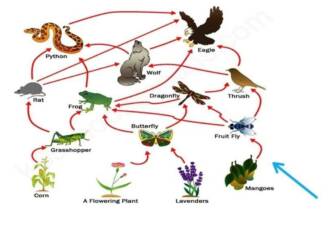
Butterflies are amazing creatures that play an important role in the food chain. They are one of the main pollinators of plants, which makes them important for biodiversity conservation. Butterflies feed on nectar and pollen, which they transfer from one flower to another, contributing to the pollination of plants and ensuring their reproduction.
However, adult butterflies and their caterpillars are prey for birds, lizards, frogs and other predators. Thus, butterflies play a key role in the food chain, providing food for other organisms and maintaining balance in the ecosystem.
It is interesting to note that some species of butterflies have special defense mechanisms, such as bright colors or bad smells, to scare away predators. It also contributes to biodiversity conservation by alerting other organisms that they are poisonous or unpalatable to eat.
Thus, butterflies are not only beautiful and fascinate, but also play an important role in maintaining ecological balance. They are plant pollinators and a food source for other organisms, making them an integral part of the food chain. Therefore, the protection and conservation of butterflies is an important task for maintaining biodiversity and ecosystem stability.
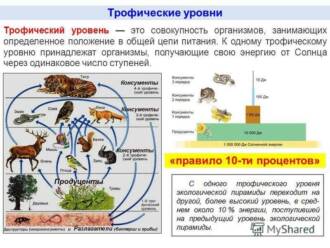
Butterflies are important links in the food chain

Butterflies are one of the important links in the food chain in nature. They play the role of both consumers and suppliers of food for other organisms. Butterflies are a food source for many animals, including birds, lizards, and frogs. They provide not only protein, but also vitamins and minerals necessary for the health of these animals.
On the other hand, butterflies also play an important role in the distribution of pollen and plant pollination. They carry pollen from one flower to another, helping plants reproduce. This is especially important for flowering plants, because without pollination they will not be able to form seeds and reproduce.
Butterflies also serve as food for other insects such as spiders and insectivorous insects. They are an important component of the food chain, providing energy and nutrients to other organisms in the ecosystem.
In addition, butterflies serve as indicators of the ecological state. Their presence or absence may indicate the quality of the environment. If butterflies disappear or their numbers are declining, this may indicate problems in the ecosystem, such as air pollution or habitat loss.
Thus, butterflies play an important role in the food chain and the ecosystem as a whole. They provide food for other organisms, help pollinate plants, and serve as indicators of ecological health. The conservation of butterflies and their habitats is an important task for maintaining biodiversity and ecological balance.
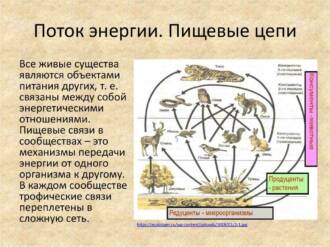
Butterflies as a food source for other organisms
Butterflies play an important role in the food chain, being a food source for many other organisms. They serve as food for a variety of predators, including birds, lizards, frogs, and insects.
Birds. Many bird species prefer to feed on butterflies. Butterflies are an important part of the diet for birds, especially during spring and summer migration when they need extra food to maintain energy and stamina.
Lizards and frogs. Many species of lizards and frogs also feed on butterflies. Butterflies are an important food source for these reptiles and amphibians, which use them as a food base.
Insects. Some insect species such as spiders and wasps also rely on butterflies as a source of food. They use butterflies in their diet to get the necessary nutrients to survive and reproduce.
In general, butterflies play an important role in the food chain, providing food for many other organisms. Their presence and diversity are key factors in maintaining the ecological balance and biodiversity in nature.
Butterflies as plant pollinators
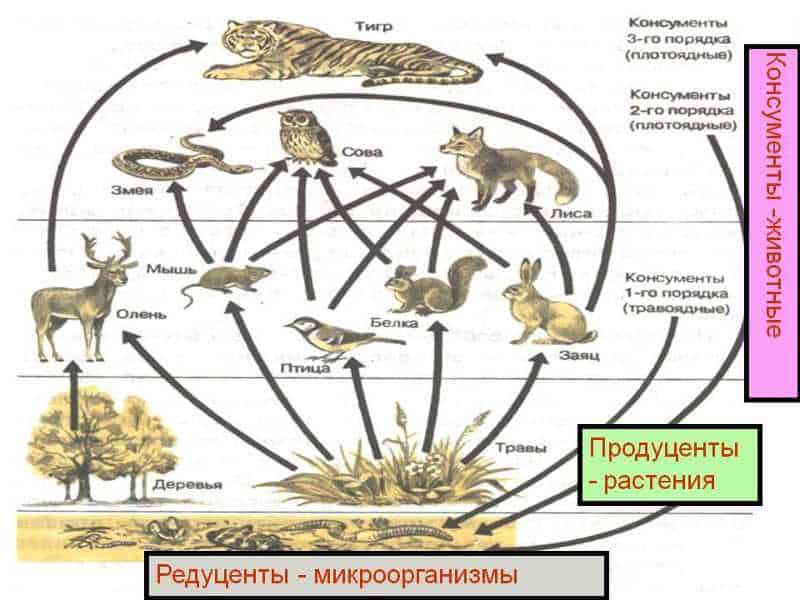
Butterflies play an important role in the pollination of plants, promoting their reproduction and diversity. They are one of the most efficient pollinators and many plants depend on them to produce seeds and fruits.
Pollination The transfer of pollen from the stamen of a flower to the pistil or stigma. Butterflies perform this function when they collect nectar and pollen sticks to their body or wings. When visiting another flower, the pollen is transferred to its stigma or pistil, which allows the plant to be fertilized and produce seeds or fruits.
Like pollinators, butterflies overcome various obstacles, such as a flower tube or pollen sacs, in order to reach the nectar. They can also fly at high speeds and cover long distances, which increases the chances of pollinating different plants.
Some species of butterflies have specialized relationships with certain types of plants. For example, monophages only feed on one species of plant, making them important for that plant's pollination. Such interactions promote mutual dependence between butterflies and plants, ensuring their mutual benefit and diversity in nature.
Butterflies as indicators of the ecological state
Butterflies are among the most sensitive organisms to changes in the environment. Their presence and diversity in a particular area can be used as indicators of the ecological state of the region.
First of all, changes in the butterfly population may indicate disturbances in the ecosystem. For example, a decrease in the number and diversity of butterflies may indicate air pollution, soil degradation, or the destruction of natural habitats.
In addition, butterflies are important plant pollinators. They carry pollen from one flower to another, facilitating the pollination process and allowing plants to reproduce. If the butterfly population declines, this can lead to a decrease in the number of plants and, as a result, disruption of the food chain in this ecosystem.
The use of butterflies as indicators of ecological state allows monitoring and assessing changes in the environment at an early stage. This makes it possible to take the necessary measures to preserve and restore biodiversity, as well as maintain the sustainability of the ecosystem.
Butterflies and their role in the decomposition cycle of organic matter

Butterflies play an important role in the decomposition cycle of organic matter. They are one of the main pollinators of flowers, which contributes to the spread of pollen and ensures the pollination process of plants. Thanks to this, butterflies contribute to the reproduction and conservation of many plant species, which in turn is the basis for the food chain of other organisms.
In addition, butterflies also have an important function in the decomposition of organic material. During their development, butterflies go through several stages, including eggs, caterpillars, pupae and adults. Butterfly caterpillars are important decomposers of plant material as they feed on leaves and other plant parts. They process organic material, release substances necessary for their growth and development, and leave food residues that further decompose and pour into the soil.
Through their role in the decomposition of organic material, butterflies help to improve the soil and enrich it with nutrients. This creates favorable conditions for the growth and development of various plants, which in turn serve as food for other organisms in the food chain.
Butterflies and their impact on plant populations
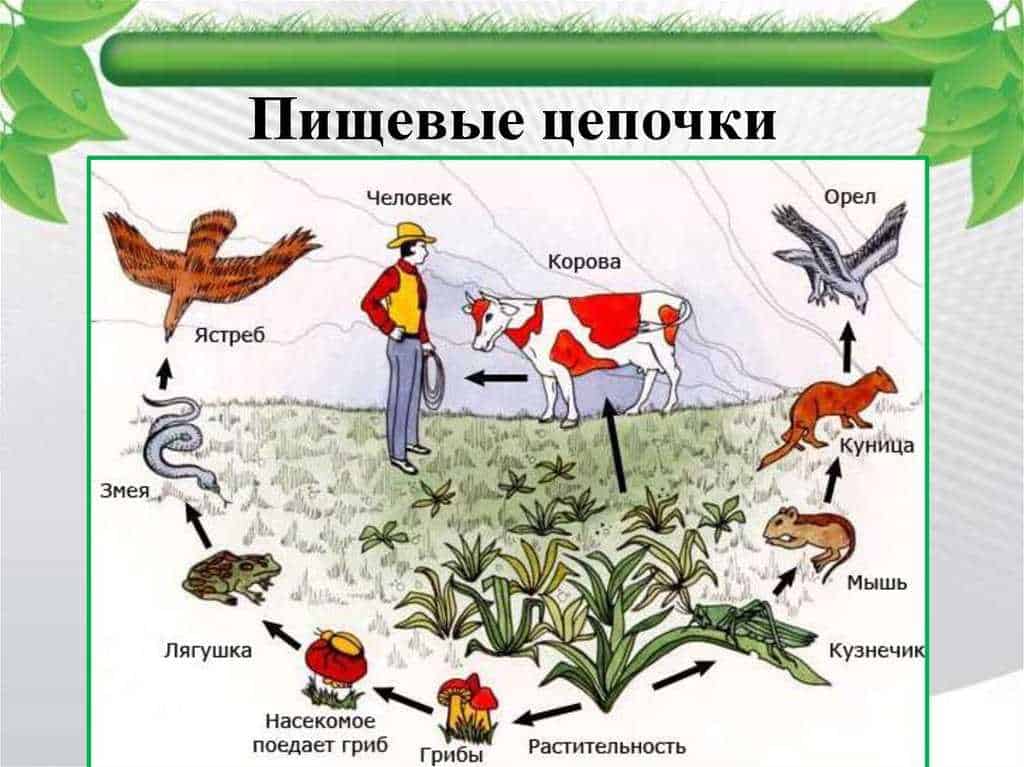
Butterflies play an important role in plant populations as they are one of the main pollinators. They carry pollen from one flower to another, ensuring the fertilization and reproduction of plants.
Pollination by butterflies contributes to an increase in the number of plants and their diversity. Plants pollinated by butterflies are more likely to produce seeds and maintain their population. This is especially important in agricultural settings, where many crops depend on pollination to produce crops.
Butterflies can also influence plant breeding. They prefer to pollinate flowers with certain characteristics, such as bright color, sweet fragrance, or a certain shape. This could lead to evolutionary changes in plants, as those most attractive to butterflies will have a better chance of reproducing and passing on their genes to the next generation.
On the other hand, some species of butterflies can harm plants by feeding on their leaves or bark. This can lead to the weakening of plants and a decrease in their ability to reproduce. However, in general, the positive impact of butterflies on the plant population still prevails, as they are an integral part of the ecosystem and contribute to its balance and diversity.
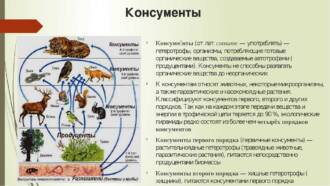
Butterflies and their role in biological pest control
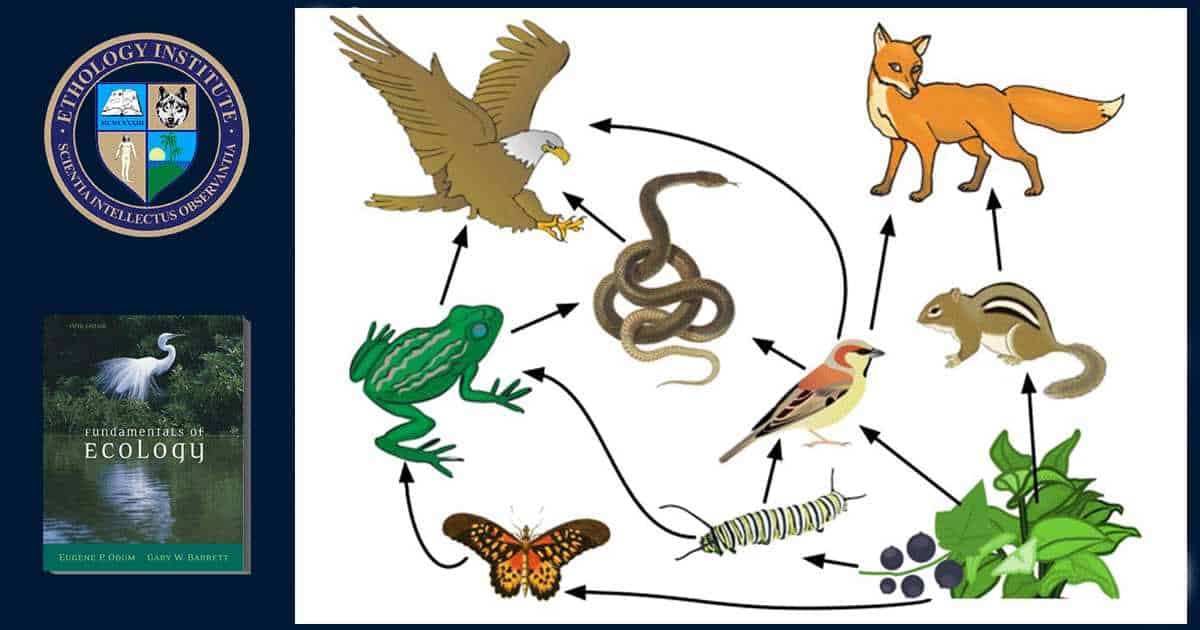
Butterflies play an important role in biological pest control in natural ecosystems. They are natural predators of many insect species that can cause significant damage to agriculture and wild plants.
One example of this role of butterflies is pest control of the leaf beetle family. Many butterflies from this family lay their eggs on the leaves of plants, which, after hatching, become food for the caterpillars. Caterpillars actively feed on leaves, which can lead to a significant yield. However, some species of butterflies, such as hawks and swallowtails, are predators of leaf beetle caterpillars and help control their numbers.
Another example of the role of butterflies in pest control is in the control of leaf-dropping pests. Some butterflies, such as squirrels, lay their eggs on plant leaves. Squirrel caterpillars feed on leaves, and they build nests on the leaves, which protect them from predators. This can be a problem for gardeners and farmers, as the caterpillars can destroy large numbers of plants. However, some species of butterflies, such as parasitoid caterpillars, are predators of squirrel caterpillars and help reduce their numbers.
In this way, butterflies play an important role in biological pest control, helping to control the abundance of insects that can harm plants and agriculture. Their presence in ecosystems contributes to maintaining the balance in nature and is an important factor for the conservation of biodiversity.
Butterflies and their importance for the nutrition of birds and mammals
Butterflies play an important role in the food chain, providing food for birds and mammals. Most species of butterflies are herbivorous, feeding on the nectar of flowers and plant juices. They play the role of pollinators, transferring pollen from one flower to another, due to which the fertilization of plants and the formation of fruits occurs.
Many birds feed on butterflies. They actively hunt them, using their witty abilities and speed of flight. For many bird species, butterflies make up a significant part of their diet and are a source of essential nutrients.
Butterflies are also an important food source for some mammals. For example, some species of bats and flying dogs feed on butterflies. They use their unique flying skills to catch a butterfly in flight and eat it. Butterflies are an indispensable part of their diet, especially during times when other food sources are limited.
Thus, butterflies play an important role in the food chain, providing food for birds and mammals. Their presence and diversity are key elements of an ecosystem, maintaining biological balance and providing food for other organisms in nature.
Butterflies as an object of research and biodiversity conservation
Butterflies are one of the most popular objects of biodiversity research. Their colorful appearance, diversity of species, and wide distribution make them unique subjects to study.
Scientists study butterflies to understand their role in ecosystems and their impact on other organisms. The biological characteristics of butterflies, such as their food preferences, migration routes, and interactions with other organisms, help scientists understand what factors influence biodiversity and how it can be conserved.
Studying butterflies allows scientists to:
- Determine the populations and distribution of butterfly species, which allows you to assess the state of ecosystems and their changes over time;
- To study the features of reproduction and the life cycle of butterflies, which helps to understand what conditions are necessary for their survival;
- Investigate the interaction of butterflies with plants, which is an important factor in understanding the processes of pollination and distribution of plants;
- Assess the impact of climate change and human activities on butterfly populations and their ecosystems.
Butterfly research also helps develop biodiversity conservation strategies. Based on the data obtained, it is possible to identify important areas for the conservation and restoration of butterfly populations, as well as to develop measures to improve their habitat conditions.
Butterflies and their role in ecosystems
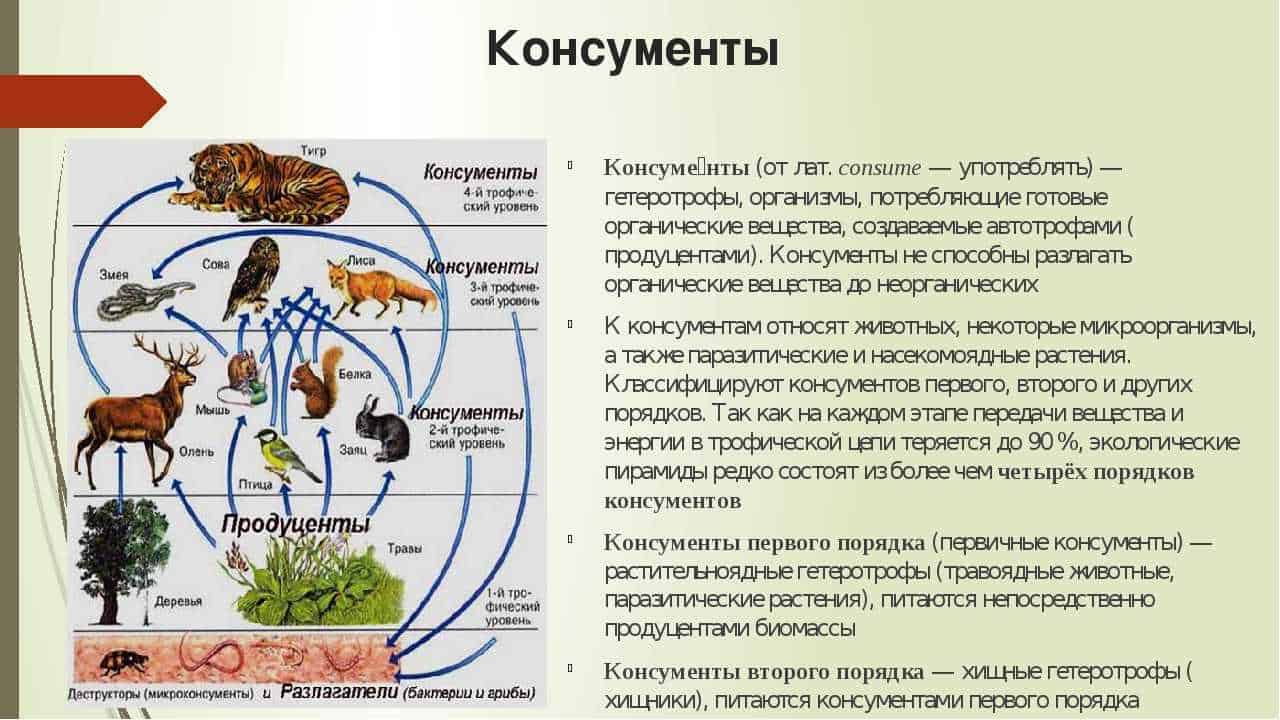
Butterflies are an important part of ecosystems, performing a number of functions that directly affect other organisms. They play the role of pollinators, carrying pollen between flowers and facilitating their reproduction. Thanks to this, butterflies contribute to the conservation of biodiversity and the sustainability of ecosystems.
Butterflies are also an important food source for other organisms. Caterpillars, which are their larvae, feed on plants by eating leaves and other plant parts. This leads to plant population control and helps to maintain a balance in the ecosystem.
Some species of butterflies also serve as a delicate indicator of the state of the environment. They are sensitive to changes in the quality and quantity of plant foods, as well as to pollution and habitat loss. Therefore, monitoring of butterfly populations can provide information on the state of the ecological environment and help in taking measures to conserve it.
In general, butterflies play an indispensable role in ecosystems, contributing to plant pollination, plant population control, and serving as an indicator of ecological status. Their presence and diversity are important indicators of the health and resilience of natural communities.