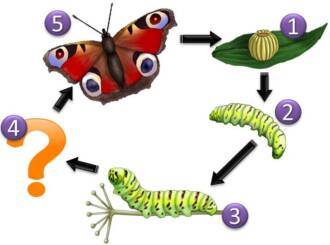
The cabbage white butterfly, or scientific name Plutella xylostella, is one of the most well-known and diverse butterfly species. Its amazing life cycle begins with an egg that is laid on the leaves of cabbage plants. Cabbage white eggs are small and firmly attached to the plant. After a few days, the egg hatches into a larva that begins to actively feed and grow.
The cabbage larva is very predatory and can eat a significant amount of cabbage leaves, which can cause serious damage to crops. In the process of its growth, the larva goes through several stages of molting, changing its appearance and increasing its size. In the final stage, the larva turns into a pupa, which attaches itself to a plant or other suitable surface.
Over the course of a few days, an incredible transformation occurs: an adult cabbage white butterfly emerges from the pupa. The cabbage white butterfly is small in size and has a colorful coloring that helps it camouflage itself among the leaves. The adult cabbage white butterfly does not live long, and during this time it actively reproduces to continue its amazing life cycle again.
Cabbage life cycle: from egg to larva

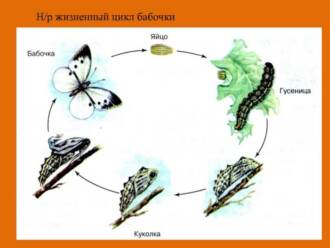
Cabbage is an insect that belongs to the butterfly family. The life cycle of cabbage goes through several stages of development, starting with an egg and ending with a full-fledged larva.
Early in its life, the cabbage lady lays her eggs on the upper side of cabbage leaves or other cruciferous plants. The eggs are oval in shape and small in size. They can be set aside both individually and in groups.
After the eggs hatch, larvae appear - the first stage of cabbage development. The larvae are small and have long legs. They actively feed on the cabbage leaves on which they are located. During this stage, the larvae go through several molts, increasing in size and undergoing changes in their appearance.
After the end of the larval stage, the cabbage turns into a chrysalis - a sleeping stage of development. The pupa has a coating that provides it with protection from the external environment. Important transformation processes take place inside the pupa, as a result of which the cabbage will turn into an adult insect.
After some time, the chrysalis splits and an adult cabbage butterfly flies out of it. The butterfly has wings that allow it to fly. She also has a characteristic color that can protect her from predators.
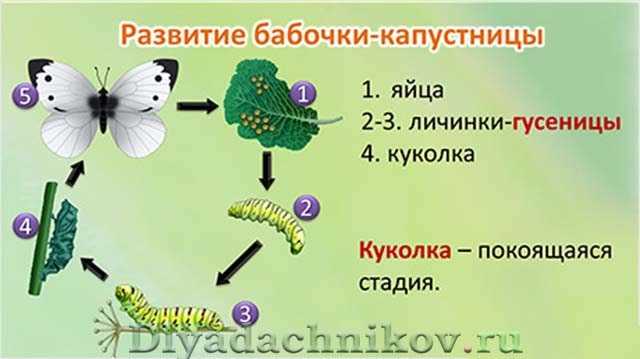
Thus, the cabbage life cycle goes through several stages of development, starting with an egg, through a larva and a pupa, and ending with an adult insect - a butterfly.
Stage 1: The Egg – The Beginning of the Cabbage White’s Mysterious Life

The egg is the first stage in the exciting life of the cabbage white. It is the beginning of the entire process of the insect's developmental history.
The cabbage egg has a special appearance that makes it different from other eggs. It is oval in shape and white in color. Each egg is about 1 mm in size and has a thin shell that protects it from external influences.
Cabbage eggs are laid on cabbage leaves, which allows them to be close to a food source for future larvae. The mother cabbage leaves several eggs on each leaf to ensure the survival of as many offspring as possible.
The incubation period for cabbage eggs can range from several days to several weeks, depending on environmental conditions. At this time, the development of the larva inside the egg occurs.
The entire life stage of the cabbage starts with an egg, and it is this that is the beginning of the mysterious and amazing process of transformation of this insect.
Stage 2: Transformation from Egg to Hungry Caterpillar

After the cabbage moth's tiny egg has been laid on a cabbage leaf, the second stage of its life cycle begins - the transformation from egg to caterpillar.
Initially, the cabbage egg looks like a small white dot attached to the leaf. Inside the egg is an already formed caterpillar, which is waiting for its time to hatch.
Under the influence of heat and certain environmental conditions, the egg begins to change. A small crack appears from it, through which the caterpillar crawls out.
The caterpillar immediately begins to actively eat cabbage leaves in order to gain strength and grow. Within a few weeks, it grows very quickly and gradually acquires its characteristic green color.
During this period, the caterpillar goes through several molts, when its skin becomes tight and it is forced to shed it and grow a new one. After each molt, the caterpillar gets bigger and bigger.
The cabbage caterpillar is very active at this stage of its life and is constantly looking for food. She gnaws at cabbage leaves, leaving her marks on them in the form of chewed edges. Thanks to its hunger and activity, the caterpillar grows rapidly and prepares for the next stage of its development.
Stage 3: Caterpillar - the active period of the cabbage butterfly's life
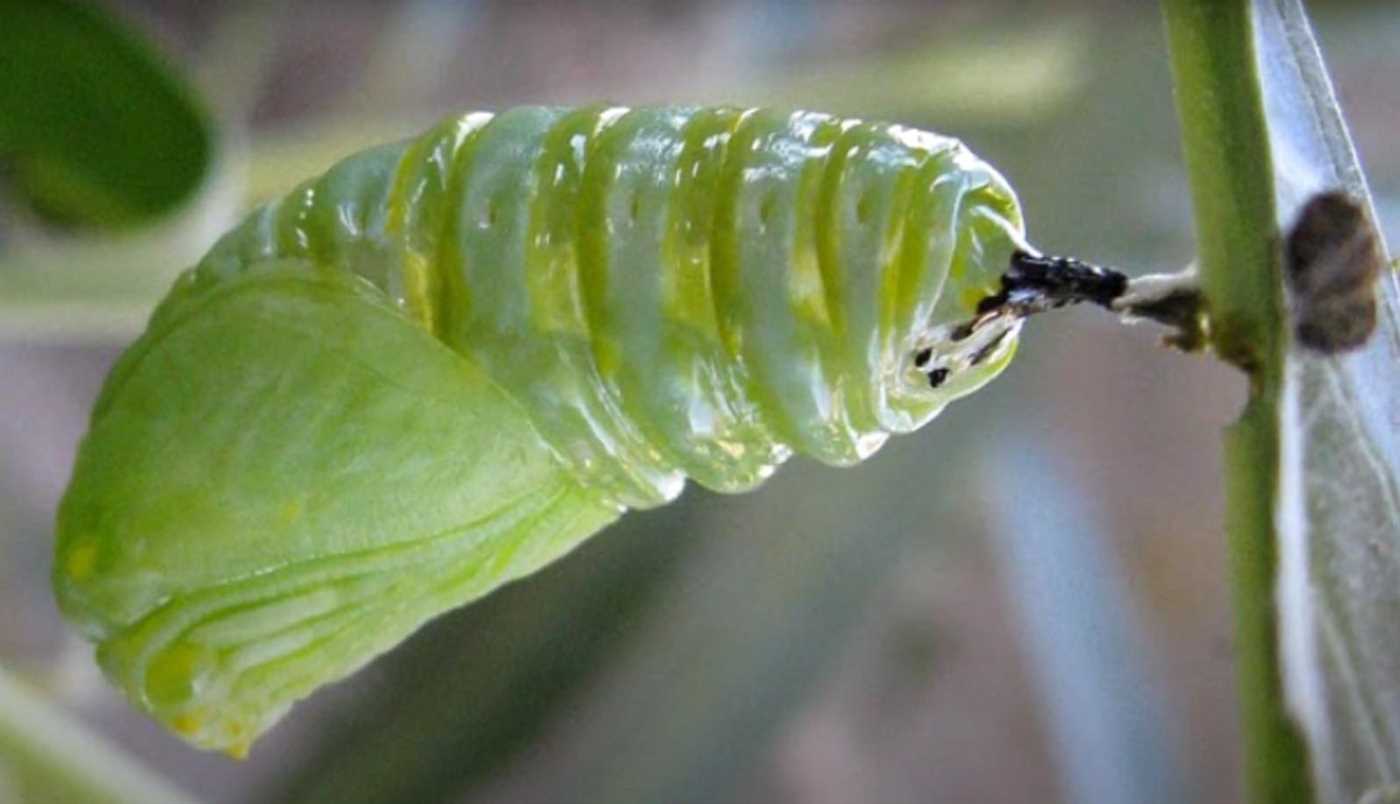

The caterpillar is the most visible and active stage of the cabbage butterfly's life. After hatching from the egg, the caterpillar begins to actively feed and grow. It has powerful jaws that help it gnaw through the leaves of cabbage and other plants.
The cabbage caterpillar has a bright color that serves as a warning to predators. It can be green, yellow or even black with bright spots or stripes. This coloration signals its toxicity and scares off enemies.
During this period, the caterpillar actively grows and gains weight. She goes through several molts, while she sheds her old skin to make room for growth. The cabbage caterpillar can reach a length of up to 5 centimeters.
An important feature of the cabbage caterpillar is its ability to create a web. She uses it to protect herself from predators and to create a cover under which she can hide.
At this stage, the cabbage caterpillar actively feeds and accumulates energy for subsequent changes that will occur in its body at the next stage of life - the pupa.
Stage 4: Spinning - Preparing for the Transformation
At this stage of the cabbage white butterfly's life cycle, an amazing transformation occurs. Once the larva reaches a certain size, it begins preparing for its final stage of development - spinning.
Spinning is the process by which the cabbage white larva releases a thin, strong thread-like material from which it creates its protective shell. This shell is called a cocoon. The cocoon is a safe haven for the future insect, where it will undergo the transformation from larva to pupa.
The cocoon created by the cabbage has a special structure. It is very strong and resistant to protect the chrysalis from external influences and predators. The cocoon is usually attached to some surface, such as plant leaves or stems, to be securely attached.
Inside the cocoon, amazing transformation processes occur. The pupa inside the cocoon undergoes a metamorphosis, as a result of which it turns into an adult insect - a cabbage white. This process takes some time and is completed when the cabbage white is fully formed and ready to emerge from the cocoon.
Stage 5: Cocoon - transitional stage
At the fifth stage of development, the cabbage white butterfly transitions from larva to imago, an adult insect. During this transitional stage, the cabbage white creates a special protective shell for itself, called a cocoon. The cocoon is a kind of shelter in which the final stages of metamorphosis occur.
The cabbage cocoon has a special structure and consists of a durable material that is created by the larva itself. It consists of a fibrous substance, which is produced by its glands and forms a dense shell. This shell protects the cabbage from external influences and provides it with suitable conditions for the final transformation.
Complex transformation processes occur inside the cocoon. The larva turns into an imago - a fully formed insect. At this time, changes in the external appearance and internal organs occur. From a herbivorous creature, the cabbage white turns into an insect capable of reproduction and searching for food. This transitional stage is the culmination of the development of the cabbage white.
Stage 6: New birth - the emergence of the larva

After passing through all the previous stages of development, the larva finally hatches from the cabbage egg. This is a small creature that immediately begins to actively move and look for food.
The cabbage larva has a cylindrical body shape and long legs, which allows it to move on the surface of plants. She also has strong jaws that help her to penetrate the leaves of plants and feed on their flesh. During this stage of development of the cabbage, the larva goes through several molts, during which it grows and changes its appearance.
The cabbage larva spends most of its time on nutrient plants and actively feeds. It is an important pest of cabbage and other cabbage crops, as it is able to eat a large number of leaves, causing significant damage to the plant.
The survival of the cabbage white larva depends on environmental conditions and food availability. It can become prey for predatory insects, birds and other animals. However, some larvae can survive and reach the next stage of their development - turning into a pupa.
Stage 7: Larva – a new stage in the life of the cabbage white
First changes

After hatching from the egg, the cabbage turns into a small larva, ready for new adventures. At this stage, there are significant changes in her appearance and behavior. The larva acquires a peculiar appearance that helps it survive and develop.
Growing appetite
The cabbage larva feeds actively, consuming a large amount of food, mainly of plant origin. Her appetite is constantly growing, and she is constantly looking for and swallowing new cabbage leaves. During this period, the larva passes through several molts, growing and increasing its size.
Protective measures
The cabbage larva actively uses various defense mechanisms to avoid danger. It can curl into a ball, hide under leaves, and, if necessary, perform jerks to scare away predators. Thanks to these self-protection measures, the larva maintains its life and continues its development.
Stage 8: The pupa is the last step before transformation.
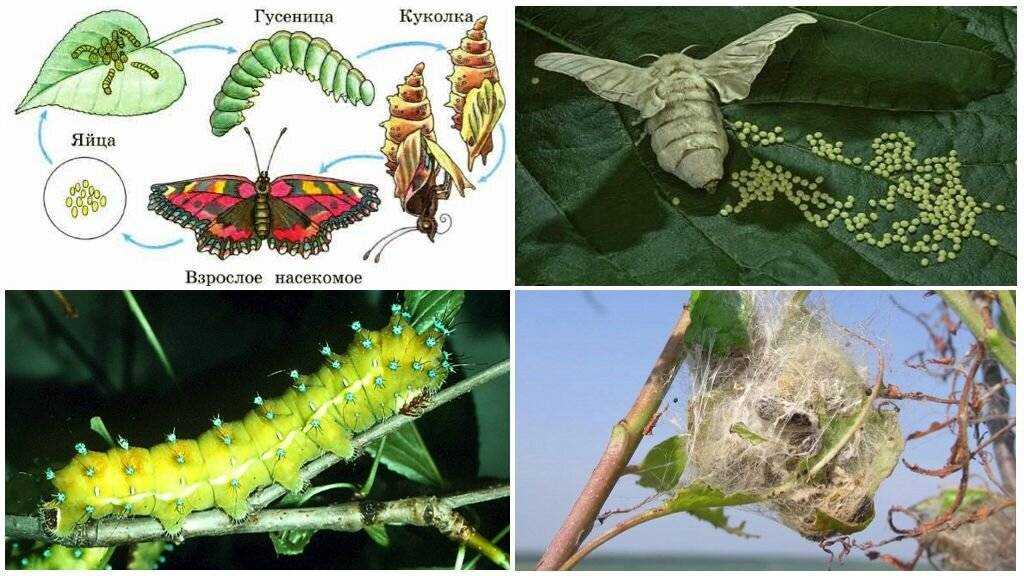
At this stage, the cabbage passes the last step before turning into an adult butterfly. The pupa, which is formed from the larva, is a special stage in the life of this insect.
The cabbage chrysalis has a hard shell that protects it from external influences. Amazing transformations take place inside the pupa: the larva turns into a butterfly. At this time, there is a complete restructuring of organs, tissues and body systems.
Outwardly, the cabbage chrysalis appears to be covered with a greenish coat, which helps it blend in with its environment and provides protection from predators. The pupa is attached to a plant or other surface with a special adhesive substance.
The period that the cabbage spends in the chrysalis can last from several days to several weeks. During this time, the complete transformation of the larva into a butterfly takes place, and the pupa is preparing to emerge into the light.
The pupa is the last step before the cabbage white butterfly becomes an adult. It is a unique stage in the life of this insect and represents an amazing transformation that takes place inside a closed shell.
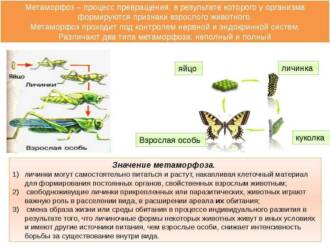
Stage 9: Amazing transformations: from chrysalis to adult insect
After the cabbage white pupa has completed all the previous stages of its development, it prepares for the most amazing transformation – turning into an adult insect. This stage is called metamorphosis.
Metamorphosis in cabbage occurs inside the pupa. At first, when the chrysalis has just formed, it has a light green color and a soft body. Gradually, changes occur inside the pupa: wings, legs and other parts of the body of an adult insect are formed.
As the cabbage white develops, its color becomes darker. The pupa becomes hard and more like an adult. At the end of the metamorphosis, the pupa turns into an adult cabbage white - an insect with a black body and bright orange wings.
An adult cabbage no longer needs food and carries seeds that will become new cabbages. She makes flights, distributing seeds over long distances and helping cabbage plants to conquer new territories.