Butterflies, or insects near Lepidopter, are one of the most amazing groups of animals on Earth. They attract attention with their beautiful colors and graceful wings, as well as their unique abilities and behavior. The definition and classification of butterflies play an important role in the study of their diversity.
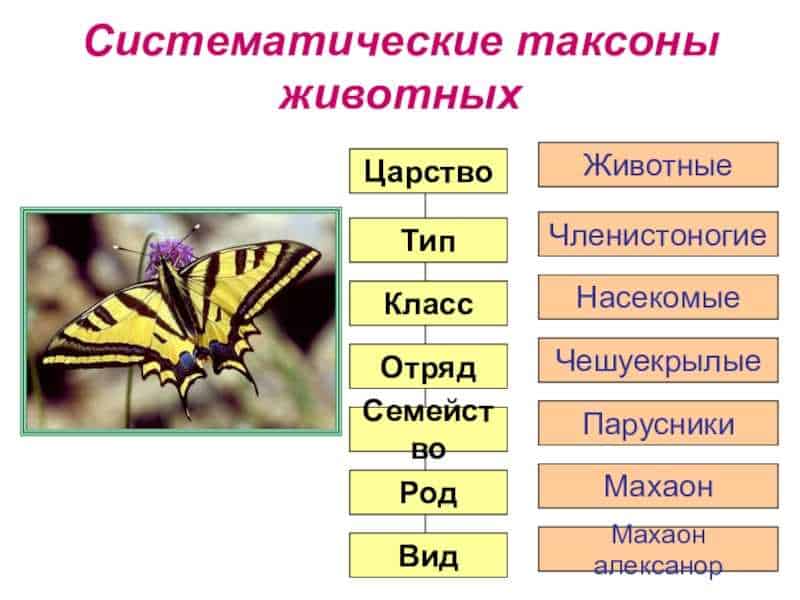
The taxonomy of butterflies is based on their morphological, genetic and behavioral characteristics. Butterflies are divided into several families, including whites, pigeons, homoptera, scoops and others. Each family has its own characteristics and differences in the structure of the wings, body anatomy and lifestyle.
Butterfly classification also includes genera and species. Genera combine butterflies with common characteristics and close family ties, and species are groups of butterflies that can interbreed and give birth to offspring. Butterfly species can vary in color, size, lifestyle, and geographic distribution.
Butterfly definition: what are these insects?
Butterflies are winged insects belonging to the Lepidoptera order. They are distinguished by the beautiful color of the wings, often decorated with a variety of patterns and designs. Butterflies are one of the most common and well-known insects, they can be found in almost all corners of the planet, with the exception of some arctic and antarctic regions.
Butterfly wings are made up of thin integumentary tissue covered with tiny scales that give them their bright color. Most butterflies are active during the day and feed on the nectar of flowers. They play an important role in plant pollination and are important links in the ecosystem. Butterflies go through a complete cycle of development, starting from an egg, then a larva, a pupa, and finally an adult insect.
There is a huge variety of butterfly species, their number exceeds 180,000. Butterflies can be of very different sizes - from tiny species with a wingspan of only a few millimeters to giant ones whose wingspan exceeds 25 cm. They also differ in the shape and color of the wings, which makes them real works of art of nature. Butterflies are the object of study by many scientists, and their beauty and originality attract the attention of many people.
Butterfly diversity: differences and classification
Butterflies are a group of insects that attract attention with their beauty and diversity. They differ from other insects in their wings, which are covered with tiny scales that create unique patterns and colors. The classification of butterflies is based on differences in their appearance, as well as on the features of their life cycle and behavior.
Butterfly families

There are a large number of families of butterflies, each of which has its own characteristic features. Some of the more common families include:
- Peacocks - butterflies of this family are distinguished by bright colors and large wings with an ornament resembling peacock feathers.
- scoops - these butterflies have small wings and have excellent camouflage that allows them to hide from predators.
- golubyanki - butterflies of this family usually have a delicate blue or purple color, and their wings are decorated with thin black lines.
- Machaons - these butterflies attract attention with their bright orange wings with black patterns.
Butterfly species
Each family of butterflies includes many species that differ not only in appearance, but also in behavior. Some species of butterflies migrate long distances, while others prefer to live in certain ecosystems, such as tropical forests or mountainous areas. Each species of butterfly has its own unique features and adaptations that allow them to survive in different environments.
The role of butterflies in the ecosystem
Butterflies play an important role in the ecosystem. They are pollinators of many plants, carrying pollen on their legs and promoting plant reproduction. In addition, butterflies are a food source for many animals such as birds and bats. Their presence in nature testifies to the richness and diversity of the ecosystem.
Structure and anatomy of butterflies: main features
Butterflies, like all insects, have a characteristic anatomical structure. They consist of a head, thorax and abdomen. The butterfly's head contains a pair of large compound eyes that allow it to perceive light and movement. Also on the head are antennae, which play an important role in orientation and searching for food.
The chest of a butterfly consists of thirty-two segments, on which six legs and two pairs of wings are located. Butterfly legs are designed to move and hold on the surface. Butterfly wings are the main instrument for flight. They are covered with thin scales that give them colorful colors and unique patterns.
The abdomen of butterflies consists of several segments, each of which contains the stomach and intestines, which are responsible for digestion. Also in the abdomen are a variety of glands that perform various functions, for example, glands that secrete pheromones to attract a partner.
Thus, the structure and anatomy of butterflies includes a head with eyes and antennae, a chest with legs and wings, and an abdomen with digestive organs and specialized glands. These features allow butterflies to successfully exist in their habitat and perform important functions in the ecosystem.
Butterfly food plants: where they live and what they eat

Butterflies are insects that go through developmental stages including eggs, caterpillars, pupae and adults. Each stage has its own specific nutritional needs. Forage plants are plants that serve as a food source for caterpillars and adult butterflies.
Caterpillars usually feed on the leaves of plants, with each species of butterfly being able to be specialized on certain plants. Some caterpillars may only feed on one type of plant, while others may feed on several species. Some of the most common food plants for caterpillars include spurge, nettle, St. John's wort, cabbage, and fruit trees.
Adult butterflies, or adults, usually feed on the nectar of flowers. They use their long proboscis to reach nectar that contains sugars and other nutrients. Nectar is the main source of energy for adult butterflies. However, some species of butterflies can also feed on fruit juices and plant juices.
Butterfly habitats depend on their preferred food plants. Some butterflies may be specialized for certain ecosystems such as forests, grasslands, or deserts. Other species of butterflies can be adapted to different environments and live in a variety of places, including gardens, parks, and even city fringes.
The study of butterfly food plants is an important part of their classification and understanding of their ecology. Knowing where and what butterflies eat helps preserve their habitats and offer suitable conditions for them to reproduce and survive.
Evolution and origin of butterflies: development history
Butterflies are one of the most diverse and successful orders of insects that exist on Earth. Their history of development dates back to long before the appearance of man. Studying their evolution allows us to better understand the processes that have led to such a wealth of species and adaptations.
Butterflies have undergone many changes over millions of years. They have gone from primitive groups of insects to complex and diverse organisms. During the evolutionary process, butterflies have acquired unique adaptations that allow them to survive and reproduce in various ecosystems and conditions.
Studies of genetic material and fossil finds indicate that butterflies appeared about 200 million years ago. They are believed to have evolved from ancient insects like modern-day moths and butterflies. However, the exact details of the origin of butterflies are still the subject of scientific research and debate.
As butterflies evolved, there was a division into various families and species. Today, there are about 180,000 species of butterflies, each with its own unique characteristics and adaptations. Most butterflies belong to the Lepidoptera order, which includes such families as the Variegated, Shrub, Blueberry and many others.
The evolution and origin of butterflies continues to this day. Many factors, such as climate change, destruction of natural habitats and human impact, affect their development and survival. Therefore, the study and conservation of the biodiversity of butterflies are important tasks of modern science and nature conservation.
The important role of butterflies in the ecosystem: why they are necessary

Butterflies play an important role in the ecosystem and are an integral part of the biological diversity of our planet. They perform many functions that contribute to maintaining the balance in nature.
Pollination of plants
One of the main functions of butterflies is pollination of plants. When visiting flowers, butterflies transfer pollen from one plant to another, facilitating their pollination. This not only helps plants reproduce, but also ensures the preservation and diversity of the plant world.
Role in the food chain
Butterflies are an important link in the food chain. Adult butterflies serve as a food source for many animals, including birds, frogs, and insectivores. Butterfly larvae are also food for a variety of animals, including spiders, birds, and mammals. Thus, butterflies play an important role in maintaining the food chain in an ecosystem.
Environmental indicators

The state of a butterfly population can serve as an indicator of the state of the environment. Changes in the number and species diversity of butterflies may indicate a violation of the ecological balance, pollution or loss of natural habitats. Therefore, the study of butterflies and their populations allows us to obtain information about the state of the environment and take measures to preserve and restore it.
In general, butterflies play an indispensable role in the ecosystem, providing pollination of plants, participating in the food chain and serving as indicators of the state of the environment. Therefore, they are necessary to maintain biological diversity and balance in nature.
Defense mechanisms of butterflies: how they survive in nature

Butterflies have various defense mechanisms that help them survive in nature. One such mechanism is camouflage. Many species of butterflies have coloration that allows them to blend in with their surroundings. For example, some butterflies have wings with spots similar to the eyes of birds of prey, which divert attention from their real body and protect them from attack.
In addition, butterflies may use mimicry for defense. They may mimic other dangerous or nasty species to scare off predators. For example, some butterflies have a coloration similar to bright and poisonous beetles or wasps. This makes predators think they are dangerous and inedible.
Another defense mechanism of butterflies is their ability to secrete disgusting substances or poisonous chemical compounds. When the butterfly senses danger, it can secrete these substances from its glands and scare off predators. Some butterflies also have spines or spines on their bodies, making them unpleasant to touch.
In general, the defense mechanisms of butterflies help them survive in nature by preventing predators from attacking and keeping them safe. The study of these mechanisms allows us to better understand the adaptation and evolution of these amazing creatures.