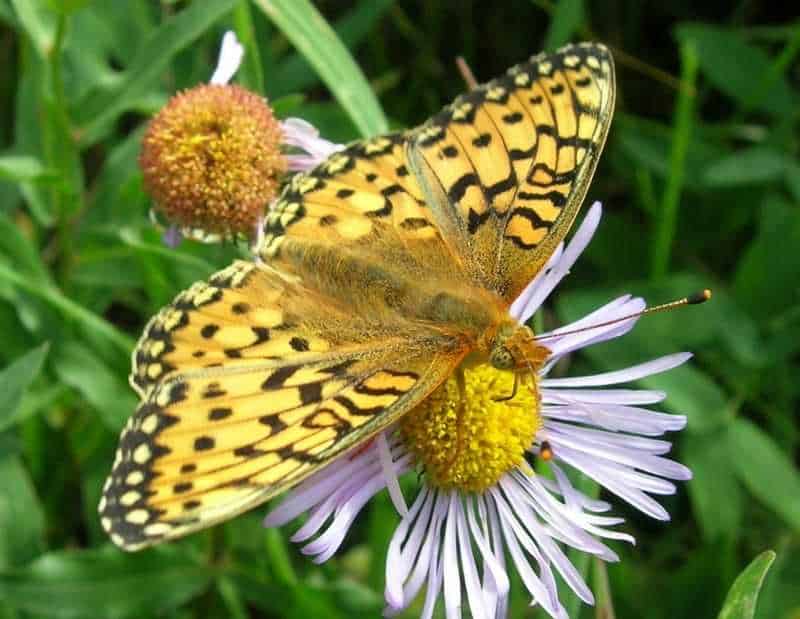
leopard butterfly - is a beautiful and bright representative of the insect world, distinguished by its unusual coloring and unique lifestyle. It received the name "leopard" due to its colorful and varied patterns on the wings, which resemble the coloring of a leopard.
Lifestyle of a leopard butterfly is also interesting and surprising. It is nocturnal and active mainly at night. During the day, she sleeps, hiding from predators in dense vegetation or under the covers of trees. At night, she comes out into the light and hunts for the nectar of flowers, preferring flowers with bright and sweet smells.
The distribution of the leopard butterfly includes most of the territory of Eurasia. It is found in forests, gardens, parks and other places with ample vegetation. A distinctive feature of the distribution of this species is its adaptability to various climatic conditions. The leopard butterfly has a wide range of tolerance to temperature fluctuations and can adapt to different habitats.
The leopard butterfly is an amazing creation of nature, which not only pleases the eye with its colorful appearance, but also plays an important role in the pollination of plants. Its unique lifestyle and distribution features make it a real treasure of nature and an object of study for scientists and insect lovers.
Appearance and features of a leopard butterfly
The leopard butterfly is one of the most beautiful and exotic types of butterflies. It has bright and varied colors that resemble the picturesque patterns of a leopard. The body of the butterfly is covered with small scales, which gives it a special smoothness and shine.
One of the features of the leopard butterfly is its large wings, which can reach impressive sizes. The wings of this butterfly have a complex structure and are decorated with various patterns and designs. They can be either a uniform color or combined, with bright spots and stripes.
The leopard butterfly also has long and thin antennae that help it navigate in space and find food. These antennae are sensitive organs and allow the butterfly to perceive odors and other chemical signals.
Despite its beauty, the leopard butterfly also has protective mechanisms. It can hide against the background of the environment due to its coloration, which helps it blend into the vegetation. In addition, she can move quickly and maneuver in the air, making her a difficult target for predators.
Ways to feed a leopard butterfly
The leopard butterfly is a predator, so its feeding methods are based on hunting other insects. She actively consumes food during her short adult life span, which lasts only a few weeks.
The leopard butterfly's main source of food is flower nectar. It uses its long tentacles to reach the nectar secreted by various types of flowers. The leopard butterfly prefers flowers that bloom at night or in the early morning hours, as it is a nocturnal creature.
In addition to nectar, the leopard butterfly also feeds on sap and plant sap, which it extracts with its nose. She drinks juices from damaged plants or used fruits, receiving the necessary nutrients for her development and survival.
In addition, the leopard butterfly can feed on other insects such as small beetles and flies. She uses her sharp jaws and claws to grab her prey and consume it. This allows her to get the necessary protein and energy for her active life.
Thus, the leopard moth's feeding habits include the consumption of flower nectar, plant saps and saps, and hunting other insects. This provides it with the necessary energy and nutrients for its survival and development.
Reproduction and development of a leopard butterfly
The leopard butterfly, like most butterflies, goes through a development cycle consisting of several stages: eggs, caterpillar, pupa and imago.
The female leopard butterfly lays its eggs on suitable plants, which after some time turn into caterpillars. Caterpillars of the leopard butterfly are brightly colored and have well-developed jaws for feeding. They actively feed on the leaves of their host plants, which allows them to gain weight and grow.
After several molts, the caterpillar of the leopard butterfly turns into a chrysalis. The pupa is a resting stage stage during which internal transformations occur. Externally, the chrysalis of a leopard butterfly has a protective color that masks it among the environment.
After some time, an imago is formed in the chrysalis - an adult leopard butterfly. It hatches from the chrysalis and spends a little time in peace until its wings are completely dry and straightened. After this, the butterfly is ready to fly and reproduce.
In general, the process of reproduction and development of the leopard butterfly is amazing and unique. It allows this beautiful insect to overcome all stages of the life cycle and continue its genus.
Leopard Butterfly Migrations
The leopard butterfly is known for its long-distance migrations in search of favorable conditions for breeding and feeding. These migrations are an important part of the life cycle of this butterfly species.
During the migration period, leopard butterflies can travel great distances, reaching new habitats. They prefer warm climates and usually migrate south to avoid adverse winter conditions.
During migrations, the leopard butterfly can cross obstacles such as oceans and mountain ranges. They use the wind as a means of transportation and can fly hundreds of kilometers a day.
The migrations of the leopard moth allow this species to expand its distribution and find new food sources. Through these migrations, a butterfly population can be maintained and developed over many generations.
Habitat and distribution range of the leopard butterfly
The leopard butterfly lives in a variety of types of environments, including rainforests, savannas, island landscapes, and mountainous regions. She prefers areas with dense vegetation where she can find food and shelter.
The distribution range of the leopard butterfly covers most of South and Southeast Asia. It is found in countries such as India, Myanmar, Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia and the Philippines. In these regions, the leopard butterfly inhabits various types of forests, including tropical rainforests and mixed forests.
The leopard butterfly has a wide distribution area, but its numbers are declining due to the loss of natural habitats due to deforestation and agricultural development. It is also exposed to threats from pollution and climate change. Due to its beautiful coloration and elegant movements, the leopard butterfly is a popular subject for observation and photography in its natural environment.
Ways to protect a leopard butterfly from predators

The leopard butterfly has several effective ways to protect itself from predators. One of them is crypsis, the butterfly's ability to blend into its surroundings thanks to its coloring. The dark spots on the leopard butterfly's wings help it blend into the grass and twigs, making it invisible to predators.
In addition, the leopard butterfly has the ability of mimicry. It mimics the color and shape of certain types of butterflies that are avoided by predators because of their poisonousness or unpleasant taste. Thus, the leopard butterfly scares off predators, making them an unattractive target for attack.
Another way to protect the leopard butterfly is its fast and agile flight behavior. It is able to quickly change direction of flight and accelerate sharply, which makes it difficult for predators to catch it. This allows the butterfly to avoid danger and increases its chances of survival.
In addition, the leopard butterfly has an unusual wing structure that helps it survive in the event of a predator attack. When trying to grab a butterfly, its wings can break or come off, leaving the predator with an empty piece. This distracts the attention of the predator and gives the butterfly time to escape.
Overall, the leopard butterfly has several effective predator defenses that allow it to survive in the wild and continue its lifestyle.
The impact of human activity on the number of leopard butterflies
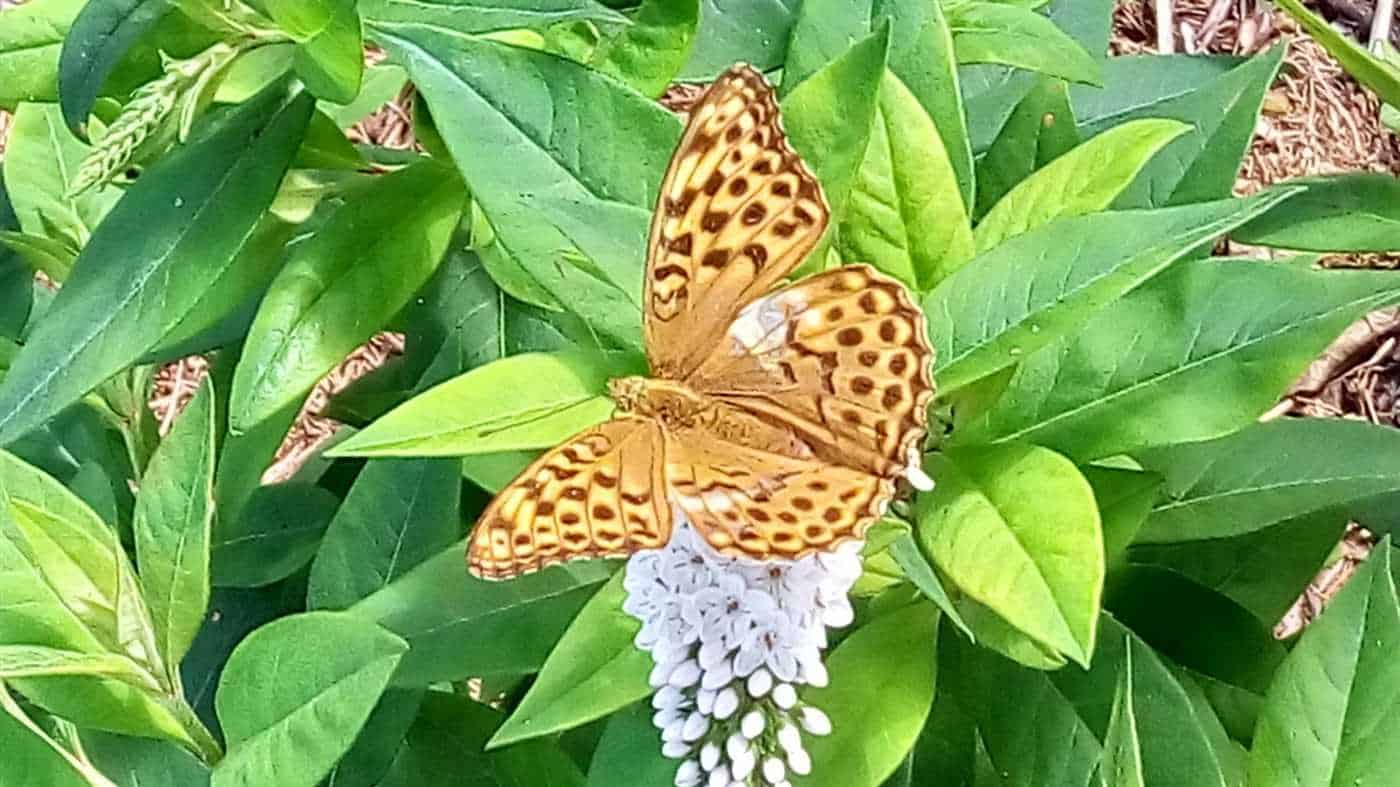

Human activity has a negative impact on the number of leopard butterflies. One of the main reasons for the decline in the population of this species is the destruction of natural habitats.
Due to the expansion of agricultural land and the development of forest areas, the leopard butterfly is losing its places for breeding and foraging. This leads to a reduction in its numbers and the threat of extinction.
The use of pesticides in agricultural activities is also of particular danger to the leopard butterfly. These toxic substances enter its natural habitat and have a toxic effect on the population. Butterflies that come into contact with pesticides can die and suffer from problems with reproduction and development of offspring.
In addition, the illegal trade in leopard butterflies also negatively affects their numbers. The hunting of these beautiful insects for the purpose of collecting or selling on the black market leads to their scarcity in nature and threatens the conservation of the species.
In this regard, in order to preserve the population of the leopard butterfly, it is necessary to take measures to protect and restore its habitats, as well as to prohibit the use of hazardous pesticides. In addition, cooperation with law enforcement agencies is needed to combat the illegal trade in this species of butterflies. This is the only way to ensure the conservation of the leopard butterfly and its abundance in the future.
Threats and challenges facing the leopard butterfly

The leopard butterfly, like many other butterfly species, faces a number of threats and problems that can negatively impact its population and survival.
1. Destruction of natural habitats
One of the main threats to the leopard butterfly is the destruction of its natural habitats. As a result of the expansion of agriculture, construction and infrastructure projects, a significant part of the forest and grassland on which this butterfly lives is disappearing. This leads to a decrease in the population size and a reduction in the distribution area.
2. Climate change
Climate change is also a major concern for the leopard butterfly. Global warming and extreme weather conditions such as droughts and floods can negatively affect its development, nutrition and reproduction. Climate change could lead to population decline and even extinction of this species.
3. Use of pesticides and insecticides
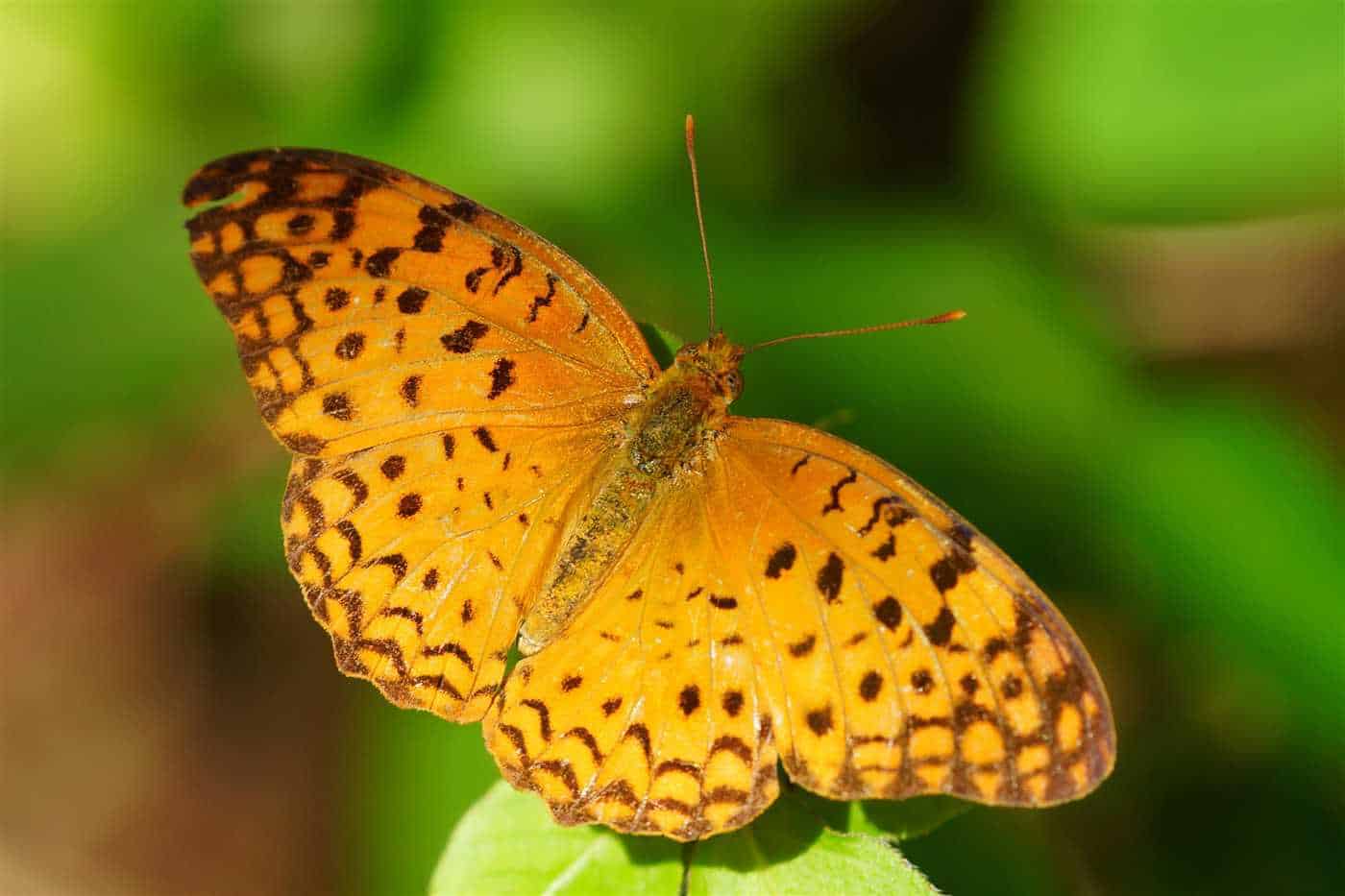

The use of pesticides and insecticides in agriculture and gardening also poses a threat to the leopard butterfly. These chemicals can poison and kill the butterflies, as well as their food sources, such as plants and flowers. Continued exposure to pesticides can lead to population declines and disruption of the ecosystem balance.
In general, the conservation of the leopard moth requires complex measures such as the establishment of reserves and protected areas, the control of the use of chemicals and the implementation of habitat restoration programs. This will preserve the unique species and ensure its long-term survival.
Features of the behavior of a leopard butterfly
The leopard butterfly, or also known as Euploea mulciber, has a number of interesting features in its behavior. Firstly, this butterfly is an active diurnal species, which distinguishes it from many other butterflies. She prefers to fly in bright sunny times, when the flowers and other plants on which she feeds are most active.
Secondly, the leopard butterfly has high maneuverability and the ability to quickly change the direction of flight. This allows it to avoid predators and search for food efficiently. When the leopard butterfly senses danger, it can instantly change its flight direction, making it a difficult target for predators.
It is also worth noting that leopard butterflies have a unique camouflage ability. Their wings have black and white stripes that resemble the coloring and pattern of a leopard. This helps them blend in with their environment and camouflage themselves from predators. When a butterfly sits on a flower or leaf, it becomes almost indistinguishable.
The role of the leopard butterfly in the ecosystem

The leopard butterfly plays an important role in the ecosystem, participating in the pollination process and being a source of food for other animals.
Pollination:
The leopard butterfly is a pollinator of plant flowers that produce nectar. When a butterfly visits a flower, pollen grains attach to its body and are transferred to other flowers. In this way, the butterfly contributes to the diversity and reproduction of plants in the ecosystem.
Food for other animals:
Larvae of the leopard butterfly serve as a food source for other animals such as birds and insectivorous mammals. Birds actively prey on larvae and caterpillars of the leopard moth, increasing their population and maintaining a balance in the food chain.
Conservation of biodiversity:
The leopard butterfly is an indicator of the state of the environment. Its presence or absence may indicate changes in the ecosystem. The continuation of its life and the preservation of the population contribute to the conservation of biodiversity and the health of the ecosystem as a whole.
Myths and legends about the leopard butterfly

The leopard butterfly attracts attention with its bright color and unusual appearance, which gives rise to many myths and legends associated with this beautiful insect.
1. Symbol of strength and beauty
Many peoples considered the leopard butterfly a symbol of strength and beauty. Its bright and rich colors, reminiscent of the coloring of a leopard, inspired people to be creative and awaken their inner strength.
2. Amulet from evil spirits
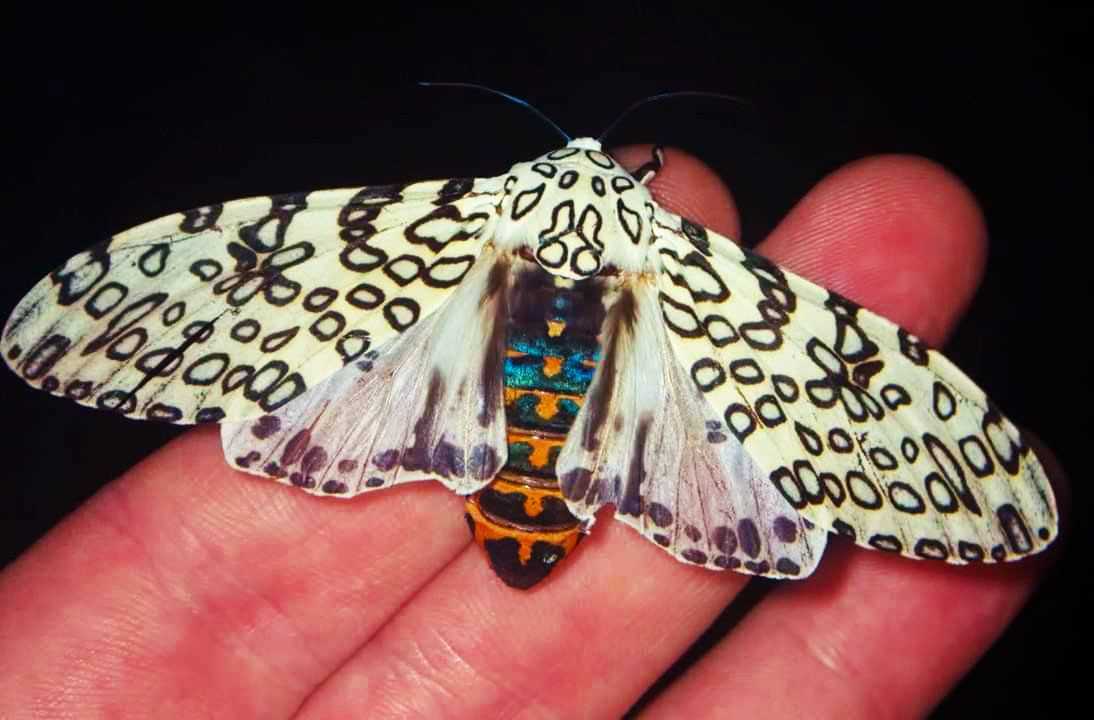

In some cultures, the leopard butterfly was considered a talisman against evil spirits and negative energy. They believed that her presence could ward off all the negative and bring prosperity and protection.
3. Mediator between the worlds
According to one of the legends, the leopard butterfly is an intermediary between the worlds of the living and the dead. They believe that she is able to transfer the souls of the dead to the light side and help them on their way to the afterlife.
4. Harbinger of change

In some cultures, it was believed that the appearance of a leopard butterfly in the house or near a person is a harbinger of change. It was believed that she brings news of the imminent beginning of a new period in a person's life and gives him strength and wisdom to cope with changes.
Beliefs and legends about the leopard butterfly continue to live in the modern world, and it remains one of the most mysterious and amazing creatures of nature.