Butterflies are one of the most beautiful and amazing groups of insects. Their beautiful wings and bright colors attract people's attention and admiration. But few people think about how butterflies provide themselves with food and what effect it has on their physiology.
One of the key food sources for butterflies is nectar, a sweet liquid they obtain from visiting flowers. Nectar contains carbohydrates necessary for butterflies, which are the main source of energy. Thanks to this, butterflies can fly and move actively, look for partners and look for places to lay eggs. The nectar also contains vitamins and minerals needed to maintain the health and normal physiology of butterflies.
But feeding on nectar not only provides energy and nutrients, it also plays a key role in the reproduction of butterflies. Nectar is an attractive signal to the opposite sex that helps butterflies find breeding partners. In addition, nectar serves as a food source for caterpillars, which feed on nectar-containing plant foods and develop into a chrysalis and then an adult butterfly.
The role of nutrition in butterfly physiology
Nutrition is one of the key factors that determine the physiology and life cycle of butterflies. They go through several developmental stages including eggs, caterpillars, pupae and finally adults. Each stage has its own nutritional characteristics and requires certain nutrients for normal development.
Feeding eggs and caterpillars
Butterfly eggs and caterpillars usually feed on plants, which provide essential nutrients. They may feed on the leaves, stems, or flowers of various plants. Some species of butterflies have a preference for certain plants and cannot develop on others. It is important to note that the feeding of caterpillars is the most active stage and requires a large amount of food to ensure their growth and development.
Feeding pupae and adults
When the caterpillar reaches the last stage of its development, it enters the pupal stage. At this point, she stops feeding and begins to undergo metamorphosis. Adult butterflies emerging from pupae have a completely different diet. They feed on the nectar of flowers, which is the main source of energy for them. The nectar contains sugars, amino acids and other nutrients necessary for the metabolic processes and flight of butterflies.
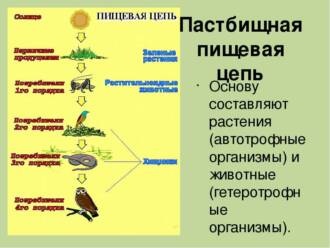
In general, nutrition plays a critical role in the physiology of butterflies, providing them with energy and essential nutrients for development and survival. The variety of plants on which they feed, as well as the way they acquire food at different stages of the life cycle, reflect the adaptive strategies of these amazing creatures.
Butterflies and their food

Butterflies are winged insects that go through a complex life cycle that includes several stages of development. One of the key components of this cycle is the feeding of butterflies.
Nutrition is an important part of butterfly physiology, as it provides energy for their activity and growth. Butterflies get their nutrients from the nectar contained in the flowers. Nectar is a sweet, sugary liquid secreted by plants to attract insects.
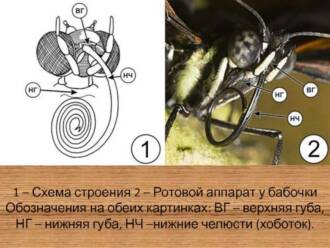
Butterflies, like other insects, have a special mouth structure called a proboscis. The proboscis is a long tube that butterflies use to suck nectar from flowers. They develop with this proboscis and learn to use it to get food.
Butterflies select flowers for food based on their taste preferences and nutrient needs. They prefer flowers of a certain color, shape and scent. Some butterflies prefer the flowers of certain plant species, which may be due to the presence of certain nutrients in their nectar.
Butterfly nutrition plays an important role not only in their physiology, but also in their ecological interactions. Butterflies are important plant pollinators, as they carry pollen between flowers when they visit, aiding plant reproduction. Thus, the nutrition of butterflies is of great importance for biodiversity and ecosystem resilience.
Importance of nectar for butterflies

Nectar plays an important role in the life of butterflies, being their main source of nutrition. Butterflies, like other insects, are heterotrophs, meaning they cannot synthesize their own food. They are completely dependent on external nutrition, and nectar is one of the main sources of energy for them.
Nutrients in nectar
Nectar contains not only sugars but also other nutrients such as amino acids, vitamins and minerals. The content and composition of nutrients in nectar can vary depending on the plants that produce it. Nectar is rich not only in energy substances, but also in substances necessary for the life of the body.
Beneficial relationships with plants
Butterflies play an important role in plant pollination by carrying pollen from one flower to another. In exchange for nectar, butterflies help plants reproduce and maintain their genetic diversity. Such relationships are beneficial for both butterflies and plants, their symbiosis allows both species to survive and reproduce.
The influence of nectar on the development of butterflies
Getting enough nutrients from nectar is an important factor for the development of butterflies. Feeding on nectar allows butterflies to get enough energy for growth and development, as well as to maintain their vital functions. Without nectar, butterflies will not be able to develop normally and survive in their environment.
Importance of Nectar for Butterfly Survival
Nectar is not only a source of energy for butterflies, but also an important factor for their survival. Butterflies, like other insects, have a high metabolism and quickly lose energy reserves. Regular feeding on nectar allows them to maintain their energy levels and survive in difficult environmental conditions.
Nectar as a source of energy

Nectar is the main food source for butterflies and plays an important role in their physiology. It contains essential nutrients that provide energy to carry out various life processes.
Butterflies obtain energy from nectar by consuming it through their elongated mouthparts, the labium. Nectar contains sugars such as fructose and glucose, which are the primary energy sources for the butterflies' metabolic processes.
In addition to sugars, nectar also contains various vitamins, minerals and amino acids. These nutrients play an important role in maintaining the health and development of butterflies. For example, vitamins help support the immune system, and amino acids are the building blocks for tissue growth and development.
Nectar is also an important source of water for butterflies. Water is essential for maintaining hydration and the proper functioning of the body. Butterflies can obtain water from nectar, supplementing their diet and providing the necessary level of hydration.
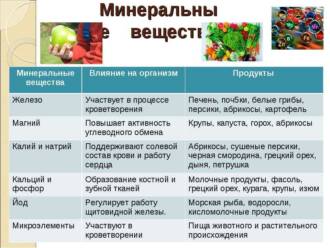
Vitamins and minerals in nectar
The nectar that butterflies get from flowers is a source of important vitamins and minerals necessary for their health and development. Vitamins play a key role in ensuring the normal functioning of the body of butterflies, participating in metabolic processes and supporting the immune system.
Nectar contains a variety of vitamins such as vitamin C, vitamin E, vitamin A, and vitamin K. Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant that helps protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. Vitamin E promotes skin health and has anti-inflammatory properties. Vitamin A is essential for maintaining healthy eyes and the immune system, and vitamin K is involved in the blood clotting process.
In addition to vitamins, nectar also contains various minerals such as potassium, calcium, magnesium and iron. Potassium plays an important role in maintaining the normal functioning of the heart and nervous system. Calcium and magnesium are essential for healthy bones and muscles, while iron is involved in the transport of oxygen throughout the body.
All these vitamins and minerals contained in the nectar allow butterflies to receive not only energy for their movement and reproduction, but also the necessary nutrients to maintain health and life.
The effect of nectar on reproductive function
Nectar plays an important role in the reproductive function of butterflies. It is the main source of nutrition for adult butterflies and allows them to accumulate enough energy for reproduction. The nectar-rich flowers attract butterflies with their fragrance and bright colors, which helps them find a breeding partner.
Nectar contains not only sugars, but also other nutrients, such as amino acids and vitamins, which are necessary for the proper functioning of the reproductive system of butterflies. They help maintain ovarian health and promote proper egg development.
In addition, nectar also contains pheromones, which play an important role in attracting a breeding partner. Pheromones are chemicals that are released by female butterflies and attract males. When eating nectar, butterflies receive these pheromones and can increase their attractiveness to males.
In general, the role of nectar in the reproductive function of butterflies cannot be underestimated. It not only provides them with the energy they need, but also the nutrients that keep their reproductive system healthy and functioning properly. Thanks to nectar, butterflies can successfully reproduce and maintain their populations for generations.
Interaction of butterflies with flowers
Butterflies and flowers have a very close relationship, which is important for both parties. Butterflies are the main pollinators of flowers, and flowers, in turn, provide butterflies with the necessary food in the form of nectar.
One of the ways butterflies interact with flowers is to attract attention. Flowers can be bright and beautiful to attract butterflies with their colors and fragrance. Butterflies, in turn, have a variety of colors and patterns on their wings, which also serve to attract the attention of flowers.
Butterflies use a variety of methods to find colors, including sight and smell. They can see colors that humans cannot distinguish, and are able to navigate by the fragrance that flowers give off. Butterflies can also sense ultraviolet light, which helps them determine where a flower is.
When a butterfly finds a flower, it unfolds its long proboscis to reach the nectar that is deep inside the flower. They use their proboscis to suck nectar from the flower. At this point, there is an interaction between the butterfly and the flower, which allows both parties to benefit.
Interestingly, some species of butterflies are specialized pollinators of certain flowers. They can be adapted to a certain type of flower in order to gain access to its nectar. For example, hummingbirds have a long proboscis that allows them to reach the nectar inside the long tubular flowers.
Thus, the interaction of butterflies with flowers plays an important role in their life cycle and pollination of flowers. Butterflies get the food they need, and flowers get help in pollinating and distributing their pollen, which helps them to reproduce and maintain the species.
Features of nutrition of butterflies in different stages of the life cycle

Butterflies, like many other insects, go through several stages in their life cycle: from egg to larva, from larva to pupa, and from pupa to adult. Each of these stages has its own nutritional characteristics.
Eggs
At this stage of butterfly development, they feed on plant materials that are deposited on plants. Butterfly eggs can be laid both on leaves and on stems or flowers. The size of eggs and their number can vary greatly depending on the type of butterfly.
Larvae
When butterfly eggs hatch, they hatch into larvae. Butterfly larvae are active food consumers and feed on plant materials such as plant leaves or stems. They usually have strong jaws that help them chew their food before swallowing it.
It is important to note that different species of butterflies may have different preferences for the plants they feed on. Some butterfly larvae prefer certain types of plants, while others may feed on a wide variety of plants.
pupae
After the larvae reach a certain size and undergo the necessary transformations, they turn into pupae. At this stage of butterfly development, they do not feed, as their main task is to transform into an adult. Pupae can be found in different places, such as on branches, leaves, or even underground.
It is important to note that the duration of this stage may vary depending on the species of butterflies and environmental conditions. After passing through this stage, the butterflies are ready to emerge and continue their life cycle.
The role of nectar in butterfly migration
Migration is an important part of the life cycle of many butterfly species. In the process of their journey, butterflies cover huge distances, moving from one habitat to another. The role of nectar in the migration of butterflies cannot be underestimated, as it is their main food source during long flights.
During migration, butterflies expend a huge amount of energy, and in order to maintain their activity and endurance, they need to receive enough nutrients. The nectar contained in the flowers is a source of carbohydrates, fructose and glucose, which provide energy for flight and support all physiological processes of the butterfly's body.
In addition, nectar is also an important source of water for butterflies during migration. While migrating, butterflies can face adverse weather conditions, such as heat and drought. Under these conditions, water plays an important role in keeping the body hydrated. Butterflies drink nectar to stay hydrated and prevent dehydration, allowing them to survive extreme situations.
Thus, nectar plays a key role in the migration of butterflies, providing them with the necessary nutrients and water to maintain their endurance and survival during long flights.
The Importance of Plant Diversity to Butterflies
For butterflies, plant diversity plays a key role in their life cycle and nutrition. Butterflies go through several stages of development, starting from the egg and ending with the adult (adult). In each of these stages, butterflies require specific plants for feeding and reproduction.
The importance of plant diversity to butterflies is evident in several ways. First, each species of butterfly has its own preferences in choosing plants for laying eggs. Some species of butterflies lay their eggs only on certain plants, which are the only food source for the caterpillars. If these plants are absent from the environment, then butterfly species may be threatened with extinction.
Secondly, the diversity of plants affects the nutrition of butterflies. Adult butterflies feed on nectar, which they obtain from plant flowers. Plant diversity provides more opportunities for butterflies to find and obtain nutritious nectar. This is especially important during periods when certain types of plants are flowering, while others have already withered. If plant diversity is limited, then butterflies may face food shortages and become vulnerable to predators and disease.
Thus, maintaining plant diversity is an important aspect of butterfly protection and conservation. The creation and maintenance of ecosystems rich in plant diversity helps to provide sufficient food and breeding conditions for butterflies, which contributes to the conservation of their abundance and species diversity.
Threats to feeding butterflies and their impact on populations
Nutrition plays an important role in the life of butterflies, as nectar is the main source of energy for them. However, there are various threats that can negatively impact food availability and ultimately butterfly populations.
1. Destruction of natural habitats

With the development of cities and industry, many natural habitats of butterflies are being destroyed. Lack of suitable growth conditions for the plants on which the butterflies feed can lead to reduced nectar availability and reduced butterfly populations.
2. Use of pesticides

The use of pesticides in agriculture can have a negative impact on the plants on which the butterflies feed. They can destroy nectar plants or leave toxic residues on them, making food unsuitable for butterflies. Pesticides can also negatively affect the very physiology of butterflies and their ability to feed.
3. Climate change
Climate change may affect the availability of food for butterflies. Some of the plant species they feed on can be sensitive to changes in temperature, rainfall, and seasonality. If conditions become less favorable for the growth of these plants, butterflies may face a lack of food and a deterioration in their nutrition.
All these threats can lead to a decline in butterfly populations, and in some cases even to their extinction. Therefore, it is important to take measures to preserve and restore the natural habitats of butterflies, control the use of pesticides and take measures to reduce the impact of climate change on their diet.
Read more: