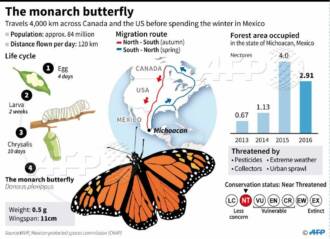
The cabbage goose, also known as the white-headed goose, is one of the most well-known goose species. They live in the northern regions of Eurasia and America and migrate over long distances in search of food and warmer nesting sites. Migration of cabbage is an amazing phenomenon that includes long flights and the coordinated work of the entire population.
Seasonal changes play an important role in the life of cabbage. They have a thick, white down coat that helps them survive the cold winter conditions. In the spring, when the snow melts and food becomes available, they begin migrating north to find pastures and nesting sites. At this time, cabbage becomes especially active, and their loud cry can be heard for many kilometers around.
The ecosystem in which the cabbage lives is also amazing. They usually nest on the banks of lakes and rivers where they will find food and safety for their chicks. Cabbage bugs feed on a variety of plants, including cabbage, cereals, and herbs. They are also important anglers, their long necks allowing them to reach the bottom of lakes and rivers to catch fish.
The cabbage goose is an amazing species of goose that impresses with its migration, adaptation to seasonal changes and its important role in the ecosystem. Its presence in the northern regions of Eurasia and America is proof of its amazing ability to survive and adapt to the harsh conditions of northern latitudes.
Interesting Cabbage Facts:
1. Migrations: Cabbage is a migratory bird that makes long-distance migrations. It spends the winter in warm countries such as South Africa and South America and returns to its nests in Europe and Asia in the summer.
2. Seasonal changes: Cabbage has a bright plumage that changes depending on the season. In summer, she dresses in bright colors to attract a partner, and in winter, the plumage becomes dimmer and inconspicuous to hide from predators.
3. Ecosystem: Cabbage plays an important role in the ecosystem as it feeds on insects and other pests that can damage plants and agriculture. Its presence helps maintain the balance in nature and improves the quality of the soil.
4. Nesting: Cabbage builds its nests on trees or reeds near water bodies. She uses grass, twigs, and other materials to create a cozy and safe breeding area.
5. Reproduction: Cabbage is a monogamous bird, it stays with one partner for life. Together they bear and feed offspring. The female lays 3 to 6 eggs, which she incubates for about 30 days. The chicks stay in the nest for about 6 weeks before learning to fly and becoming independent.
6. Protection: Cabbage has various defense mechanisms against predators. She can use her plumage to create an illusion and blend with her surroundings. In addition, she can make loud noises or release a scent to distract enemies from her nests.
Cabbage migrations:
The cabbage, or northern pegasus, is one of the most distant migrants among birds. Every autumn, these birds begin their journey to the south, overcoming great distances. They migrate from the northern regions, where they spend the summer, to warmer places for the winter.
Migration of cabbages occurs along certain routes that they follow year after year. They use familiar landmarks such as mountains, rivers, and lakes to find their way. Each autumn and spring turns into a real test for these birds, but their innate instinct for navigation helps them successfully overcome thousands of kilometers.
During migration, cabbage can cover a distance of up to 15,000 kilometers within a few weeks. They fly at altitudes ranging from a few hundred to several thousand meters, using thermal currents to conserve energy. During the journey, they cross the borders of several countries and even continents.
The migrations of the cabbagefish are not only important for the bird itself, but also for the ecosystem in which it lives. During migration, they spread seeds and contribute to the diversity of the plant world. In addition, they are food for birds of prey and animals on their way, which helps to maintain the balance in nature.
Seasonal changes of cabbage:
The cabbage white is a migratory bird that travels long distances each year in search of food and suitable nesting sites.
In the spring, with the arrival of warm weather, the cabbage worm begins its journey from wintering in the southern countries back to its native nesting grounds. It actively searches for fertile fields and meadows where enough seeds and insects can be found for food.
In the summer, the cabbage lady actively builds nests and feeds her chicks. She uses various materials such as sticks, grass and feathers to create a strong nest that protects her chicks from predators and the weather.
In the autumn, when the time of departure comes, the cabbage flock gathers in large flocks and prepares for a long flight. She stocks up on fat to cover the long journey, and, together with other birds, goes south, where she will spend the winter.
During the winter, cabbage finds warm places to overwinter, such as tropical rainforests or coasts. Here she will feed on a variety of vegetation and insects to maintain her energy until her spring migration.
Cabbage ecosystem:

Cabbage is an important component of the ecosystem, where it plays the role of a food and shelter source for many living organisms. It provides food for many types of insects such as butterflies, caterpillars and beetles that feed on leaves and other parts of the plant.
Cabbage also provides shelter and breeding grounds for various species of birds and small animals. Some birds use cabbage as a place to build nests and raise their offspring. Small animals, such as mice and moles, can also live in the vicinity of cabbage, hiding from predators.
In addition, cabbage helps to maintain biodiversity in the ecosystem by attracting various types of beneficial insects such as bees and predatory beetles. Bees pollinate cabbage flowers, which contributes to its reproduction and preservation of the population. Predatory beetles, in turn, help control pests such as caterpillars and other insects that can wreak havoc on cabbage.
Features of the behavior of cabbage:
The cabbage white is a migratory bird that exhibits a number of peculiarities in its behavior.
Cabbage has a high degree of socialization and prefers to live in large flocks. This allows the bird to provide itself with a greater degree of safety by detecting danger with higher efficiency and quickly responding to it.
Cabbage is actively involved in the search for food and uses its witty skills to find food. She may look for food on the ground, bushes or tree branches.
Cabbage also shows interest in its own territory and protects it from other birds. She can use various sounds and chants to scare competitors away from her territory.
During seasonal migrations, cabbage shows an amazing ability to navigate long distances. She uses various landmarks, such as landscape features and the Earth's magnetic fields, to find her way. This allows her to successfully migrate long distances and return to the same place every year.
Impact of cabbage on the environment:
Cabbage, as one of the insect species, has a significant impact on the environment. Its activities have both positive and negative consequences.
Positive influence:
1. Pollination function. Cabbage is an important pollinator for many plants, including crops. Her visit to the flowers promotes pollination and the formation of fruits, which affects the increase in yield.
2. Participation in the circulation of substances. Cabbage is a decomposer of organic material, including falling leaves, fallen trees, and other plant debris. It helps break down organic material and return it to the soil as nutrients.
Bad influence:

1. Damage to crops. Cabbage can be a pest to many crops, including cabbage, broccoli, cauliflower, and others. It feeds on the leaves and stems of plants, which can lead to significant crop losses.
2. Spread of diseases. Cabbage can be a carrier of various diseases that affect crops. It can carry viruses, bacteria and fungi that can cause disease and damage to plants.
In general, cabbage plays an important role in the ecosystem, however, its impact on the environment can be both positive and negative, depending on the context and conditions of existence.
Cabbage population in different regions:
Cabbage is a widespread insect species that lives in various regions of the world. Cabbage populations can vary considerably depending on climatic conditions, the availability of food resources, and the presence of natural enemies.
In the northern regions, where winters are long and cold, the cabbage population usually decreases or disappears completely. Some individuals may migrate south in search of warmer wintering grounds.
In the southern regions, where the climate is warmer and more temperate, cabbage populations may be more stable. Here, insects have more opportunities to reproduce and search for food, which contributes to the growth and development of the population.
However, even in temperate climates, cabbage populations can be subject to seasonal changes. In the spring and summer, when food resources are more available, cabbage populations tend to increase. However, in autumn and winter, when food resources are limited, the population may decline.
Also, the cabbage population can be different in different ecosystems. In some places where natural enemies of the cabbage, such as predatory insects or birds, are present, the population may be lower. In other places, where there are few or no natural enemies, cabbage populations may be higher.
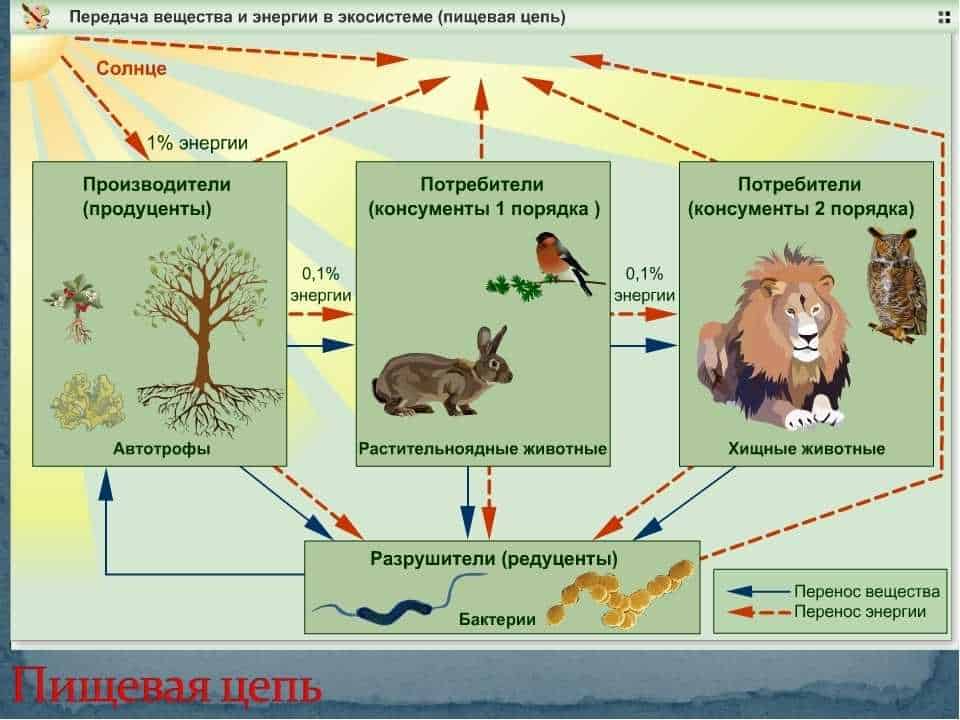
The role of cabbage in the food chain:

Cabbage is one of the important components of the food chain in its ecosystem. This insect is a parasitoid and feeds on pests of cabbage crops such as the cabbage caterpillar whitefly.
Cabbage performs the role of biological control, regulating the pest population. Its larvae develop inside the body of caterpillars and feed on their tissues, which leads to their death. Thus, cabbage helps prevent the mass reproduction of harmful insects and preserve the yield of cabbage crops.
Cabbage is also food for other organisms in the food chain. For example, birds, spiders, and other predators feed on adult cabbages. Thus, cabbage serves as a source of nutrition for the upper links of the food chain, maintaining a balance in the ecosystem.
Ways to protect cabbage from predators:
Cabbage, like many other plants, is attacked by various predators. One of the most common predators are insects such as aphids, ants, caterpillars and beetles. To protect cabbage from these predators, you can use various methods:
1. Biological control
Biological control is the use of natural enemies of predators to destroy their population. Predatory insect larvae such as ladybugs and hymenoptera can be used to control aphids. They feed on aphids and will help reduce their numbers. You can also use pheromones or other attracting substances to attract predators to the area where the cabbage is located.
2. Mechanical protection
Mechanical protection includes the use of various barriers to prevent predators from accessing the cabbage. For example, you can install nets or stretch special films over plants to prevent insects from entering. You can also use traps for beetles and other insects to reduce their numbers and protect the cabbage.
3. Chemical protection

Chemical defense involves the use of chemicals to kill predators. For example, you can use insecticides or repellents that repel insects from cabbage. However, when using chemicals, care must be taken and instructions must be followed so as not to harm the environment and human health.
The choice of how to protect cabbage from predators depends on the specific conditions and preferences of the gardener. It is important to approach the issue of plant protection with an ecological and sustainable methodology in order to maintain a balance in the ecosystem and ensure the healthy growth and development of cabbage.
Unique Cabbage Adaptations:
1. Mimicry

Cabbage has a unique mimicry ability that allows her to blend in with her surroundings and deceive her enemies. She is able to change the color of her skin to match the color of the leaves and stems of the plants she inhabits. This adaptation helps cabbage to avoid danger and go unnoticed by predators.
2. The disgust of predators

Cabbage has special glands located on its skin that emit an unpleasant odor. This smell repels many predators, including insects and birds, who are reluctant to eat cabbage because of the unpleasant taste and smell.
3. Adaptation to cold conditions
Cabbage perfectly adapted to the cold conditions of the northern regions. It is able to tolerate low temperatures and even freeze to survive the winter. Cabbage has special antifreeze substances in its blood that prevent the formation of ice crystals and keep it viable even in extreme frosts.
4. Ability to quickly reproduce
Cabbage has a high reproductive capacity and is able to reproduce rapidly to ensure the survival of its species. She is able to produce a large number of offspring in one season and has a short development period, which allows her to quickly multiply and adapt to new conditions.
5. Interaction with other organisms

Cabbage develops unique relationships with other organisms such as ants and parasitic insects. It can release certain chemicals that attract ants and cause them to defend the cabbage from predators. In addition, cabbage can be home to other species of insects that feed on its larvae and help control their population.
Change in the number of cabbage over time:

Cabbage numbers can vary greatly over time and depend on many factors such as food availability, habitat conditions, and competition with other species.
During cabbage migrations, their numbers can increase significantly. During this time, they travel long distances in search of food and suitable breeding conditions. As a result of migrations, the number of cabbage can reach its peak.
However, after the end of migrations, the number of cabbage can decrease. This may be due to depletion of food resources, changing habitat conditions, or competition with other bird species.
Seasonal changes can also affect cabbage numbers. For example, in winter, when food becomes more limited, cabbage numbers may decrease. However, in spring and summer, when there is more food, cabbage numbers may increase.
The ecosystem also plays an important role in changing the abundance of cabbage. If the ecosystem provides enough food and suitable conditions for reproduction, cabbage numbers can grow. However, if the ecosystem becomes unstable or insufficiently fertile, cabbage numbers may decline.