air currents, which allows them to save energy and cover long distances. Butterflies can also choose routes that provide optimal flight conditions, such as avoiding strong winds or using thermal currents to reach higher altitudes and cross mountain ridges.