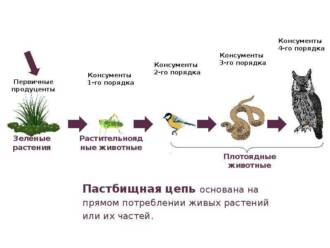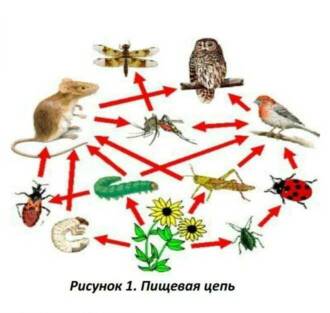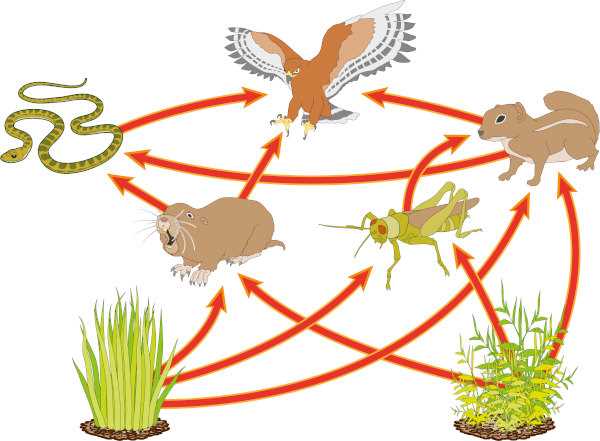
Butterflies play a key role in ecological systems and are of great importance in the food chain. They are important pollinators of plants, contributing to the reproduction of many species of flowers and trees. Butterflies also serve as a food source for many animals, including birds, frogs, and insectivores.
One of the main ways that butterflies affect an ecosystem is through the pollination of flowers. When butterflies feed on nectar, pollen grains stick to their legs and bodies. Then, when the butterfly flies to another plant, it carries the pollen with it and pollinates it. This process promotes plant reproduction, which in turn maintains biodiversity and ecosystem health.
In addition, butterflies serve as an important food source for many animals. Adult butterflies are highly nutritious and are tasty prey for birds, frogs and other insectivorous animals. Butterfly larvae also serve as food for many types of insectivores, including spiders, birds, and mammals. Because of this, butterflies play an important role in the food chain and maintain a balance in the ecosystem.
In general, butterflies are not only beautiful creatures, but also an integral part of the ecological system. Their role in plant pollination and their importance in the food chain make them indispensable for maintaining biodiversity and the health of natural communities. Therefore, the conservation and protection of butterflies is an important task for the conservation of the ecosystem as a whole.
The role of butterflies in ecology
Butterflies play a key role in ecology, making important contributions to the food chain and environmental biodiversity. They are important pollinators of plants, contributing to their reproduction and distribution.
Butterflies, being direct pollinators, transfer pollen from one flower to another, contributing to the pollination of plants. They play an important role in maintaining the genetic diversity of plants and maintaining their populations. Through this process, new hybrids and varieties arise, which contribute to the evolution of plants.
Butterflies also serve as a food source for many animals. They are part of the food chain where they act as prey for birds, frogs, lizards and other predators. The consumption of butterflies by other animals helps maintain balance in the food chain and provides food for many animal species.
In addition, butterflies are indicators of environmental quality. Their presence or absence may indicate the state of the ecosystem. Butterfly population changes can be linked to air pollution, pesticide use, and destruction of natural habitats.
The key role of butterflies in the food chain

Butterflies play an important role in the food chain, serving as a food source for many other animals. Adult butterflies feed on the nectar of flowers, making them important plant pollinators. They carry pollen from one flower to another, contributing to the pollination process and ensuring plant diversity in the ecosystem.
Butterflies also serve as food for many other animals, including birds, bats, lizards, and insectivores. Their bright colors and unique patterns serve as a signal to predators that they are poisonous or unsuitable for food. This is an example of mimicry, where butterflies use their coloration to protect themselves from predators and keep themselves alive.
Butterflies are also important food resources for young birds that feed on their caterpillars. Butterfly caterpillars are rich in protein and energy, making them an attractive food source for many birds. The consumption of butterfly caterpillars promotes the growth and development of birds and provides them with the necessary nutrients to survive and reproduce.
Thus, butterflies play an important role in the food chain, providing food and protection for many other animals. Their presence in the ecosystem contributes to the balance and diversity of life, making them an integral part of nature.
The importance of butterflies for plants
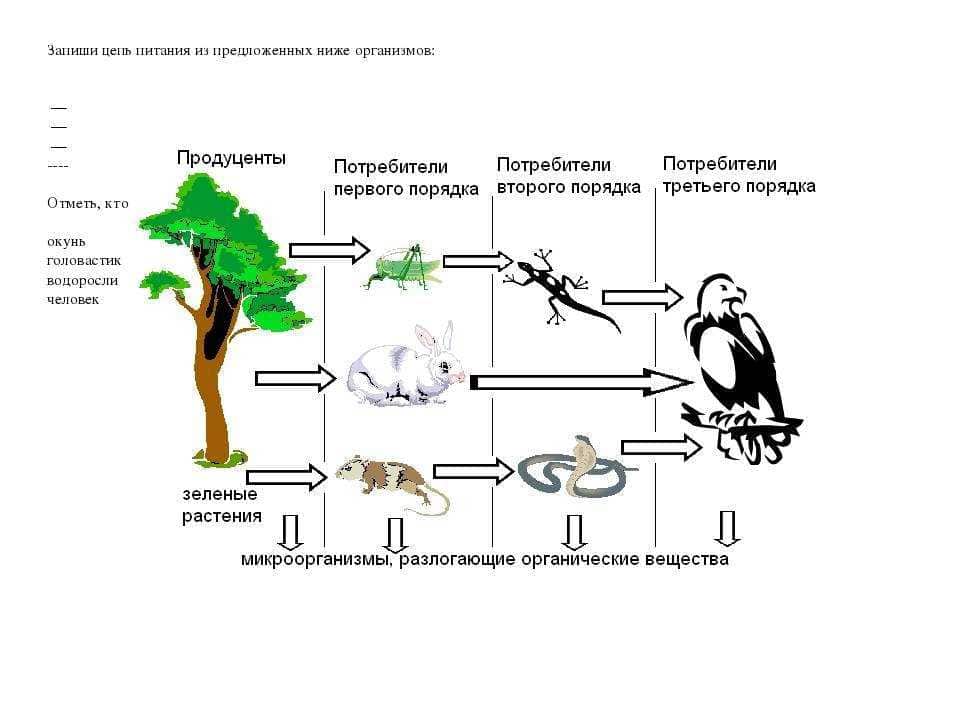
1. Flower pollinators
Butterflies play an important role in the pollination of flowers. They are attracted to the nectar secreted by the flowers, and when they visit a flower they carry pollen from one flower to another. This helps plants reproduce and ensures their genetic diversity.
2. Seed distributors
Some species of butterflies are important dispersers of plant seeds. After feeding on flowers, butterflies can carry seeds on their legs or on their bodies. Then, when the butterfly flies to another plant, the seeds can fall off and begin a new cycle of growth and reproduction.
3. Pest exterminators
Some species of butterflies are predators of other insects that can be harmful to plants. For example, cutworms feed on caterpillars, which can cause significant damage to crops. In this way, butterflies help control pest populations and protect plants.
4. Food source for other animals
Caterpillars, which are butterfly larvae, serve as a food source for many other animals, including birds and small mammals. Butterflies can also be food for some birds and bats. Thus, butterflies play an important role in the food chain and maintain the biological balance in the ecosystem.
Butterflies as pollinators
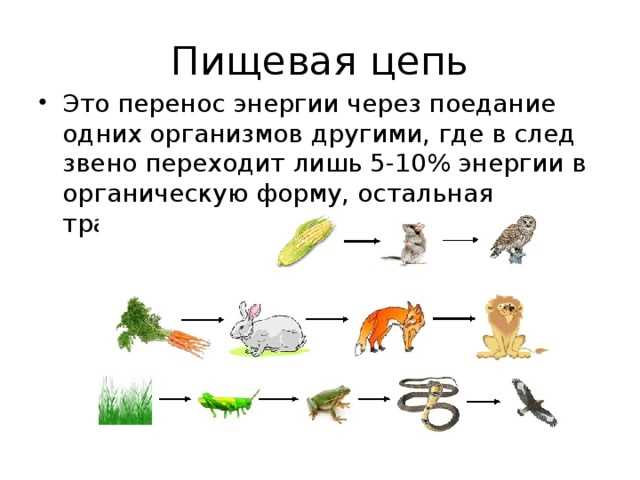
Butterflies play an important role in plant pollination, making them an integral part of the ecosystem. They are able to transfer pollen from one flower to another, ensuring the fertilization and reproduction of many plant species.
A feature of pollination by butterflies is their attractive appearance and colorful coloring of the wings, which attract insects and facilitate the pollination process.
Butterflies, like other pollinators, get their food from the nectar of flowers. While visiting a flower, a butterfly accidentally collects pollen on its body, which it then transfers to other flowers. Thus, butterflies facilitate the interbreeding of different individuals of the same plant species, which maintains genetic diversity and promotes adaptation to changing environmental conditions.
It is important to note that not all butterflies are pollinators, since not all plant species are pollinated in this way. However, for certain plant species, butterflies are the main pollinators and their absence can lead to a decrease in plant numbers and ecosystem disruption.
Butterflies and species diversity
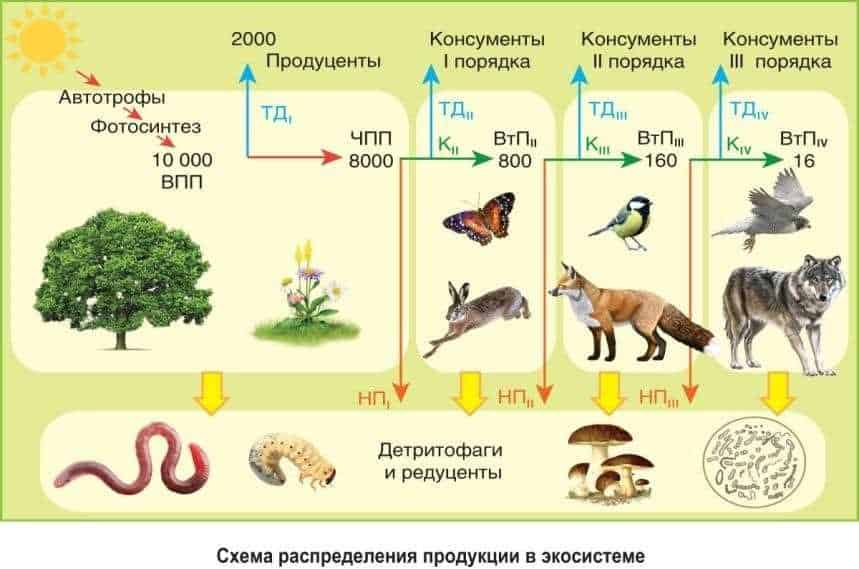
butterflies are one of the most numerous groups of insects that are found on almost all continents and in all types of ecosystems. They are an important component of biological diversity and play a key role in maintaining ecological balance.
There is a huge variety of butterfly species, estimated at several hundred thousand. This diversity is attributed to various factors such as climate, geography, and availability of food sources. Each species of butterfly has its own unique adaptations and survival strategies, allowing them to successfully adapt to different environmental conditions.
butterflies also have a variety of shapes and colors. They can be small and inconspicuous, or large and flamboyant with bright patterns on their wings. This helps them survive and reproduce, as wing coloration can serve as a signal to mates or a warning to predators.
Butterflies also play an important role in the food chain. They are food for many animals, including birds, rodents, and insects. In addition, they perform the function of plant pollinators, carrying pollen on their legs and heads and facilitating the spread of plants. Thus, they contribute to the conservation of plant diversity and the maintenance of the ecosystem as a whole.
Butterflies as an indicator of the ecological state
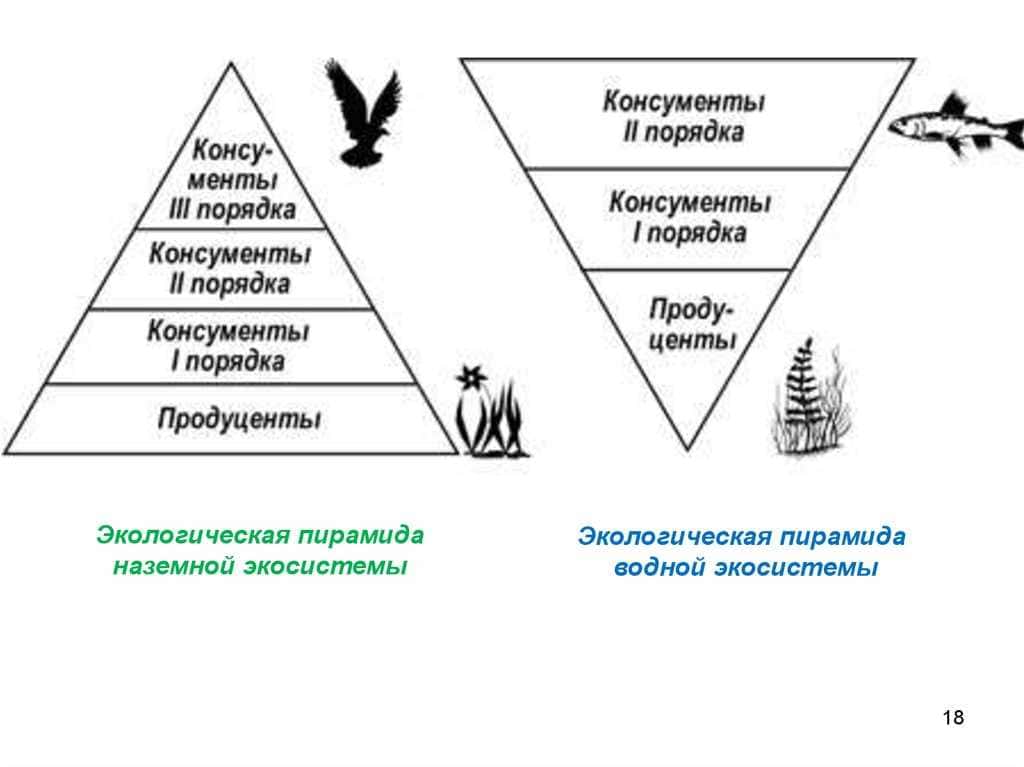
Butterflies are important indicators of the ecological state, as they are sensitive to changes in the environment. The study of butterfly populations can provide valuable information about the state of the ecosystem and the impact of anthropogenic factors.
One of the main factors that butterflies respond to is habitat change. The destruction of natural environments such as grasslands and forests is leading to a decline in butterfly populations. Butterflies require certain conditions for their reproduction and feeding, and any changes in their habitat can negatively affect their numbers.
Butterflies are also indicators of the state of biodiversity. There are butterfly species that are endemic to certain regions and can only be found in certain ecosystems. If the populations of these species are reduced or disappear, this may indicate a violation of biodiversity and the loss of unique ecosystems.
Changes in butterfly populations can also serve as an indicator of environmental pollution. They are sensitive to chemicals such as pesticides and may suffer from their use. If butterfly populations are declining or their health is deteriorating, this may indicate environmental pollution and require action to clean it up.
Studying butterfly populations and their response to changes in the environment helps scientific researchers and organizations assess ecological health and take action to improve it. They can serve as important indicators in the development and implementation of biodiversity conservation and environmental sustainability programs.
Butterflies and biological balance
Butterflies play a key role in maintaining the biological balance in an ecosystem. They are important pollinators of plants, helping them reproduce and maintain their populations. Due to their flight and the ability to transfer pollen from one flower to another, butterflies contribute to the pollination of plants and ensure their diversity and reproduction.
Butterflies are also a food source for other animals in the food chain. Many birds, lizards and other insectivorous animals feed on butterflies and their larvae. Because of this, butterflies play a role in maintaining balance in the food chain and preventing overpopulation of certain insect species.
Butterflies also serve as indicators of the ecological state of the environment. They are sensitive to changes in air and water quality, as well as pollution and changes in vegetation composition. Therefore, if butterfly species begin to disappear or their numbers decrease, this can be a signal of adverse changes in the environment and a wake-up call for conservation.
The study of butterflies and their interaction with the environment is of great scientific importance. Butterflies are one of the most diverse groups of insects on Earth, and studying their morphology, behavior, and biology allows you to learn more about the principles of evolution and the interaction of different species in nature. Through this research, we can better understand and conserve this amazing group of insects and their role in the ecosystem.
Impact of human activity on butterfly populations
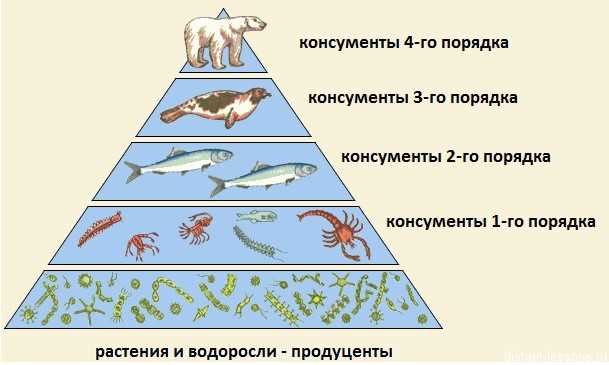
Human activities have a significant impact on butterfly populations. One of the main reasons for the decline in the number of butterflies is the destruction of their natural habitats. Deforestation, deforestation, and expansion of agricultural land result in the loss of important plant nutrients for caterpillars and nectar sources for adults.
Along with the destruction of habitats, human activities are also making changes to the environment, which can lead to an imbalance in the food chain in which butterflies play a key role. Air and water pollution, the use of pesticides and herbicides in agriculture, and the use of genetically modified crops have a negative impact on butterfly populations.
Moreover, human activities can also lead to climate change, which in turn affects the distribution and migration of butterflies. Global warming, changes in precipitation and seasonality can significantly change the living conditions of butterflies and lead to a reduction in their numbers.
To save butterflies and their important role in the ecosystem, it is necessary to take measures to protect and restore their habitats, limit the use of pesticides and herbicides, and control climate change. This is the only way to ensure the conservation of butterflies and the sustainability of the food chain in which they play an important link.
Butterfly defense mechanisms
Butterflies have various defense mechanisms that allow them to survive in the harsh natural world and avoid predators.
One such mechanism is camouflage. Many species of butterflies have coloring that allows them to blend into their surroundings. They may be colored to resemble leaves, flowers, or tree bark. This helps them remain invisible to predators such as birds or lizards.
Another defense mechanism is mimicry. Some butterflies have coloration that resembles dangerous or poisonous species. For example, the scoop butterfly has a coloration very similar to the eyes of birds of prey. This allows her to intimidate and scare away predators that might try to attack her.
Butterflies may also use frightening odors or tasty poisonous substances to protect themselves. They can secrete special pheromones or poison their predators with poison they get from certain plants. This causes predators to give up on the idea of attacking them and look for other food.
In general, the defense mechanisms of butterflies allow them to survive and play an important role in the ecology. They help butterflies escape danger and continue their life cycle, and they also serve as food for other animals in the food chain.
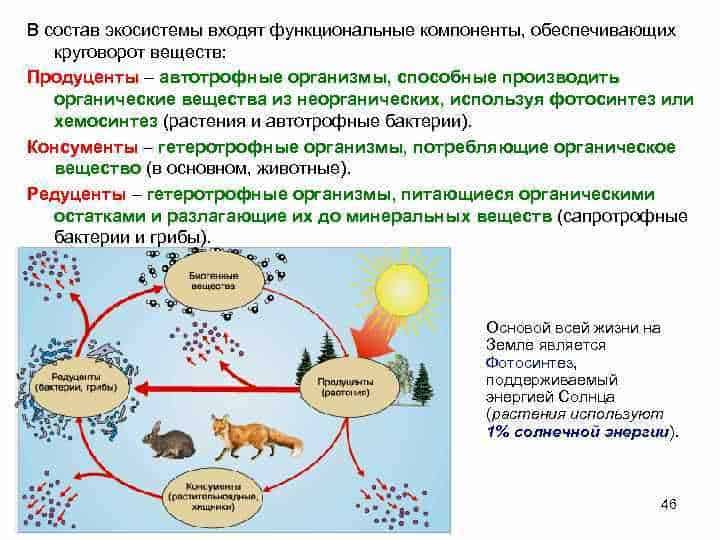
The role of butterflies in the circulation of substances
Butterflies, like other insects, play an important role in the cycle of substances in the ecosystem. They perform the function of a variety of plants, converting plant residues into nutrients, which are then used by other organisms.
Butterflies are important plant pollinators. They carry pollen from one flower to another, which contributes to the fertilization of plants and the formation of seeds. Thus, butterflies contribute to the reproduction and conservation of plant species.
In addition, butterflies play a role in the food chain. They serve as a food source for many predatory animals such as birds, frogs and lizards. As the butterflies die and decompose, their organic matter enriches the soil, promoting plant growth.
Butterflies also play an important role in biodiversity. They are one of the most diverse groups of insects and their presence in an ecosystem is evidence of its health and resilience. In addition, butterflies are indicators of environmental quality: changes in their abundance and species composition may indicate pollution or degradation of the ecosystem.
In general, butterflies play an important role in the cycle of substances in the ecosystem. They act as pollinators, feed on plant debris, serve as a food source for other animals, and are involved in maintaining biodiversity. Therefore, the conservation of butterfly populations and their habitats is an important task in the conservation of natural ecosystems.