The science that studies butterflies is called lepidopterology. This is an interesting and multifaceted area of scientific research, which includes the study of various aspects of the life of butterflies: their anatomy, behavior, migrations, classification and ecology.
Lepidopterology is a science that helps to expand our knowledge of butterflies and their role in the ecosystem. Scientists involved in this field study many species of butterflies, their morphology, wing structure, color patterns and evolutionary development.
Butterflies play an important role in nature, participating in the pollination of plants and being food for other animals. They are also indicators of the state of the environment and can serve as biomarkers to assess the quality of an ecosystem.
Lepidopterology helps scientists to better understand and protect biodiversity and promotes environmental research. The study of butterflies allows us to delve deeper into the natural world and understand how all the elements of an ecosystem are interconnected and influence each other.
What are butterflies?
Butterflies are beautiful and amazing insects that belong to the class Insecta. They are part of a large group of insects that are studied by a science called entomology.
Studying butterflies is the name of the science devoted to the study of butterflies and other insects, called lepidopterology. This science studies the diversity of butterflies, their anatomy, physiology, behavior, evolution and ecology. Lepidopterists study all aspects of butterfly life, including their migration, feeding, reproduction, and interactions with other organisms in an ecosystem.
Anatomy and physiology of butterflies

Butterflies have a complex anatomy consisting of a head, thorax, and abdomen. They have a pair of wings that allow them to fly. Butterfly wings are covered with tiny scales, which give them a bright color and protect them from external influences.
The physiology of butterflies is also interesting to study. They have amazing abilities, such as a super-sensitive sense of smell that allows them to find flowers or other breeding partners. In addition, butterflies can produce chemicals that can be poisonous to predators or used to attract mates.
Evolution and ecology of butterflies
Butterflies have an ancient history, they have existed for millions of years. Studying their evolution helps us understand how life evolved on our planet. In addition, butterflies play an important role in the ecosystem. They are the pollinators of many plants, helping them to reproduce and maintain biodiversity.
The study of butterflies allows us to better understand the nature and importance of protecting the ecosystem. These beautiful insects are not only an object of beauty and admiration, but also a key link in natural processes. Therefore, the study of butterflies is of great importance for our understanding and conservation of nature.
History of the study of butterflies
The science that studies butterflies is called lepidopterology. The history of the study of butterflies began in ancient times, when people began to pay attention to these beautiful insects.
The first mention of butterflies can be found in ancient Greek mythology. Butterflies were a symbol of the soul and the embodiment of freedom. They were often mentioned in literature and art as symbols of beauty and transformation.
However, the real scientific study of butterflies did not begin until the 18th century. During this period, scientists began to collect and classify different types of butterflies. They studied their anatomy, behavior, migration and ecology.
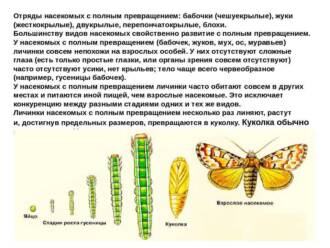
Scientists paid special attention to the process of metamorphosis in butterflies. They studied how a caterpillar emerges from an egg, which then turns into a chrysalis, and then an adult butterfly emerges from it. This was a fundamental step in understanding the life cycle of these insects.
Today, lepidopterology continues to evolve. Scientists study butterflies not only in the laboratory, but also in their natural habitat. They study their role in the ecosystem, their effect on plants and other animals.
The history of the study of butterflies testifies to our ongoing efforts to understand and appreciate the beauty and importance of these unique creatures.
The main signs of butterflies
butterflies - These are winged insects that belong to the Lepidoptera order. They are one of the most beautiful and diverse groups of insects on our planet. Butterflies are known for their bright colors and varied wing patterns, which serve to attract mates and deter predators.
They have two pairs of wings, which are usually covered with minute scales. Butterfly wings come in a variety of shapes and sizes, from small and narrow to large and wide. On the wings of butterflies, you can see a variety of patterns, colors and patterns. Some species of butterflies have transparent spots on their wings that resemble eyes and serve to intimidate predators.
butterflies undergo a complex development. They begin their lives as caterpillars, actively feeding to gain enough food for their subsequent chrysalis. In the chrysalis, the caterpillar transforms into an adult butterfly. After emerging from the chrysalis, the butterfly unfolds its wings and begins to fly in search of food and a breeding partner.
The science that studies butterflies is called liepidopterology. Liepidopterologists study the diversity of butterflies, their anatomy, behavior, ecology and evolution. They are also engaged in the classification of butterflies and the identification of new species. This science plays an important role in the conservation of biodiversity and nature conservation, as many species of butterflies are indicators of the ecological state of various regions.
Butterfly taxonomy
Taxonomy is a science that studies and classifies living organisms. It helps to establish relationships between different species and determine their place in the taxonomic hierarchy. Butterfly taxonomy uses various methods, including morphological study, genetic analysis, and behavioral characteristics.
Butterflies are winged insects that belong to the order Lepidoptera. They are characterized by beautiful wings with a variety of colors and patterns. Butterfly taxonomy helps classify them into different families, genera, and species.
The most common families of butterflies include Pestrushkovyh, Scoop, Cabbage, Pyatipyadev, Field and others. Each family contains genera, which in turn include different species. Butterfly taxonomy helps determine which family and genus each species belongs to.
Studying the taxonomy of butterflies is essential to understanding their diversity, evolution, and ecology. It allows scientists and butterfly enthusiasts to classify and identify different species, as well as study their biological features and interactions with the environment.
Butterfly Research Methods

The science that studies butterflies is called lepidopterology. To study these beautiful insects, there are many research methods that allow you to learn more about their behavior, ecology and diversity.
1. Observation and data collection
One of the main methods of researching butterflies is observation and data collection. Scientists observe butterflies in their natural habitat, studying their behavior, migration and interaction with other organisms. Butterflies are also collected for further analysis and classification.
2. Use of traps and baits

To attract and catch butterflies, scientists use various baits such as pheromones and plant extracts. Traps such as light and scent traps help collect large numbers of butterflies for research and analysis of their population, species diversity and distribution.
3. Genetic research

Modern methods of genetic analysis make it possible to study butterflies at the level of their DNA. Scientists can study genetic diversity, relationships between species and populations, and study the genes responsible for certain traits and behaviors.
4. Microscopic studies

To study the morphology and anatomy of butterflies, microscopic research methods are used. Scientists are examining the structure of the wings, eyes, antennae and digestive organs of butterflies to better understand their adaptations and evolution.
Thus, combining these methods allows lepidopterists to expand our knowledge of butterflies, their role in the ecosystem, and their impact on the environment. These studies help to preserve their diversity and protect them from threats such as habitat loss and climate change.
Butterfly spread
The science that studies butterflies is called lepidopterology. This science investigates various aspects of the life of butterflies, including their distribution. Butterflies live on almost all continents, with the exception of Antarctica, and inhabit a wide variety of ecosystems.
The distribution of butterflies is determined by their ability to migrate. Some species of butterflies are able to travel considerable distances in search of food, breeding sites, or more favorable living conditions. One famous example of butterfly migration is the monarch butterfly migration in North America.
Butterfly migration is due to their ability to fly long distances. Butterflies use various mechanisms to navigate, such as visual cues, the Earth's magnetic field, and smells. These mechanisms allow butterflies to find their way to their destination and return back.
The distribution of butterflies also depends on their interactions with other organisms. Some butterflies depend on certain plant species for their food source or oviposition site. In turn, butterflies play an important ecological role by pollinating flowers and helping to distribute pollen.
Studying the distribution of butterflies allows you to learn more about the diversity of their species, adaptation to different environmental conditions and the impact on the environment. This is important for biodiversity conservation and understanding of the ecological processes that govern our planet.
Butterfly anatomy
The study of butterfly anatomy is one of the main tasks of the science called entomology. Scientists study butterflies to understand their structure, the functions of their organs, and their adaptation to the environment.
Butterflies have a characteristic body structure consisting of a head, thorax, and abdomen. The head is usually small and contains compound eyes, antennae, and lips. Butterfly eyes are made up of many small facets, allowing them to see the world around them in many directions. The antennae serve as a sensory organ and help butterflies find food and breeding partners.
The thorax of butterflies is a powerful motor department that controls the wings. Butterflies usually have two pairs of wings that can move independently. The wings consist of a transparent integumentary plate called the pterygoid squamosal. The scales give the wings bright colors and unique patterns that serve to deceive predators and attract the attention of mates.
The abdomen of butterflies contains the organs of digestion, reproduction and respiration. They have special openings called spirals through which they receive oxygen. Butterflies also have special glands that secrete secretions to create pheromones that are used to communicate and attract the attention of mates.
Butterfly evolution
Butterflies are one of the most beautiful and amazing creatures of nature. But how did they get to their current form? The science that studies the evolution of butterflies is called lepidopterology.
Studying the evolution of butterflies allows us to understand how they evolved and adapted to changing environmental conditions over millions of years. Through this, we can better understand the mechanisms that underlie biodiversity and adaptation.
One of the main features of butterflies is their transformation from a caterpillar to a chrysalis and, finally, to an adult butterfly. This process, called metamorphosis, was the result of many years of evolution and allowed butterflies to adapt to different conditions of existence.
In the process of evolution, butterflies have acquired a variety of shapes and colors that help them survive and reproduce. Some butterflies have developed the ability to mimic, mimicking dangerous or inedible species to avoid predators. Other butterflies have bright and colorful colors that serve as signals to attract mates during breeding.
Studying the evolution of butterflies allows us not only to enjoy their beauty, but also to better understand the amazing mechanisms of nature that led to such a variety of species and forms. Lepidopterology plays an important role in the conservation of biodiversity and helps us protect these unique creatures from the threats they face in today's world.
Butterfly Life Cycle Biology

Butterflies are amazing creatures that attract attention with their colorful appearance and ease of flight. But they are also of interest to science, which studies their life cycle and behavior. This science is called lepidopterology.
The life cycle of butterflies includes several stages of development: egg, caterpillar, pupa and adult. Each stage has its own characteristics and functions.
Egg
Butterflies lay their eggs on various plants that serve as food for caterpillars. Eggs can be of different sizes and shapes, depending on the type of butterfly. They usually have a bright color and are protected by a hard shell.
Caterpillar
The egg hatches into a caterpillar, which is an active and nutritious developmental stage. Caterpillars eat plant foods and grow actively. They have a well developed jaw for chewing food.
Caterpillars can have different colors and body shapes. They may also be covered with hairs or spines that act as a defense against predators.
chrysalis
After the caterpillar reaches a certain size, it forms a chrysalis. A pupa is a resting stage of development in which internal changes occur in the body. The caterpillar turns into a chrysalis, forming a protective cocoon or scaly shell around itself.
adult
An adult, a butterfly, hatches from the pupa. She emerges from her cocoon or scaly shell and unfurls her wings. The adult has colorfully patterned wings and can fly.
Adult butterflies usually feed on the nectar of flowers and play an important role in plant pollination. They are also involved in the process of reproduction and the transfer of genetic information.
Studying the life cycle biology of butterflies allows lepidopterists to better understand their unique adaptations and interactions with their environment.
The importance of butterflies to the ecosystem
Butterflies are one of the most beautiful and amazing phenomena of wildlife. They attract attention with their bright colors and graceful flight. However, in addition to their aesthetic value, butterflies play an important role in the ecosystem.
The scientific discipline that studies butterflies is called lepidopterology. Its main goal is to study the diversity, biology, and behavior of butterflies. Lepidopterists conduct research to understand what species of butterflies exist, where they fit into food chains, and how they interact with other organisms.
Butterflies are important plant pollinators. They carry pollen from one flower to another, facilitating the pollination process and allowing plants to reproduce. Because of this, butterflies play a key role in maintaining biodiversity and preserving the integrity of the ecosystem.
In addition, butterflies serve as a food source for many other organisms. Butterfly larvae are the main food for birds, lizards, frogs and other animals. They also serve as food for other insects such as spiders and beetles. In this way, butterflies play an important role in food chains and maintaining balance in nature.
It is important to note that butterflies are indicators of the state of the environment. Changes in their abundance and diversity may indicate disturbances in the ecosystem. Therefore, the conservation of butterflies and their habitat is essential to maintain the health of the ecosystem and biodiversity.
In general, butterflies play an important role in the ecosystem, serving as pollinators, food sources, and indicators of the state of the environment. The study of butterflies allows us to deepen our knowledge of wildlife and contributes to maintaining its balance.
Butterfly Threats and Conservation

The scientific discipline that studies butterflies is called lepidopterology. These amazing creatures, which are among the most beautiful and diverse creatures on the planet, face various threats that can cause irreparable harm to them.
One of the main threats to butterflies is the loss and destruction of their natural habitats. The expansion of cities and industrial zones, deforestation and changing agricultural practices lead to a decrease in the area on which butterflies can live. This leads to a reduction in populations and even the extinction of some species.
In addition to habitat loss, butterflies also face threats from human activity. The use of pesticides in agriculture and horticulture, as well as air and water pollution, adversely affects the health and survival of these insects. As a result, some species of butterflies are becoming increasingly vulnerable and subject to extinction.
Butterfly protection is an important task carried out by scientists and environmentalists. They conduct research to better understand the nature and behavior of butterflies and develop methods to conserve their habitats. Activities are also carried out to raise public awareness of the importance of butterflies and the need to protect them. Some regions create reserves and protected areas where butterflies are provided with a safe place to live and breed.
In general, butterfly conservation is an important aspect of biodiversity conservation and ecological balance. The study and protection of these colorful insects allows for the conservation of unique species and the health of the ecosystems in which they exist.
Interesting facts about butterflies
Butterflies are amazing creatures that attract attention with their beauty and grace. But the science that studies butterflies has its own name. It is called lepidopterology. Interestingly, this word comes from the Greek words "lepis" (scale) and "pteron" (wing), which describes the peculiarity of the structure of butterflies' wings.
Unique Wings
One of the most fascinating features of butterflies is their wings. They are covered with fine scales that create a spectacular and varied color coating. Each scale has its own color and shape, which makes butterfly wings unique and unrepeatable.
In addition, butterfly wings have the ability to reflect and refract light, creating the effect of overflow and sparkle. This allows butterflies to attract the attention of partners, and also serves as a means of deception for enemies and predators.
Migration and metamorphosis
Butterflies are known for their long distance migrations. Some species may travel hundreds or thousands of kilometers to find suitable breeding grounds or better living conditions. This is an amazing ability that makes butterflies real travelers.
However, the most amazing thing about the life cycle of butterflies is their metamorphosis. They go through several stages of development, starting from an egg, then a larva, a pupa, and finally turning into beautiful and winged butterflies. This process is one of the most amazing phenomena of nature and symbolizes change and transformation.
All these interesting facts about butterflies make them amazing creatures worthy of attention and study. Lepidopterology is a science that helps us understand and appreciate the beauty and wonder of these delicate creatures.