Butterflies are considered one of the most beautiful creatures of nature, but, unfortunately, they can become carriers of various viruses and diseases. Studies show that some butterflies can carry infections that are dangerous to humans. Therefore, it is important to understand which types of butterflies are potential carriers of viruses and what security measures should be followed to minimize the risk of infection.
One of the best known butterfly-borne viruses is the Zika virus. This virus is transmitted through mosquito bites, but butterflies can also become carriers. Butterflies that feed on plants, which are also a source of food for mosquitoes, can become infected with the virus and pass it on. Research suggests that certain types of butterflies, such as the tiger hulk, may carry the Zika virus.
In addition to the Zika virus, butterflies can also carry other infections such as the herpes simplex virus and influenza virus. These viruses are transmitted through airborne droplets, but butterflies can also carry them. Studies show that some types of butterflies, such as white cabbage, can be carriers of the herpes simplex virus.
In light of these studies, it is important to take certain precautions when dealing with butterflies. It is recommended to avoid direct contact with butterflies, especially if they are in the wild where the risk of contracting viruses and diseases is higher. When visiting butterflies or gardens where butterflies are kept, hand hygiene should be practiced and touching of the face should be avoided after contact with butterflies.
The role of butterflies in the transmission of infections

Butterflies, including various types of moths, can play an important role in the transmission of infections. Their interaction with various plants and insects can contribute to the spread of viruses and diseases.
1. Pollen butterflies: Some species of butterflies feed on the nectar of flowers and at the same time transfer pollen from one flower to another. This can lead to infection of plants with viruses and diseases. For example, pollen moths can carry viruses that cause various plant infections, such as mosaic or plant yellowing.
2. Virus carriers: Some types of butterflies can be carriers of viruses that infect humans and animals. They can feed on plants infected with viruses and transfer them to other plants or insects. This can lead to the spread of infections among living organisms.
3. Butterflies as indicators of health: Some research suggests that changes in butterfly populations may be indicative of the presence or spread of certain infections. For example, a decrease in the number of certain species of butterflies may indicate the presence of harmful substances or infections in the environment that can be dangerous to humans and animals.
Overall, the role of butterflies in the transmission of infections is complex and requires further research. Understanding this role can help develop safety and control measures to prevent the spread of infections through butterflies and protect human and animal health.
Studies on the influence of butterflies on the spread of viruses and diseases

Butterflies, as part of the natural ecosystem, play an important role in the spread of viruses and diseases. Studies show that some species of butterflies can be carriers of various pathogens and transmit them to other organisms.
One example of such research is the study of the role of butterflies in the transmission of tobacco mosaic virus. This virus causes serious crop losses in agriculture. Researchers have found that some species of butterflies, such as white butterflies, can carry this virus and transfer it to plants, causing it to spread.
Another study showed that butterflies can also carry diseases such as the Zika virus. The Zika virus is transmitted by mosquito bites, but researchers have found that some moth species can also be infected with the virus and transmit it to other organisms, including humans.
Studies of the influence of butterflies on the spread of viruses and diseases are of great practical importance. They allow us to more accurately define the role of butterflies in infection chains and develop safety measures to prevent the spread of viruses and diseases through butterflies. Such measures include controlling the butterfly population, using insecticides, and educating people about the risks and precautions to take when exposed to butterflies.
Dangers associated with butterflies as carriers of infections
Butterflies, in addition to their beauty and aesthetic value, can also be dangerous as carriers of infections. They can carry microorganisms and viruses that can become a source of various diseases.
One example is the tuberculosis butterfly. This butterfly may be infected with the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which causes this dangerous infectious disease. When a butterfly lands on a plant or flower, it can leave behind bacteria that enter the environment and can be transmitted to humans.
Another danger associated with butterflies is the possibility of infection being transmitted through their wings. Studies have shown that various microorganisms, including bacteria and viruses, can live on the surface of butterfly wings. If a person touches the wings of a butterfly and then touches the face or wound, it can become a source of infection.
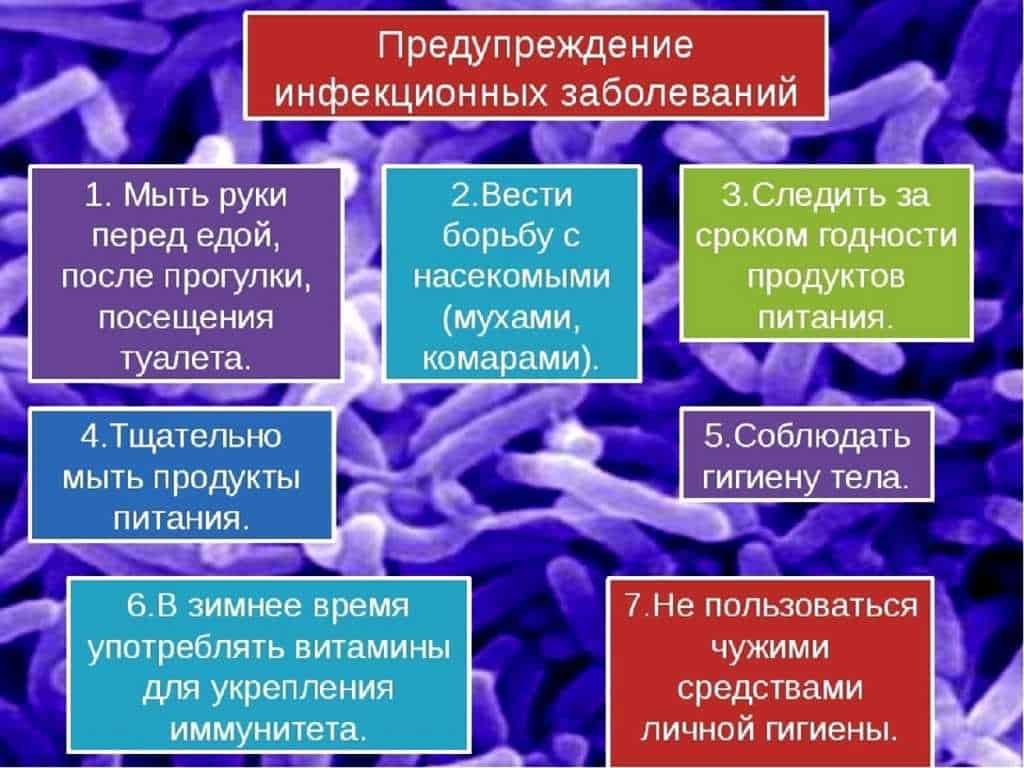
To prevent the transmission of infections associated with butterflies, certain safety precautions must be followed. It is important to avoid contact with butterflies, especially if they show visible signs of infection such as discharge or damaged wings. It is also recommended to regularly wash your hands with soap and water and use antiseptic after contact with butterflies or their environment.
Public places where butterflies are often found, such as botanical gardens or parks, should follow hygiene measures to prevent possible transmission of infections. This may include regularly disinfecting surfaces and plants, as well as informing visitors of possible risks and precautions.
In general, it is necessary to be aware of the potential dangers associated with butterflies as carriers of infections and take appropriate safety measures to protect yourself and others from possible risks of disease.
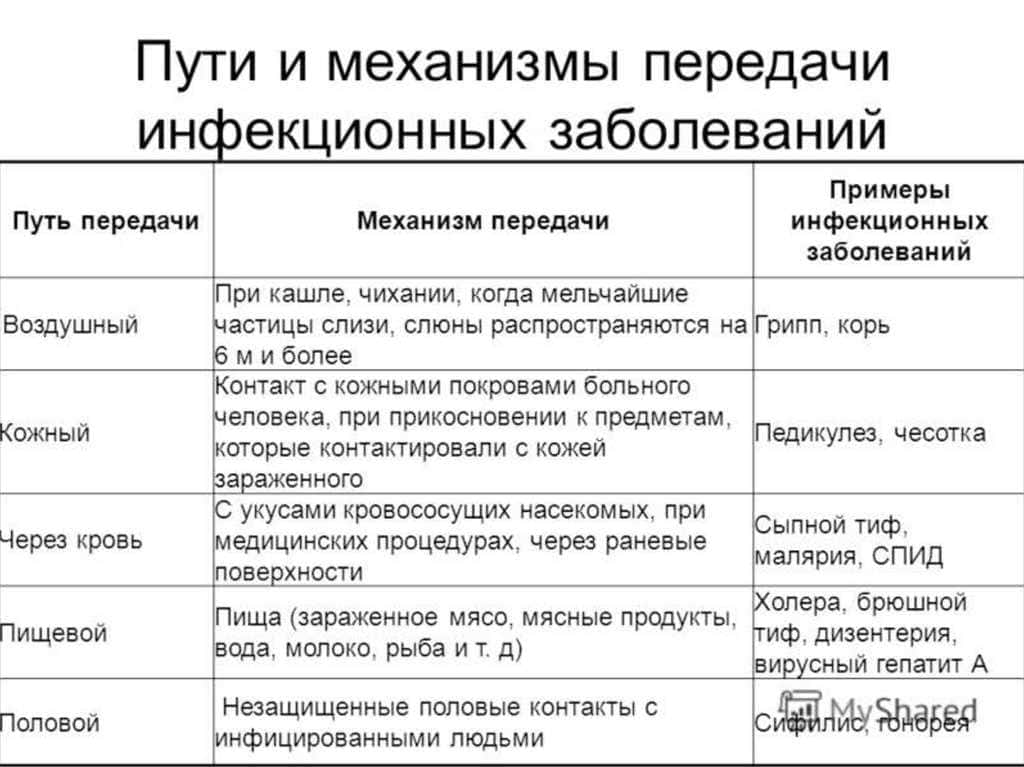
Mechanisms of transmission of viruses and diseases through butterflies

Butterflies are one of the most common types of insects that can be carriers of various viruses and diseases. These winged creatures may be involved in the spread of infections by transferring them from plants to plants or from animals to humans.
Virus transmission through pollen

Butterflies play an important role in the process of pollination of plants, transferring pollen from one flower to another. However, they can also carry viruses that are found on these plants. When a butterfly lands on a flower, it can infect it with a virus or disease and then transfer them to other plants that it visits afterwards.
Transfer of viruses through contact

Butterflies can carry viruses and diseases that can be transmitted through contact with their body or wings. For example, when a butterfly lands on food or an object, it can leave microorganisms on it that can cause infection. If a person or animal touches this item, they can become infected with the virus or disease that was on the butterfly.
Security measures
To prevent the transmission of viruses and diseases through butterflies, certain safety precautions must be followed. First, touching butterflies should be avoided, especially if they look sick or damaged. Secondly, it is recommended to frequently wash your hands with soap and water after touching butterflies or their larvae. It is also important to avoid contact with surfaces that may harbor micro-organisms carried by butterflies.
Typical viruses and diseases transmitted through butterflies

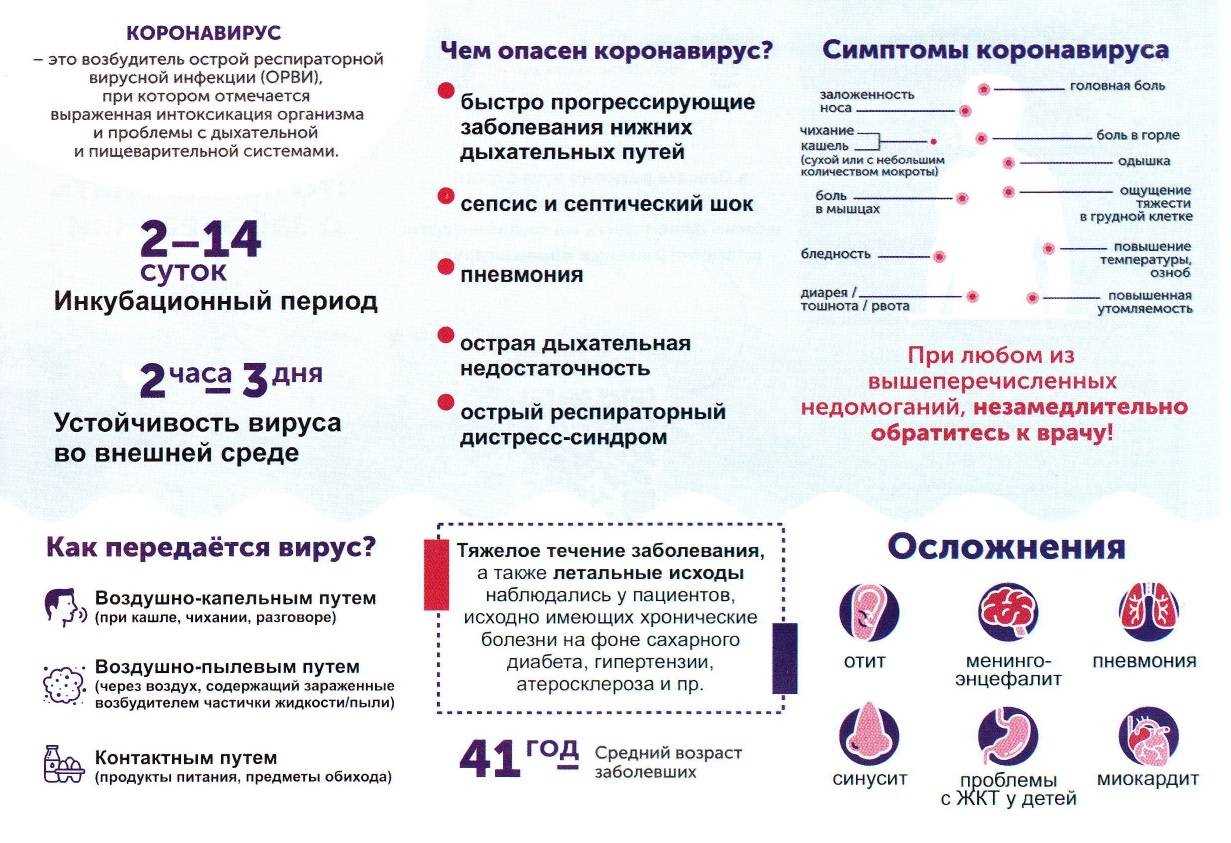
Butterflies are carriers of various viruses and diseases that can be dangerous to plants and animals. Butterfly-borne viruses can cause various symptoms and serious consequences.
One typical butterfly-borne virus is poison smoke virus. This virus can infect various types of plants, causing the death of their leaves and stems. Butterflies that feed on infected plants can become carriers of the virus and transmit it to other plants.
Another common butterfly-borne virus is polyhedria virus. This virus infects caterpillars and can lead to their mass death. Butterflies hatched from infected caterpillars may also become infected and transmit the virus to other caterpillars.
In addition to viruses, diseases such as fungal infections can also be transmitted through butterflies. Some fungi can infect butterflies and lead to a decrease in their population. The disease can be transmitted from infected butterflies to healthy ones through contact or food.
To prevent the spread of viruses and diseases transmitted through butterflies, safety measures must be taken. It is important to ensure hygienic conditions in places where butterflies are kept, to regularly disinfect and monitor the health of the population. It is also recommended to isolate infected butterflies from healthy ones and apply preventive measures such as vaccination and maintaining a healthy environment for butterflies to live.
Safety measures for contact with butterflies
1. Avoid direct contact with live butterflies. While most butterflies are harmless to humans, some species can carry infections or cause allergic reactions. Therefore, it is recommended not to touch the butterflies with your hands and not to allow them to land on your face or other exposed parts of your body.
2. Use protective equipment. If you are working with live butterflies in a lab or plan to visit a place where they are kept, it is recommended that you wear gloves, a mask and goggles. This will reduce the risk of infection and allergic reactions.
3. Follow the rules of hygiene. Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water after handling butterflies or visiting areas where they are kept. This will help remove possible germs or other harmful substances that may be on the surface of the butterflies.
4. Study information about the type of butterflies. If you are studying butterflies, it is important to be aware of the characteristics of specific species. Some butterflies may have toxic substances or cause allergic reactions in people with special sensitivities. Therefore, before working with a new species of butterflies, it is recommended to study information about it.
5. Turn to professionals. If you have any doubts or questions about the safety of working with butterflies, it is best to seek the help of a professional or butterfly specialist. They will be able to make recommendations and provide the necessary information for safe operation.
6. Keep clean and tidy. If you keep butterflies at home or work in a laboratory, it is important to clean the area regularly and keep it clean. This will help prevent the spread of infections and reduce the risk of disease.
Vaccination and prevention of butterfly-borne diseases
Butterfly-borne diseases can have serious consequences for human health. However, there are effective methods of vaccination and prevention that help prevent the spread of these diseases.
Vaccination
Vaccination is one of the most effective ways to prevent butterfly-borne diseases. Special vaccines are being developed to protect against specific viruses that can be transmitted through butterflies. Vaccines contain weakened or killed viruses that stimulate the body's immune system to produce antibodies that can fight infection.
Preventive measures

In addition to vaccination, there are also preventive measures that help prevent disease transmission through butterflies. These measures include the following:
- Avoid contact with butterflies, especially if they show visible signs of infection.
- Maintain personal hygiene by washing your hands regularly with soap and water.
- Use personal protective equipment such as masks and gloves when handling butterflies or their products.
- Observe safety regulations when handling and disposing of butterflies and their waste.
It is also important to monitor your health, undergo regular medical examinations and follow the recommendations of doctors. If symptoms of a butterfly-borne disease appear, medical attention should be sought immediately.
Development of drugs against diseases transmitted through butterflies
Butterfly-borne diseases are a major problem in the medical world. They can cause a variety of illnesses in humans, from mild cold symptoms to more dangerous and even fatal conditions. Therefore, the development of drugs that can fight these diseases is an important task for the scientific community.
One of the main directions in the development of drugs against diseases transmitted through butterflies is the study of viruses and bacteria that cause them. Scientists study the structure and function of these microorganisms, their modes of transmission and interaction with the human body. This allows you to identify key points that can be influenced by drugs.
Another important aspect of drug development is the search for new active substances that can have an antiviral or antibacterial effect. Scientists are investigating various plants, microorganisms and synthetic compounds in search of new compounds that may be effective in combating butterfly-borne diseases.
Another important aspect is the development of special forms of drugs that can be effectively used to treat diseases transmitted through butterflies. This may be the creation of tablets, injectables, creams or sprays. Each form should be optimal to achieve maximum effect and ease of use.
In general, the development of drugs against diseases transmitted through butterflies is a complex and multifaceted process that requires the joint participation of scientists from different specialties. And only by joint efforts can significant success be achieved in the fight against these dangerous diseases.
Read more: