Antennae are an important tool for butterflies, helping them navigate their surroundings. Antennae are a pair of thin, flexible organs located on the head of butterflies. They act as a kind of “nose” and “steering wheel” for these winged creatures.
Butterfly antennae perform several functions. First, they serve as an organ of smell. Due to their sensitivity, the antennae allow butterflies to find food sources and breeding partners. The antennae are able to capture even the faintest odors, which allows butterflies to find flowers with nectar at a considerable distance.
Secondly, the antennae play an important role in the orientation of butterflies in space. They help determine the direction of the wind and understand where the source of the smell or sound is located. Thanks to this, butterflies can choose the most favorable flight direction and avoid obstacles.
Butterfly antennae are also sensitive to changes in temperature and humidity. This allows them to adapt to different weather conditions and choose the best place to rest or breed.
Butterflies and their antennae: a unique sense of orientation
The antennae are one of the most important parts of butterflies. They help these colorful insects navigate in space and find food. Butterfly antennae are true sense organs that can perceive various signals from the environment.
Butterfly antennae perform several functions:
- Orientation in space. Thanks to the antennae, butterflies can determine their position in space and distinguish the direction of movement. The antennae help them navigate during the flight and find their way to the target.
- Search for food. Butterfly antennae have sensory receptors that allow them to locate food sources. Through these receptors, butterflies can detect the scents of flowers and nectar that attract them to a specific location.
- Hazard detection. Butterfly antennae help them detect danger. Due to their sensitivity, the antennae can respond to changes in airflow, sounds, and other external signals, alerting butterflies to potential danger.
Butterfly antennae are unique organs that allow them to successfully navigate their environment and cope with daily tasks. Without antennae, butterflies would be less successful at finding food and meeting breeding partners.
The structure of the antennae: a distinctive feature of butterflies
1. Antennae: organs of touch and orientation

Antennae are a characteristic feature of butterflies and perform important functions in their lives. They are paired organs located on the head of a butterfly. The antennae serve to sense the world around them and help butterflies navigate in space.
2. The structure of the antennae: types and parts

Butterfly antennae consist of several parts, each of which performs its own function. The main parts of the antennae are the root segment, the club, and the klypus. The root segment is closest to the head and functions as a support for the rest of the antennae. The club is a thickening of the antennae and has various receptors that allow butterflies to perceive various signals from the environment. The clipus is the terminal segment of the antennae and helps the butterflies hold them in position.
3. Features of the antennae of different types of butterflies
Butterfly antennae come in a variety of shapes and sizes depending on the species. For example, moths tend to have fluffier and broader antennae, which helps them navigate in the dark. In diurnal butterflies, antennae can be thinner and longer, allowing them to sense their environment more accurately. In addition, some species of butterflies may have antennae with different colors and patterns, which act as signals to other individuals of their species.
In general, the structure of the antennae of butterflies is a hallmark of these beautiful insects. The antennae help them navigate in space, perceive the environment and communicate with other individuals of their species. Studying the antennae of butterflies allows you to better understand their behavior and adaptation to various environmental conditions.
The main function of the antennae: orientation in space
The antennae are an important organ for butterflies, helping them to navigate in space. They perform a number of functions that allow insects to successfully navigate and find food.
The main function of the antennae is to sense the chemicals that are in the air. Thanks to special receptors on the antennae, butterflies can detect the smells and pheromones of other individuals. This allows them to find breeding partners and avoid danger.
In addition, the antennae help butterflies to determine the direction and intensity of the wind. They contain a kind of capsule with nerve cells that respond to changes in the air flow. Thanks to this, butterflies can easily navigate and choose the right direction of flight.
The antennae also help butterflies navigate in space by sensing touch. The antennae contain sensitive hairs that react to contact with objects. This allows insects to avoid collisions with obstacles and to determine the shape and size of objects around them.
Overall, antennae are an important tool for butterflies to help them navigate and find everything they need to survive. Without antennae, these delicate insects would be much more vulnerable to external influences and would not be able to successfully adapt to the environment.
Sensory hairs: the key to successful foraging
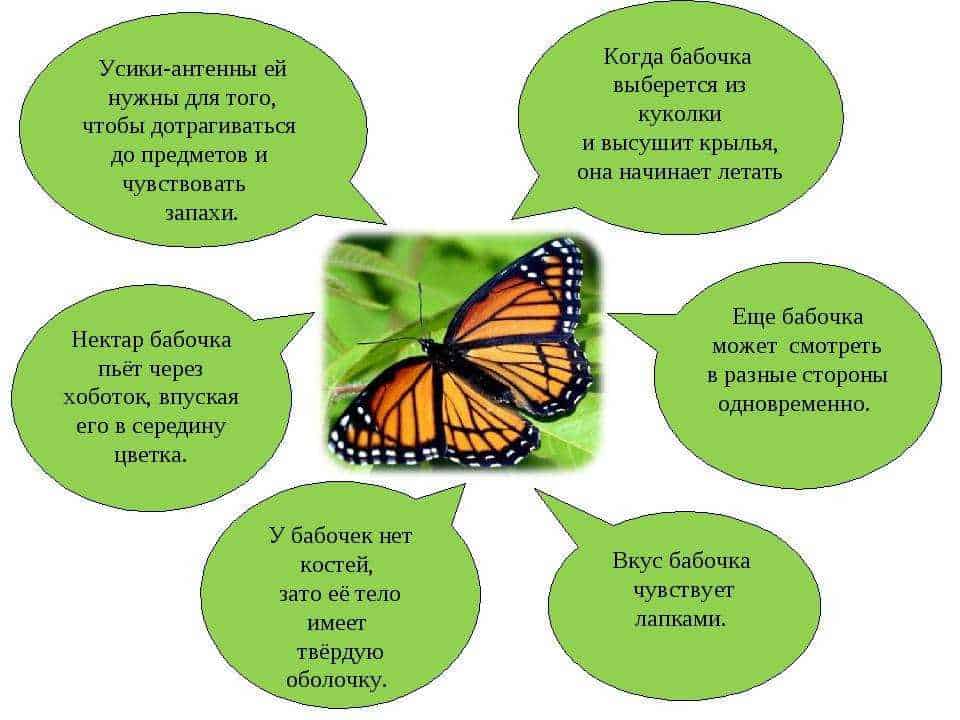
Butterfly antennae are a unique sensory organ that allows them to successfully navigate and find food. They play an important role in the life of these beautiful insects.
The antennae are made up of many sensory hairs that help butterflies sense their environment. Each hair contains a nerve cell that responds to various stimuli such as smells, vibrations, and temperature.
Thanks to the antennae, butterflies can determine the presence of food in the environment. They can detect flower and nectar scents over long distances. The antennae also help butterflies find places to lay their eggs and find breeding partners.
In addition, antennae allow butterflies to determine the direction of air currents. They help butterflies navigate and find their way to their destination. This is especially important for migrations when butterflies have to travel long distances.
In general, sensory hairs on the antennae of butterflies are an integral part of their body. They allow butterflies to successfully navigate and find food, which is a key factor in their survival and reproduction.
Antennae and navigation: how butterflies find their way home
Butterfly antennae play an important role in their ability to navigate in space and find their way home. The antennae are made up of many sensory hairs called sensilla that help butterflies perceive and navigate their environment.
One of the main functions of antennae in butterflies is the sense of smell. The antennal sensilla allow butterflies to detect and recognize a variety of odors, including flowers, food, and pheromones from other butterflies. This allows them to find a food source and breeding partners.
In addition, the antennae help butterflies navigate in space and find their way home. Thanks to the sensilla on their antennae, butterflies can sense the Earth's magnetic field and use it as a navigational tool. This allows them to determine their position and direction of movement relative to the magnetic field and find their way back to their shelter.
Butterfly antennae also help them navigate by visible landmarks. Thanks to sensilla, butterflies can perceive air currents, changes in humidity and other environmental factors that help them determine the direction of movement and the distance to the target.
Thus, antennae play a key role in butterfly navigation. They help them perceive smells, navigate the Earth's magnetic field, and find their way home. Due to their unique abilities, butterflies are able to successfully move in the environment and perform their vital functions.
Antennae and the search for a partner: signals of love in the world of butterflies
navigation tool
Antennae are small antennae located on the head of butterflies. They play an important role in orientation and finding a partner. Antennae contain many receptors that help butterflies sense their surroundings.
Butterflies use their antennae to determine the direction and distance of objects. They can sense smells, tastes, and even vibrations, allowing them to locate flowers, food, and tribesmen.
Love Signals

Butterfly antennae also play an important role in attracting breeding partners. Males and females use their antennae to exchange chemical signals that indicate their readiness to mate.
Males release pheromones that attract females and help them find a suitable mate. Females may also release pheromones in response, signaling their readiness to mate. Antennae play a role not only in attracting partners, but also in recognizing their own species features.
Unique Features
Each butterfly species has unique antennae features that help them attract mates and navigate their environment. Some species of butterflies have long antennae to enable them to detect distant scents, while others have short antennae for more accurate distance reading.
The antennae of butterflies are an amazing tool that helps them survive and reproduce. They serve not only for orientation, but also for exchanging information with partners. Thanks to the antennae, butterflies can find food, avoid danger, and find a suitable partner for reproduction.
Antennae and Communication with Other Butterflies: Information Transfer

Antennae in butterflies play an important role in communication with other individuals of their species. They are a kind of antennas that allow you to transmit and receive various signals and information. Thanks to the antennae, butterflies can detect other individuals, determine their sex and age, and transmit signals about their mood and intentions.
The main function of antennae in communication with other butterflies is the transmission of pheromones. Pheromones are chemicals secreted by an organism and used to exchange information between individuals of the same species. Butterflies can secrete a variety of pheromones that help them attract mates for reproduction, mark their territory, warn of danger, or transmit other signals.
With the help of antennae, butterflies can detect traces of pheromones left by other individuals. They are able to determine the direction and intensity of a smell, which helps them to navigate in space and find food sources or partners. The antennae also allow butterflies to determine whether the smell of another individual belongs to their own species or to another, which is important for reproduction and the maintenance of genetic diversity.
In addition to transmitting pheromones, butterfly antennae can also be used to transmit other signals. For example, when meeting with a competitor or enemy, a butterfly can spread or fold its antennae, which serves as a signal of its status and intentions. She may use her antennae to communicate with a partner while gathering food or finding a place to lay her eggs.
Thus, the antennae of butterflies are an important organ for communication and transmission of information. They allow butterflies to detect other individuals, determine their sex and age, and transmit signals about their mood and intentions. Thanks to the antennae, butterflies can navigate in space, find breeding partners and mark their territory. These complex organs help butterflies communicate with other members of their species and successfully survive in the natural environment.
The value of antennae for butterflies and their importance in nature
Antennae in butterflies are an important sensory organ and play a significant role in their orientation in space and interaction with the environment. The antennae contain many small sensory hairs that help butterflies perceive environmental information such as smells, wind, and temperature.
One of the main functions of antennae in butterflies is spatial orientation. Antennae allow butterflies to determine the direction and distance to a source of smell or other objects. Antennae allow them to find food, determine places to lay eggs, and find partners for reproduction.
The antennae also help butterflies recognize other members of their species and determine the sex and age structure of the population. They facilitate communication between butterflies, allowing them to convey information about their position and intentions.
Thanks to the antennae, butterflies can also avoid danger and protect themselves from predators. They can sense the approach of danger and react quickly by flying to safety.
The exceptional sensitivity of butterflies' antennae to odors allows them to locate flowers on which they can find nectar. This is an important aspect of the interaction between butterflies and plants, as butterflies are important pollinators.