Desert regions, where high temperatures and lack of moisture are common, present special challenges for wildlife. However, despite such inhospitable conditions, the butterflies are surprisingly able to cope with the heat and dryness in the deserts. Their adaptations allow them to survive and thrive in such extreme environments.
One of the main strategies butterflies use to deal with heat is heat regulation. Some species of butterflies have special structures on their wings that allow them to reflect solar radiation and reduce heat. This helps the butterflies keep their body temperature at an optimal level.
Most butterflies also have the ability to retain moisture in their bodies. They have special mechanisms that allow them to minimize moisture loss through evaporation. For example, many species of butterflies have special scales on their wings that help them retain moisture and prevent it from evaporating.
In addition, butterflies can adapt to dry desert conditions by changing their feeding habits and choosing plants that contain more moisture. They may also actively search for water by visiting places with moist soil or drinking springs to maintain their water balance.
Overall, butterflies have amazing adaptations that allow them to survive in desert environments. They are able to regulate heat and retain moisture, and change their feeding habits to adapt to harsh environments. These little creatures show an amazing ability to adapt to the most extreme conditions and continue to thrive in them.
How butterflies survive in deserts
Butterflies are incredible creatures that have adapted to life in extreme desert conditions. They have developed a number of strategies that allow them to survive in hot and dry conditions.
thermoregulation
One such strategy is thermoregulation. Butterflies regulate their temperature to avoid overheating. They choose certain places to rest where the temperature is cooler, such as under rocks or in the shade of plants. Butterflies also know how to spread their wings to create air currents and cool their bodies.
Special adaptations
Butterflies that live in deserts have special adaptations that allow them to retain moisture in their bodies. For example, some species of butterflies have skin with a protective layer of wax that prevents moisture from evaporating. In addition, many desert butterflies are capable of migrating long distances to find more favorable conditions.
Food and water supply
Butterflies in deserts find food and water using their senses. They have sensitive antennae that help them locate food and water sources. Some types of butterflies feed on the nectar of flowers, which provide them not only with energy, but also with moisture. In addition, some butterflies are able to use the water contained in plants or on the surface of the soil.
Thus, butterflies in deserts survive due to their unique adaptations, the ability to thermoregulate and find food and water in extreme conditions. These small creatures not only surprise with their beauty, but are also real survivalists in the difficult conditions of the desert.
Moisture Conservation Mechanisms
Butterflies that live in deserts have developed various mechanisms that allow them to efficiently retain moisture and survive in extreme conditions of dryness and heat.
Skin and integumentary wings
One of the mechanisms for maintaining moisture in butterflies is the special structure and composition of their skin and integumentary wings. They have a coating made up of wax or oil that helps keep moisture inside the butterfly's body. This coating prevents evaporation of moisture and protects against overheating in the sun.
Physiological adaptations
Another mechanism for maintaining moisture is the physiological adaptations of butterflies. They are able to regulate their activity depending on environmental conditions. During the hottest part of the day, they spend most of their time at rest to reduce moisture loss through evaporation. They can also reduce the activity of their organs and slow down their metabolism to conserve moisture.
food preferences

Butterflies that live in deserts choose food rich in moisture. They prefer flowers, fruits, and nectar that contain large amounts of water. This helps them get the moisture they need from their food and reduces their need to find other sources of water.
Efficient use of moisture
Butterflies can also make efficient use of limited moisture resources. They can collect moisture through microscopic hairs on their bodies and wings, and through their open respiratory organs. Thanks to these mechanisms, they are able to use every drop of moisture as efficiently as possible, minimizing its loss and ensuring their survival in extreme desert conditions.
Thick scales on wings
Butterflies living in desert conditions have thick scales on their wings, which perform an important protective function. These scales help the butterfly retain moisture in its body and prevent it from evaporating in hot and dry conditions.
The thick scales on the butterfly's wings create a microclimate that allows them to survive in the extreme desert conditions. These scales form a dense coating that keeps moisture inside the wings and does not allow it to evaporate quickly.
In addition, the thick scales on butterfly wings also act as protection against dust and sand particles that can damage delicate wings. They create a barrier that prevents the penetration of dust and sand into the wings and maintains their integrity.
Thus, the thick scales on the wings of butterflies play an important role in the adaptation of these insects to hot and dry desert conditions. They help butterflies retain moisture in their body and prevent it from evaporating, and also protect their wings from damage.
Special patterns and colors on the wings
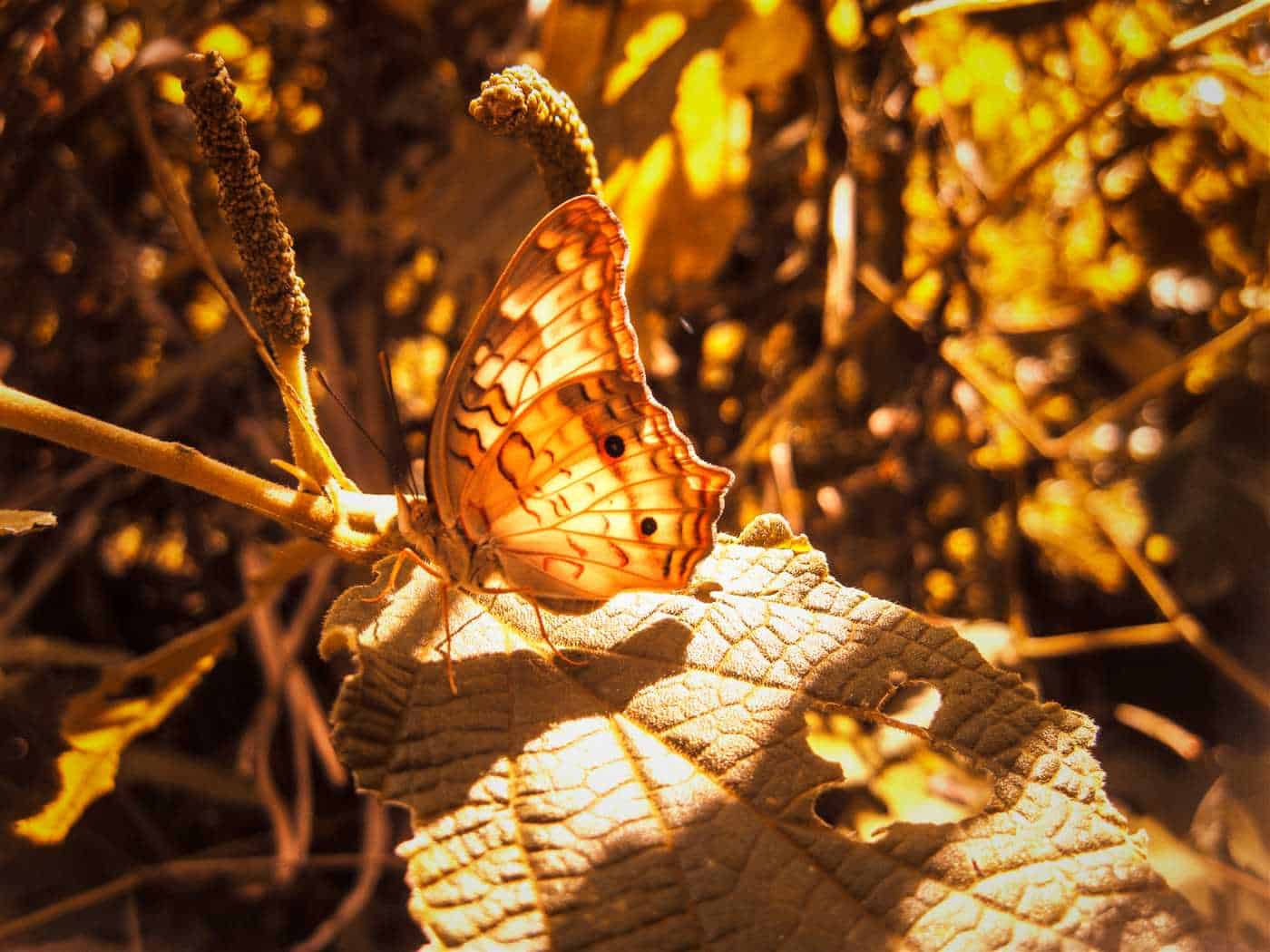

Butterflies that live in desert environments develop special patterns and colors on their wings that help them survive in harsh environments.
One of these patterns is a camouflage pattern, which allows the butterfly to blend in with the environment and be invisible to predators. The wings of desert butterflies are often covered in sandy, brown, and gray hues that pair well with sand dunes and dry vegetation.
In addition, bright and contrasting colors such as orange, red and yellow can be seen on the wings of desert butterflies. These bright colors serve as a warning to predators that the butterfly is poisonous or has an unpleasant taste. Thus, the colors on the wings of butterflies help them avoid attacks and save their lives.
The special patterns and colors on the wings of desert butterflies are the result of natural selection and adaptation to life in extreme conditions. These patterns and colors help butterflies survive and procreate in harsh desert environments.
Adaptation to the nocturnal lifestyle

Butterflies that live in deserts have peculiar mechanisms for adapting to a nocturnal lifestyle. In conditions of heat and dryness, nighttime becomes the most favorable for the activity of these insects.
Structural features
In order to survive at night, butterflies develop a number of adaptive mechanisms. For example, their wings are covered with tiny scales that help them retain moisture and protect them from overheating. In addition, some species of butterflies have special organs at the ends of their legs that allow them to suck on flower nectar and other nutrients.
Behavioral features
Butterflies that live in deserts are activated only at night, when the air temperature becomes more comfortable. During this period, they go out in search of food and breeding partners. During the day, they are hidden in shelters to avoid high temperatures and reduce moisture loss. Nighttime also helps them avoid predators that are active during the day.
Adaptation to dry conditions
Butterflies in deserts also have special mechanisms to conserve moisture. For example, some species may reduce their metabolic activity and enter a dormant state to reduce their need for water. They may also take shelter in the shade to avoid direct sunlight, which quickly dries out their bodies.
Conclusion
Butterflies living in deserts have successfully adapted to a nocturnal lifestyle in order to survive in conditions of heat and dryness. Their structural and behavioral features allow them to efficiently use resources and avoid adverse conditions. These insects are an excellent example of adaptation to extreme environmental conditions.
Behavior during a drought
During periods of drought, desert-dwelling butterflies exhibit a range of adaptive strategies to survive in the face of limited water resources. One such strategy is to reduce activity and movement. Butterflies reduce their activity and spend most of their time at rest to conserve energy and reduce their need for water.
Another strategy that butterflies use during drought is to seek shelter. They may hide under rocks, in caves, or even in empty nests of other animals. Thus, they protect themselves from direct sunlight and reduce the evaporation of moisture from the surface of their body.
Besides, some species of butterflies may change their feeding behavior during a period of drought. They may prefer plants that contain more moisture, or even switch to plant sap or foods containing more moisture to meet their water needs. This allows them to survive and maintain sufficient levels of hydration in dry conditions.
Some butterflies may also change their breeding behavior during periods of drought. They may lay fewer eggs or even stop breeding until better conditions. This allows them to save energy and resources for more surviving offspring in the future.
Using plants as a source of nutrition
In desert conditions, where heat and dryness are constant factors, butterflies are forced to look for food sources that would ensure their survival. One such source is plants that are able to adapt to extreme conditions and provide nutrients to insects.
Plants growing in desert areas have special mechanisms that allow them to survive in conditions of limited access to water and nutrients. Some of them have deep roots that can reach water in the depths of the soil, while others have the ability to accumulate and retain moisture in their stems and leaves.
Butterflies, in turn, find plants that can provide them with the necessary nutrients. They can use both flowers, rich in nectar, and leaves of some plants, containing the necessary proteins and carbohydrates. Some species of butterflies can also get food from the fruits and seeds of plants.
It is important to note that butterflies play an important role in plant pollination by carrying pollen from one flower to another. Thus, they contribute to the reproduction and conservation of plant species in desert conditions.
The use of plants as a food source is an integral part of the life cycle of butterflies and contributes to their survival in extreme desert conditions.
The unique physiology of butterflies
Butterflies have a unique physiology that allows them to survive extreme conditions such as the heat and dryness of deserts. One of the adaptations of butterflies to hot climates is the ability to regulate their body temperature.
Butterflies can change their temperature by moving their wings and body muscles. They can spread their wings to increase the heat-removing surface, or bend them to shorten that surface and retain heat. They can also use the musculature of the body to generate heat through muscle contraction.
In addition, butterflies have special mechanisms that allow them to cope with the lack of moisture in desert conditions. One such mechanism is the ability of butterflies to feed on nectar, which contains water. They may also drink water from puddles and other sources of moisture.
To retain moisture, butterflies have wing coverings that help them not lose water through evaporation. In addition, some species of butterflies can cocoon and hibernate to minimize moisture loss.
In general, the unique physiology of butterflies allows them to adapt to and survive in hot and dry desert conditions. These adaptations include the ability to regulate body temperature and retain moisture, which allows butterflies to successfully adapt to extreme climatic conditions.
Migration in search of moisture
Butterflies that live in deserts face limited access to water and high temperatures, making it difficult for them to survive. However, they develop amazing abilities in order to adapt to such conditions.
One of these ways is migration in search of moisture. Butterflies can travel great distances to find water sources that can be scattered across desert areas. They rely on smell and visual cues to find these sources.
Butterflies can also use migration to avoid extreme temperatures. They may move to cooler areas where moisture is more available and temperatures are more tolerable to them.
Migration in search of moisture is an important strategy for desert-dwelling butterflies. It allows them to survive in conditions of limited access to water and extreme temperatures. Due to their adaptive abilities, butterflies can effectively use the resources available in the desert and maintain their populations for a long time.
sunburn protection
Pigmentation
Desert butterflies have developed a special defense against sunburn – wing pigmentation. Their wings are covered with special pigments that absorb and scatter sunlight. This allows them to reduce the effects of ultraviolet radiation and prevent wing burns.
reflexes

In addition, butterflies can use reflexes to protect themselves from sunburn. They can fold their wings in such a way as to reduce the surface area exposed to solar radiation. Also, butterflies can deviate from direct sunlight, moving in the shade or among vegetation.
Adaptation

Butterflies, adapted to hot and dry desert climates, have special physiological adaptations that help them cope with heat and dryness. For example, they may reduce activity during periods of heat to conserve moisture and avoid overheating. They can also perform special wing movements to create airflow and cool themselves.
In general, desert-dwelling butterflies have developed various strategies to protect themselves from sunburn and to adapt to extreme conditions of dryness and heat. Their defense and adaptation mechanisms allow them to survive and thrive in such adverse conditions.
Interaction with other animals in the desert

Animals living in deserts are forced to find ways to interact with each other in order to survive in difficult conditions. This interaction can be both competitive and mutually beneficial.
Competition for resources
Because food resources are limited in the desert, animals are forced to compete for access to them. For example, rodents may compete for oases of drinking water, and birds of prey for prey. Competition for resources can be fierce, leading to the exclusion of weaker individuals.
Symbiosis and mutually beneficial coexistence
In deserts, you can also find examples of symbiosis, when different types of animals interact with each other and receive mutual benefit. For example, some birds can help camels clean their fur from sand, receiving food in return, and some insects pollinate flowers of plants, getting food from nectar.
Protection from predators
Animals in the desert develop various adaptive strategies to protect themselves from predators. For example, some species of lizards can change their color to blend in with their surroundings and become invisible. Also, some species of desert animals have special organs or behaviors that allow them to scare away or deceive predators.