Butterflies are one of the most beautiful creatures in the insect world, but they can also cause serious problems for gardens and plants. External parasites such as caterpillars and caterpillar jackdaws can cause significant damage to plants by feeding on their leaves and stems. In addition, some parasites can multiply in the garden, creating even more problems. In this article, we will look at how to protect your garden from the breeding and harm of external butterfly parasites.
One of the most effective ways to control external butterfly parasites is to prevent them from breeding in the garden. To do this, you must destroy their eggs and caterpillars before they can become adult butterflies. One way to do this is to regularly inspect the plants and manually remove the eggs and caterpillars. You can also use special preparations or biological control agents that will help prevent the reproduction of parasites.
In addition, it is important to create favorable conditions for the growth and development of plants so that they are less susceptible to harm from parasites. Regular watering, fertilizing, and removing diseased or damaged plants will help strengthen their immunity and make them less attractive to outside pests. You can also apply various protection methods, such as nets and special covers, to prevent pests from accessing plants.
In conclusion, protecting your garden from the reproduction and damage of external butterfly parasites is an important task for all gardeners. Preventing reproduction, regularly inspecting and caring for plants, and using various methods of protection will help reduce the level of damage from parasites and maintain the beauty and health of the garden.
Definition and types of external parasites of butterflies

External parasites of butterflies are organisms that use butterflies as hosts for their reproduction and feeding. They can be of different species and affect different stages of development of butterflies, ranging from eggs to adults.
Types of external parasites of butterflies:

- Parasitic caterpillars — These are caterpillars of other insect species that feed on butterfly caterpillars. They can enter butterfly nests and feed on their eggs, or attack caterpillars while they are feeding.
- Parasitic Riders — are insects that lay their eggs on the caterpillar's body. After hatching, the parasite larvae begin to feed on the caterpillar's tissues, which leads to its death.
- parasitic insects — are insects that feed on the body of butterflies. They can be parasites of adults or reside inside their bodies throughout their life cycle.
- parasitic fungi - These are fungi that affect the body of butterflies, causing various diseases and infections. They can lead to deformation and death of butterflies.
To protect your garden from the reproduction and harm of external butterfly parasites, you need to take control and prevention measures. This may include the use of biological control agents such as parasitic insects, as well as the destruction of infected plants and ripe fruit, where eggs and larvae of parasites may hide. It is also helpful to regularly inspect the plants for signs of damage and apply protective measures such as insecticides.
Harm caused by external parasites of butterflies to plants
External parasites of butterflies can cause significant damage to plants, damaging both their leaves and fruits. They can cause discoloration, warping and drying of the leaves, which can eventually lead to the death of the plant.
Caterpillars are one of the most dangerous external parasites of butterflies. They feed on the leaves of plants, leaving behind ruined and gnawed leaf blades. Caterpillars can also penetrate fruits, feeding on and destroying their internal structure.
Another nasty external parasite of butterflies are larvae that feed on the root system of plants. They penetrate the ground and feed on the roots, which weakens the plant and makes it more vulnerable to various diseases and weather conditions.
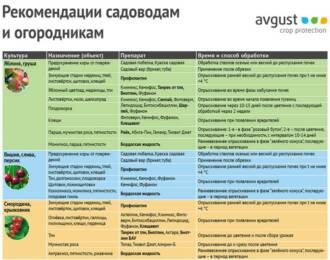
To protect plants from harm caused by external butterfly parasites, it is recommended to regularly monitor the condition of plants, use special preparations to combat caterpillars and other pests, and take preventive measures, such as destroying eggs and caterpillars before they reproduce.
Signs of damage to plants by external parasites of butterflies

Infection of plants by external butterfly parasites can have several characteristic signs that can help determine the presence of pests and take measures to eradicate them.
One of the most noticeable signs is leaf damage. Butterfly parasites often leave their eggs or caterpillars on the leaves, which actively feed on the plant mass. As a result, the leaves may be gnawed, have holes or be completely emaciated. Moreover, damage can be both scattered and grouped in certain parts of the plant.
Another sign of damage to plants by external parasites of butterflies is the presence of silk threads or cocoons on plants. Some types of butterflies, such as whiteflies, build their cocoons on the leaves or branches of a plant. This may be noticeable due to the white or light brown color of the cocoons. Also, threads of silk can be seen on the surface of the plant, indicating the presence of caterpillars or pupae.
In addition, damage to plants by external parasites of butterflies can be accompanied by a change in the appearance of plants. For example, leaves may change color or shape, stems may become weak and brittle, and flowers may fail to develop and fall off prematurely. Such changes can be caused both by the direct nutrition of the parasites and by the stress caused by their presence.
In general, noticeable signs of plant damage by external parasites of butterflies can be varied and depend on the type and stage of development of the pest. However, regular monitoring of plants and timely implementation of measures to combat parasites will help maintain the health of the garden and ensure its normal development.
Methods for protecting the garden from the reproduction of external parasites of butterflies

External parasites of butterflies can cause significant damage to the garden, breeding on plants and their leaves. However, there are various methods of protection that will help prevent the reproduction of parasites and keep plants healthy.
Selection of parasite-resistant plants

The first step in protecting your garden from external butterfly pests is to select plants that are resistant to them. Research and select plant varieties that are highly resistant to parasites such as butterflies and their caterpillars. This will reduce the risk of damage to the garden and reduce the need for chemical protection.
Physical barriers and traps
Physical barriers and traps can be used to prevent the reproduction of external moth parasites. Install mesh structures or stretch special films over plants to prevent parasites from gaining access to them. Traps can also be used to attract and trap adult moths, which will reduce their population and help protect the garden.
Natural enemies of parasites

Another method of protecting the garden from the breeding of external butterfly parasites is to attract the natural enemies of these parasites. Some insects, birds and other animals feed on caterpillars and butterflies, their eggs or larvae. Create favorable habitat for such enemies, provide shelter and food sources so that they actively destroy parasites and maintain balance in the garden.
A combination of these protection methods will help reduce the risk of external moth parasites and keep the plants in your garden healthy. Remember that regular plant inspections and a quick response to pests are also important aspects of garden protection.
Biological methods of combating external parasites of butterflies

Biological methods of controlling external butterfly parasites are an effective way to protect the garden from pests. They are based on the use of natural enemies of parasites that can control their population.
One of these methods is the introduction of predatory insects such as wasps and predatory beetles. They can feed on the larvae of parasitic butterflies, which leads to a decrease in their numbers and less damage to the garden.
Another biological method is the use of bacteria and viruses that are specific to harmful butterflies. These microorganisms can infect and destroy parasites, which helps in controlling their population.
There are also pheromone traps that attract male parasitic moths and help trap them. This allows you to control the pest population and prevent their reproduction.
Biological methods of combating external parasites of butterflies are environmentally friendly and do not harm the environment. They can be used in combination with other crop protection methods for best results.
Chemical methods of combating external parasites of butterflies
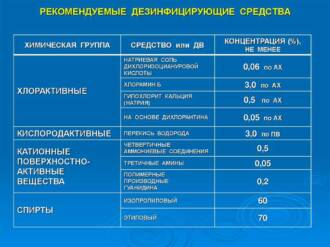
Chemical pest control methods for moths are one effective way to protect your garden from breeding and harm. To do this, various insecticides are used to help reduce pest populations and prevent damage to plants.
One of the most common chemicals are pyrethroids. These insecticides are highly effective against many types of butterflies and their caterpillars. They act on the nervous system of parasites, causing paralysis and death. Pyrethroids are usually applied as sprays or liquid solutions that are applied to plants or the soil.
For longer term protection against parasites, systemic insecticides may be used. These substances are introduced into the plant and distributed throughout its structure, including leaves, stems and roots. Thus, systemic insecticides provide protection against parasites for a long time. However, it is important to use them with care to avoid potential impact on beneficial insects and the environment.
Another way to combat external parasites of butterflies is to use pheromone traps. Pheromones are chemicals produced by females during attractive stages of development. Pheromone traps attract male parasites, which helps reduce their population and prevent reproduction. This method is safer for the environment and beneficial insects as it does not require the use of chemicals.
It is important to remember that when using chemical methods to control external parasites of butterflies, all recommendations for use and safety must be followed in order to avoid negative effects on plants, animals and humans. It is also recommended to combine chemical methods with other methods of control, such as biological control and mechanical removal of parasites, for best results.
Preventive measures to protect the garden from external butterfly parasites

External parasites of butterflies can cause significant damage to the garden and plants. To protect against them, it is necessary to take preventive measures.
1. Inspect Your Plants Regularly
Check your plants periodically for eggs, larvae or pupae of external parasites. Pay special attention to the underside of the leaves and fruits. If you notice signs of damage, immediately proceed with the steps to remove the parasites.
2. Destroy eggs and larvae
Eggs and larvae of external parasites can be destroyed mechanically. Use gloves and tongs to gently remove eggs and larvae from plants. The collected material must be destroyed to prevent further reproduction of parasites.
3. Use Biologics
Biological preparations are an effective means of combating external parasites of butterflies. They contain microorganisms or chemical compounds that adversely affect the development of parasites. When using biological products, follow the manufacturer's instructions and do not abuse their use so as not to harm beneficial organisms and the environment.
4. Use herbal decoctions and infusions

Herbal decoctions and infusions help repel external parasites of butterflies. Some plants, such as wormwood, garlic, peppermint, have a disgusting smell to parasites. Prepare a decoction or infusion of these plants and spray your plants with it. This will help keep pests away and protect the garden from their reproduction.
By following these preventive measures, you can effectively protect your garden from external butterfly parasites and keep it beautiful and productive.