Butterflies are amazing creatures that have fantastic beauty and unique mechanisms of breathing and movement. They belong to the class of insects and are among the most beautiful representatives of this group. Butterflies are able to fly long distances, perform complex maneuvers and attract attention with their unusual coloring.
The breathing mechanisms of butterflies are an amazing combination of physiological processes. They breathe through three pairs of holes called stigmas, which are located on the sides of their bodies. Air passes through these holes and enters the tracheae, thin tubes that penetrate all the butterfly’s organs. In this way, the butterfly receives the necessary amount of oxygen for its vital functions.
The movement of butterflies is carried out with the help of wings, which they spread and compress during the flight. Butterfly wings have a special structure that allows them to move and maneuver flexibly in the air. In addition, butterflies are able to change the angle of their wings, which allows them to fly at different speeds and perform various maneuvers. Butterflies also use mechanisms that allow them to land on vertical surfaces, such as walls or tree trunks, thanks to special legs on their legs.
The structure of the wings and their role in movement
Butterfly wings are graceful and complex organs that perform not only the function of flight, but also play an important role in the movement of these insects. They consist of two pairs, front and back, which are connected to each other and to the body of the butterfly.
The forewings of butterflies are usually larger and wider than the hindwings. They have a complex structure consisting of corollas, veins and microscopic scales. Each scale contains a pigment that determines the color of the wing. The wings are densely covered with such scales, which creates a mosaic effect and makes them strong and flexible.
Butterfly hindwings are usually smaller and serve for finer control of movement. They also have a complex structure, but are often less brightly colored than the forewings. The rear wings can be especially important for quick maneuvering and changing direction in flight.
Butterfly wings play a key role in their movement. They create the force needed to lift and hold the butterfly in the air. When a butterfly spreads its wings, they create a whirlwind around them, which helps create lift. Butterflies can also change the shape and angle of their wings to control the direction and speed of their flight.
Butterfly wings also serve to communicate and protect. They may use bright colors and patterns on their wings to attract the attention of mates or deter predators. They may also use their wings to create sound signals by shaking them or tapping surfaces to attract attention or warn of possible danger.
Features of the respiratory system of butterflies
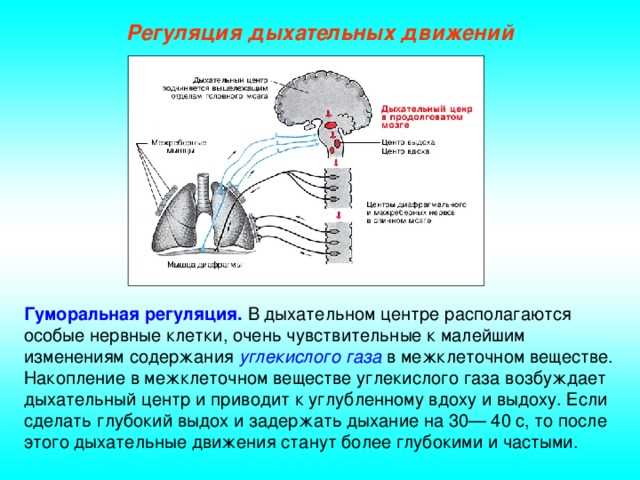
The respiratory system of butterflies is distinguished by its features and allows them to efficiently receive oxygen from the environment. The main respiratory organs of butterflies are the tracheae, which are thin tubes that run through the entire body of the insect.
Butterfly tracheae have numerous processes - tracheae, which penetrate into all organs and tissues of the insect, providing oxygen delivery. This structure of the respiratory system allows butterflies to carry out efficient breathing even with a small size and complex structure of their body.
Moreover, the tracheae of butterflies are connected to a system of air sacs that serve to store and deliver oxygen. In the process of breathing, the butterfly expands and contracts the air sacs with the help of muscles, ensuring the circulation of air and oxygen throughout the body.
Thus, the respiratory system of butterflies is complex and adapted to the characteristics of their life activity. It allows butterflies to breathe efficiently and ensure their livelihoods in various environmental conditions.
Respiratory mechanisms in different species of butterflies
Respiration is an essential process for all living organisms, including butterflies. Different types of butterflies have different breathing mechanisms that ensure the supply of oxygen to their body and the removal of carbon dioxide.
Spiral breathing system
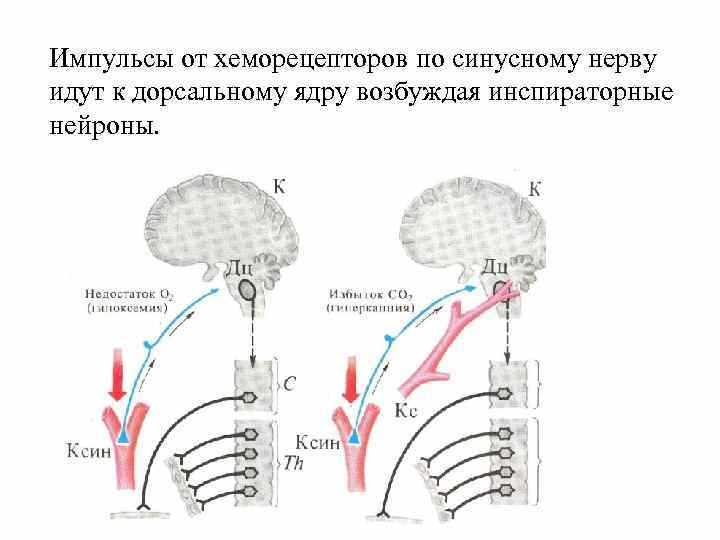
One of the most common respiratory mechanisms in butterflies is the spiral respiratory system. It is a complex system of tracheae and tracheoles that permeate all the organs of a butterfly. When a butterfly inhales air, oxygen passes through the trachea and reaches the cells and tissues of its body. The carbon dioxide is then exhaled through the same tracheae and tracheoles.
Breathing through openings on the side walls of the body
In some species of butterflies, the respiratory mechanism is carried out through holes on the side walls of their bodies. These openings, called aspirations, are found on the abdomen and thorax of the butterfly. Air enters the body through suction and is distributed through the tracheae and tracheoles. Thus, oxygen enters the tissues and cells, and carbon dioxide is excreted.
Breathing while flying
Flight is an important activity for butterflies and during flight they use special breathing mechanisms. The butterfly opens special valves called suction valves, which are located on the side walls of the body. These valves allow the butterfly to get enough oxygen while flying, as flying requires a lot of energy.
In general, the respiratory mechanisms of different species of butterflies may differ, but they all ensure the supply of oxygen to the body and the removal of carbon dioxide, which is necessary to maintain their vital activity.
The role of the malarial cycle in the respiration of butterflies

The malarial cycle plays an important role in the respiration of butterflies, providing them with the necessary amount of oxygen to sustain life. The cycle consists of several stages, starting with inhalation and ending with exhalation.
The first stage of the malaria cycle is inhalation. The butterfly expands its coils, allowing air to enter its tracheae. The tracheae are a system of tubes that run throughout the butterfly's body and deliver oxygen to its cells.
The second stage is the exchange of gases. When the air reaches the trachea, oxygen passes into the hemolymph, the fluid that fills the butterfly's body. This fluid contains special proteins called hemoglobin, which bind oxygen and transport it to the body's cells.
The third stage is exhalation. After oxygen has been delivered to the cells, carbon dioxide, which is a product of metabolism, returns back to the hemolymph. This gas is then exhaled through openings called stigmas, which are located on the side of the butterfly's body.
The malarial cycle is important for butterflies, as it provides a constant supply of oxygen and the removal of carbon dioxide from their body. Without this cycle, butterflies would not be able to maintain their vital activity and perform all the necessary functions.
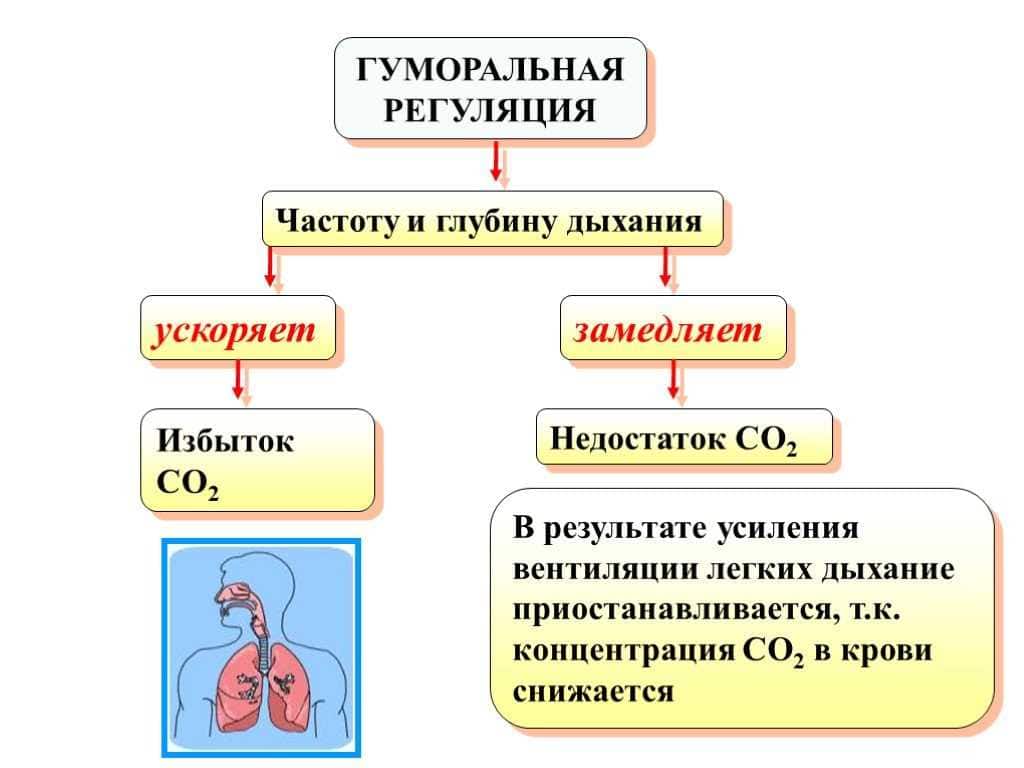
The effect of temperature on the respiration of butterflies

Ambient temperature has a significant effect on the respiratory system of butterflies. As the temperature rises, the respiration of butterflies increases, and as the temperature decreases, it slows down.
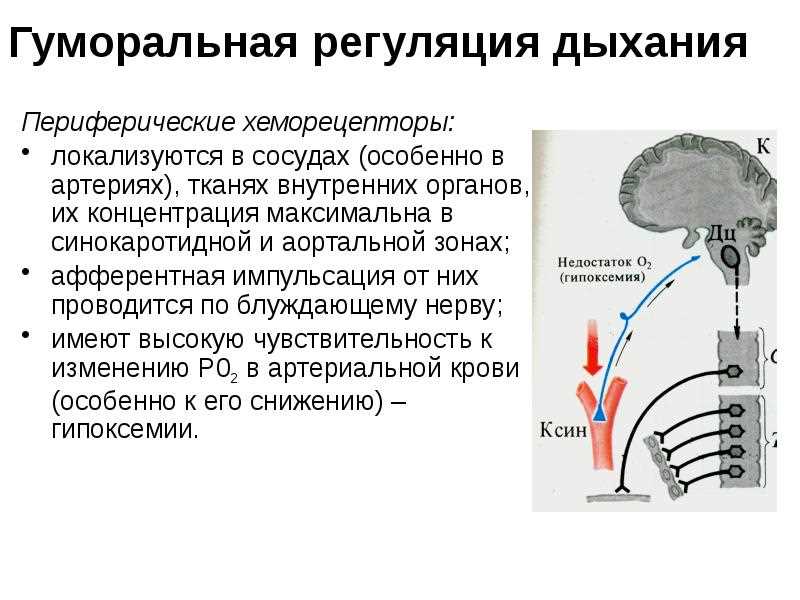
Butterfly breathing mechanism
Butterflies have a special respiratory organ - the trachea. Tracheas are located throughout the body of the butterfly and are thin tubes that penetrate all organs and tissues. Through the trachea, gases are exchanged - oxygen and carbon dioxide.
The influence of temperature on the activity of the respiratory system
When the temperature rises, butterflies activate their breathing. This is due to the fact that with an increase in temperature, the metabolic activity of the body increases, which requires more oxygen. Butterflies begin to breathe faster and deeper to meet the body's need for oxygen.
When the temperature drops, the respiration of butterflies slows down. This is because at low temperatures, the metabolic activity of the body decreases, and butterflies require less oxygen. They begin to breathe more slowly and less intensely.
Adaptation to temperature change
Butterflies have a high adaptive ability to change the temperature environment. They can regulate their temperature using various strategies such as solar thermoregulation and overheating or cooling protection mechanisms. This allows them to maintain the optimum temperature for the normal functioning of the respiratory system and the exchange of gases.
Butterfly locomotion
Butterflies use a variety of locomotion techniques that allow them to maneuver in the air and move across surfaces. Flight is one of the main ways butterflies move.
Butterflies have a light and flexible body, which allows them to move smoothly and smoothly in the air. They use their wings to generate lift and change direction. Butterflies can maneuver and turn to different angles using their wings.
In addition to flying, butterflies can also move on the surface using their legs. They have six legs to help them navigate plants or other surfaces. Thanks to the special attachments on the legs, the butterflies can be easily attached to different surfaces.
Another interesting way of moving in some species of butterflies is gliding. They can use their light weight and large wings to glide over long distances without actively moving their wings. This method of movement allows them to cover large distances and cross obstacles such as rivers and forest clearings.
In general, the way butterflies move varies depending on their species and environment. They have unique adaptations that allow them to move efficiently and survive in their habitats.
Features of the aircraft in butterflies
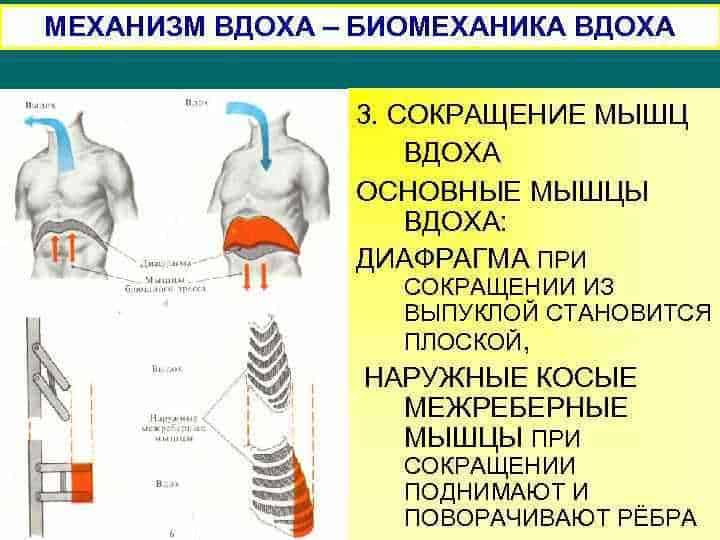
The flying machine of butterflies is a set of wings that allow them to make light and graceful flights. Butterfly wings have a number of features that provide them with unique abilities in the air.
1. Butterfly wings have a complex structure. Each wing is made up of many narrow plates called veins that give the wing strength and stability. The veins form a network that keeps the wing in position during flight.
2. Butterfly wings are covered with tiny scales. The scales perform a number of functions: they protect the wings from damage, help the butterfly float in the air, and enable it to produce colored reflections. Butterfly scales can be of various shapes and colors, which gives them beauty and attractiveness.
3. Butterfly wings can move independently. In butterflies, the front and hind wings are connected by special joints, allowing them to move independently of each other. This allows the butterfly to change direction, turn and maneuver in the air.
4. Butterfly wings are capable of generating lifting force. Butterfly wings have a special shape that allows them to generate lift as they move through the air. This allows butterflies to fly without visible effort and to be maintained in the air for a long time.
5. Butterfly wings can change their shape. Due to the special structure of veins and scales, butterfly wings can change their shape depending on the needs of flight. This allows them to adapt to different conditions and provides flexibility and maneuverability in the air.
Thus, the flying machine of butterflies is a complex and unique structure that allows them to perform light and graceful flights, and also provides them with protection, beauty and maneuverability in the air.
Aerodynamic principles of butterfly flight

The flight of butterflies is based on certain aerodynamic principles that allow them to maneuver and maintain balance in the air. The basic principles of the flight of butterflies are associated with the shape and structure of their wings, as well as with the features of their movement.
Butterfly wings have a complex structure, consisting of strong and flexible veins covered with thin membranes. This structure allows butterfly wings to generate lift as they move through the air. Lift is generated by vortex flows around the wings, which create a pressure difference between the top and bottom of the wing. This allows the butterflies to maintain their flight and maneuver in the air.
The movement of the butterflies' wings also plays an important role in the aerodynamics of their flight. Butterflies can change the angle and frequency of their wings, which allows them to change their flight direction and speed. They can also maneuver using asymmetrical wing movement - one wing can move up and the other down. This helps them turn and change direction without much effort.
An important aspect of butterfly flight aerodynamics is also the size and shape of their wings. Different species of butterflies have wings of different shapes, from wide and rounded to narrow and pointed. The shape of the wings affects the aerodynamic characteristics of flight, such as lift and air resistance. Butterflies with wide wings can fly slowly and maneuver, while butterflies with narrow and pointed wings can develop high speeds.
Thus, the aerodynamic principles of the flight of butterflies are based on the shape and structure of their wings, as well as on the features of their movement. These principles allow butterflies to maneuver, maintain balance, and fly at different speeds and directions.
Butterfly flight speed and agility
Butterflies, being one of the most beautiful creatures on the planet, also have impressive speed and maneuverability in flight. Their small size and lightweight wing construction allow them to achieve high speeds and perform complex maneuvers in the air.
The main movement of butterflies is carried out due to the powerful and rhythmic flapping of the wings. Butterfly wings are made up of thin plates, which are interconnected by joints. This allows them to move freely and change the shape of the wing during flight.
Thanks to this wing design, butterflies can change the angle of attack and direction of flight depending on the situation. They are able to quickly accelerate, slow down and turn in the air, which makes them very maneuverable and allows them to avoid danger.
Butterflies can also use what is called "gliding flight," where they close their wings and allow themselves to float on air currents. This helps them save energy and cover long distances without much effort.
Thus, the speed and maneuverability of the flight of butterflies provide them not only with the ability to move quickly, but also to survive in their natural environment.
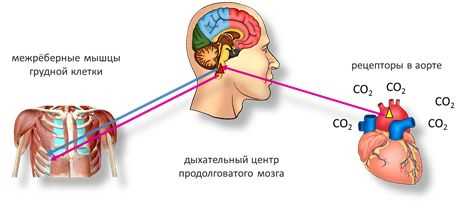
The relationship between respiration and movement in butterflies
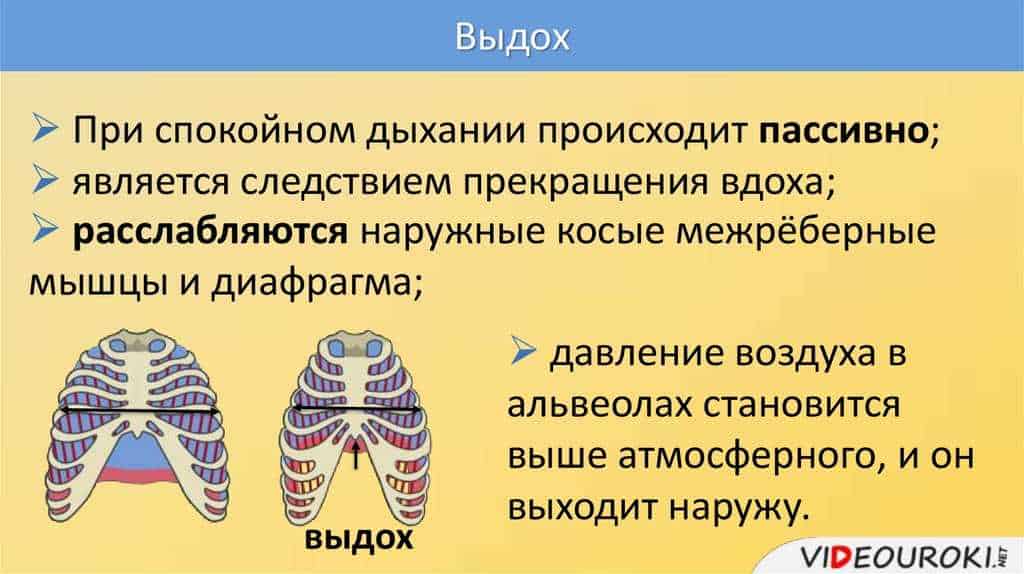
Breathing and movement in butterflies are closely related and ensure their vital activity. The respiratory system of butterflies is a network of tubular canals called tracheae that permeate all organs and tissues. It allows butterflies to take oxygen from the air and give off carbon dioxide needed to burn food and generate energy.
Butterflies move by contracting and relaxing the muscles that move their wings. To maintain activity and energy consumption during flight, butterflies use a large amount of oxygen. Therefore, respiration plays a key role in providing movement in these insects.
When a butterfly flies, it moves its wings in the air, which requires a lot of energy. During flight, the wings of a butterfly make rapid and rhythmic movements to create the lift needed to maintain flight. At the same time, the respiratory system ensures that enough oxygen is supplied to the muscles so that they can work efficiently and support the movement of the wings.
Thus, breathing and movement in butterflies are interconnected and provide the energy needs of these insects. Thanks to their unique respiratory system and active flight, butterflies are one of nature's most graceful and elegant creatures.