
The world is inhabited by different species of butterflies, and each of them has its own unique abilities for survival. One of the most interesting and effective defense mechanisms that some species of butterflies have is mimicry. Mimicry is the ability of an animal to imitate another species or object in order to confuse its predators and avoid danger.
Butterflies use mimicry to protect themselves from predators such as birds and insectivores. They can imitate dangerous or nasty insects, such as bees or wasps. But there is another kind of mimicry. Butterflies can mimic the shape and color of leaves or flowers to blend in with their surroundings and go unnoticed.
One of the most famous examples of mimicry in butterflies is the mimicry of the species "caterpillars". These butterflies have the appearance and color of caterpillars of certain insect species that are poisonous or have an unpleasant taste. Thus, predatory birds and animals that try to eat the butterflies are disappointed and do not try to attack them anymore.
Mimicry is a unique adaptation that helps butterflies survive in a harsh world where predators are constantly lurking. Thanks to mimicry, butterflies can avoid danger and continue to exist. Their deceptive copies allow them to easily fit into the environment and remain unnoticed by predators. This is one of the most fascinating and incomprehensible phenomena of nature.
Butterflies: deceptive copies and mimicry
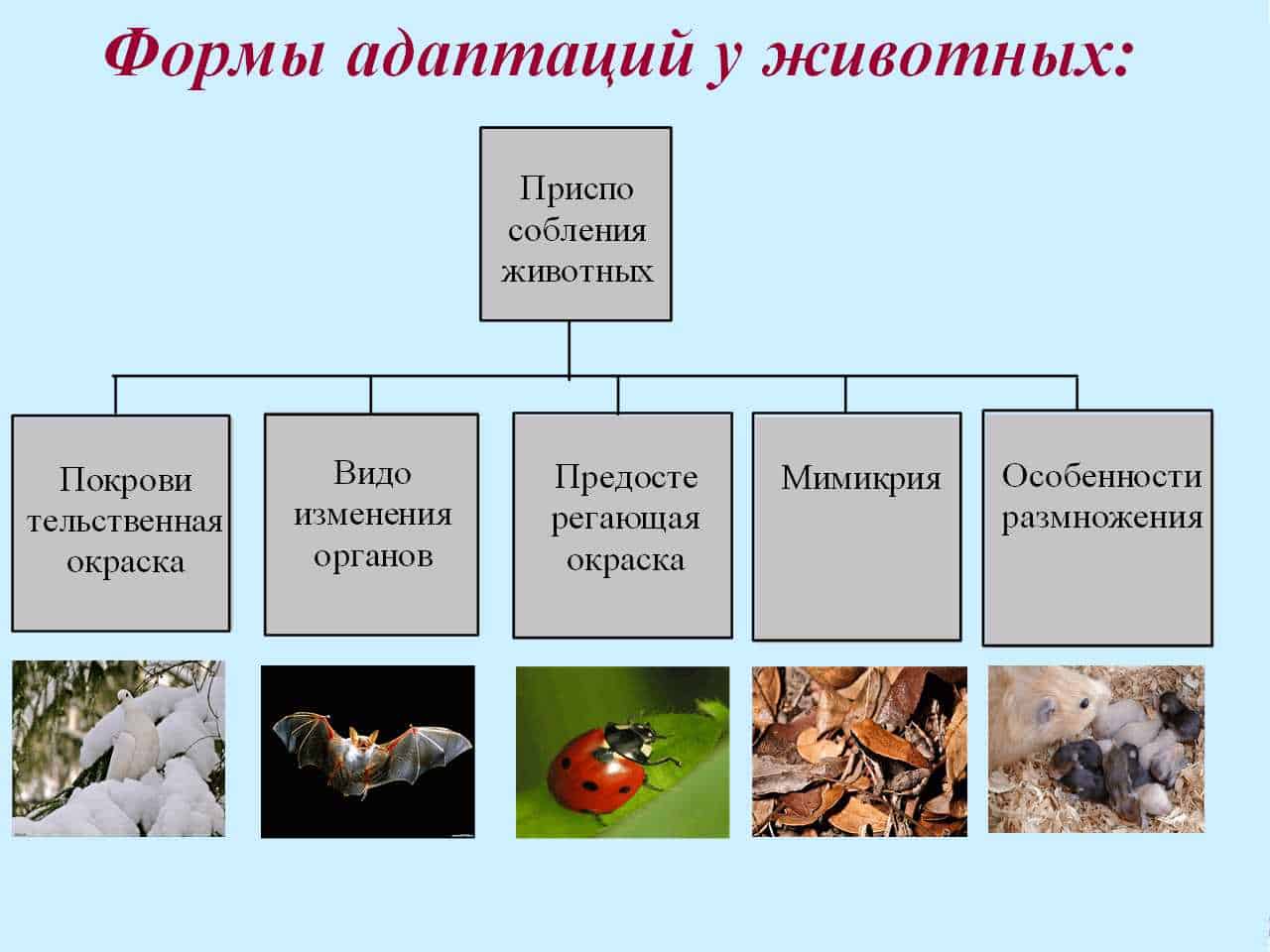
Butterflies are amazing creatures of nature that have a variety of ways of deception and mimicry. They use these techniques to survive in a harsh world where they are constantly in danger from predators.
Mimicry — one of the main methods of deception used by butterflies. They are able to imitate the appearance of other insects or even objects in the environment. For example, some butterflies can look like leaves, branches or even birds. Such mimicry allows them to hide from enemies and remain unnoticed.
Deceptive copies — Another method that butterflies use. They can imitate the appearance and behavior of other butterfly species that are dangerous to predators. For example, some harmless butterflies can imitate the bright colors and behavior of poisonous butterflies to scare off predators.
Mimicry and deceptive copies allow butterflies to effectively defend themselves against predators and increase their chances of survival. They create the illusion of danger or trouble, which deters predators and keeps the butterfly safe. These techniques also help butterflies attract breeding partners and ensure the continuation of their species.
The study of mimicry and deceptive copies in butterflies allows us to better understand their amazing adaptive capabilities and the influence of the environment on the evolution of species. This is an interesting and important area of science that helps us expand our knowledge of the animal world and nature in general.
How mimicry helps butterflies survive
Mimicry is an amazing phenomenon that helps butterflies survive in the harsh world of nature. They take the form of other objects or creatures to confuse their enemies and increase their chances of survival.
One of the most interesting examples of mimicry in butterflies is leaf mimicry. Some types of butterflies have wings that look like tree leaves. They are green in color and have veins and spots on the wings that are very similar to the leaf structure. Thanks to this mimicry, butterflies can easily blend into the surrounding vegetation and avoid danger.
Another example of mimicry in butterflies is bird mimicry. Some species of butterflies have wings that look like bird wings. They have bright colors that resemble feathers, and even individual spots that look like bird eyes. This mimicry allows butterflies to scare away predators, since many animals are afraid of birds and avoid them.
Mimicry may also be useful in protecting butterflies from predators. Some species of butterflies have bright colors and spots that serve as a signal to predators that they are poisonous or dangerous. This protects the butterflies from attack and allows them to move freely and search for food without fear.
Mimicry is one of the most amazing adaptations that helps butterflies survive in the harsh world of nature. It allows them to hide from enemies, scare off predators, and ensure safety for themselves and their offspring.
Diversity of mimicry in butterflies

Butterflies are not only beautiful creatures, but also masters of mimicry. They develop a variety of strategies to survive in the harsh natural world. Mimicry is the ability of butterflies to pretend to be other objects or living creatures to deceive predators and escape unnoticed.
Disguise — one of the most common mimicry strategies in butterflies. They can imitate their surroundings to be undetectable to their enemies. Some butterflies have wings with color patterns and designs that resemble leaves, tree bark, or even rotting fruit. This allows them to disappear into the natural environment and protect themselves from predators.
Mimicry of harmful species — This is another interesting mimicry strategy in butterflies. They can imitate harmful or poisonous species to scare off predators. For example, some butterflies have bright colors and patterns that signal their poisonousness. Predators, seeing such a butterfly, may feel disgusted or afraid to attack it, as they associate it with danger.
Mimicry of other animals — This is another amazing way of mimicry in butterflies. They can imitate other animals to confuse predators and escape. For example, some species of butterflies have wings that resemble the eyes of birds of prey or lizards. This allows them to distract the predator and escape unnoticed.
Mimicry among their own kind — This is another interesting mimicry strategy in butterflies. They can imitate other butterflies of their own species to confuse predators and escape unnoticed. Some species of butterflies have wings with unique patterns that help them blend in with other butterflies and make it difficult for predators to detect their numbers.
The variety of mimicry in butterflies is striking in its capabilities and beauty. They surprise with their ability to pretend to be other objects or living beings in order to deceive predators and survive in the harsh natural world.
Mimicry: defense or attack?

Mimicry is a natural phenomenon used by many species of animals, including butterflies, to deceive and protect themselves. Some species of butterflies have the ability to mimic, that is, imitate the appearance of other dangerous species to scare off predators and avoid attack.
Mimicry can be used as a defense mechanism to allow butterflies to survive in harsh environments. They can mimic bright and venomous species to scare off predators and keep themselves alive. For example, some butterflies can mimic the coloration and pattern of dangerous species such as bees or wasps to scare away birds and other predators that eat them.
However, mimicry can also be used offensively. Some species of butterflies may imitate species that are themselves predators in order to attract prey. For example, the swordsman butterfly imitates an ant in order to approach its prey undetected and attack it.
Mimicry can be a very effective survival strategy for butterflies, allowing them to avoid predators or successfully hunt their prey. This is a prime example of how nature can use various mechanisms to ensure the survival of species in a harsh world.
The most famous types of mimicry
Mimicry is an amazing phenomenon that occurs in various types of butterflies. They are able to imitate other animals or objects in order to deceive predators and get away from them unnoticed. There are several types of mimicry that are the most famous and impressive.
1. Müllerian imitation

This type of mimicry is named after the German naturalist Friedrich Müller. It lies in the fact that several species of butterflies imitate the appearance and behavior of other species in order to protect themselves from predators. For example, some butterflies may mimic dangerous or poisonous species to scare off predators and stay safe.
2. Batesian imitation

This type of mimicry is named after the English naturalist Henry Batesius. It manifests itself in the fact that several harmless species of butterflies mimic the appearance and behavior of dangerous or poisonous species. This allows them to scare off predators that have learned to avoid such species due to their danger.
3. Cryptic mimicry
This type of mimicry consists in the fact that butterflies imitate the environment in order to be indistinguishable for predators. Some types of butterflies have colors and patterns that blend in with grass, leaves, or tree bark. This allows them to completely hide and go unnoticed in the environment.
4. Müllerian mimicry

This type of mimicry is named after the German naturalist Friedrich Müller. It is manifested in the fact that several species of butterflies mimic the appearance and behavior of other species in order to protect themselves from predators. For example, some butterflies may mimic dangerous or poisonous species to scare off predators and stay safe.
These are just some of the best known types of mimicry in butterflies. They show the amazing adaptation of these creatures to the environment and testify to their ability to survive in a harsh world.
How butterflies imitate predators

Butterflies, in order to survive in a harsh world, resort to various strategies, one of which is mimicry or imitation of predators. They take on an appearance that looks like dangerous animals to predators in order to confuse them and protect themselves.
Some butterflies imitate predatory insects such as wasps or bees. They are brightly colored and have wing stripes that are very similar to the colors and stripes of wasps or bees. This deception allows them to avoid being attacked by predators who are afraid of being stung or bitten.
Other butterflies may mimic dangerous animals such as birds or snakes. They have wings that mimic the shape and color of the wings of birds or snakes. This type of mimicry creates the appearance of danger in butterflies and scares away predators.
Another way to imitate predators is the mimicry of taste habits. Some butterflies can mimic the smell or taste of poisonous plants to deter predators. They may have bright spots or stripes on their wings that signal their poisonousness.
Thus, butterflies use mimicry to protect themselves from predators. They imitate the appearance of dangerous animals or imitate their eating habits. This allows them to survive in a harsh world and continue to breed while maintaining their species.
Mimicry butterflies and their owners

Mimicry butterflies are species of butterflies that have the ability to mimic the appearance of other organisms. They assume the form of their masters in order to survive in a harsh world where predators are always ready to attack.
Mimicry butterflies have their own special hosts - these are the plants on which they live and reproduce. They have evolved to match the color and shape of their wings to match the appearance of leaves, flowers, or other plant parts. Thus, mimicry butterflies can safely be on their hosts without arousing suspicion among predators.
One example of mimicry butterflies and their hosts are monarch butterflies and the spurge on which they breed. Euphorbia has a bright orange color, and monarch butterflies mimic its coloration on their wings. This allows them to safely feed and breed on milkweed without being endangered by predators.
Another example of mimicry butterflies and their hosts are caterpillar butterflies and ants. Caterpillar butterflies are yellow in color and emit a strong odor similar to that of ants. They mimic the behavior of ants to confuse predators. Ants, seeing these butterflies, do not attack them, as they take them for their relatives.
Thus, mimicry butterflies and their owners have developed complex relationships that allow them to survive in a harsh world. Thanks to the ability of mimicry, these butterflies can safely stay on their owners, avoiding danger and ensuring their survival.
Mimicry and symbiosis: how is it related?

Mimicry and symbiosis are two different phenomena, but they can be linked in the animal and plant worlds. Mimicry is a survival strategy where one organism mimics another in appearance to gain an advantage. Symbiosis, on the other hand, is a relationship between two different organisms in which each benefits.
One form of mimicry is Müllerian mimicry, when one animal species imitates another species that is toxic or has an unpleasant smell. In this way, the mimic animal protects itself from predators, who avoid it, thinking that it is also dangerous. In this case, mimicry helps the animal survive and protects it from enemies.
Symbiosis is a collaboration between two organisms that benefits each of them. For example, a symbiosis between a plant and an insect can be mutually beneficial: the plant provides food or a nesting site for the insect, and in return, the insect pollinates the flowers of the plant. In this case, symbiosis helps both organisms to survive and reproduce.
Interestingly, in some cases, mimicry and symbiosis can be intertwined. For example, there are species of butterflies that mimic other species to avoid predators. However, these butterflies can also work with ants to protect them from enemies. Thus, they use both mimicry and symbiosis to ensure their survival.
Thus, mimicry and symbiosis can be linked in the world of animals and plants. Mimicry helps organisms survive by mimicking dangerous or nasty species. Symbiosis is a collaboration between two organisms that benefits each of them. Sometimes these two phenomena can intertwine, which further increases the chances of survival and reproduction of organisms.
The evolution of mimicry in butterflies

Mimicry is a fascinating adaptive strategy that various butterfly species use to survive in a harsh world. This evolutionary adaptation allows them to deceive and protect themselves from predators by appearing like other dangerous or unsightly species.
Mimicry can be of two types: targeting and protective. In the first case, the butterfly imitates a dangerous species in order to divert the attention of a predator and avoid an attack. For example, some species of butterflies imitate bright and poisonous beetles or wasps to scare away birds and other predators.
The second type of mimicry is protective — is an imitation of other species that pose a danger to predators. For example, some butterflies imitate leaves or branches to hide from enemies, while others imitate birds to be unnoticeable and not attract attention.
The process of evolution of mimicry in butterflies is the result of natural selection. Initially, in a population of butterflies, individuals with different colors and patterns on the wings may be present. Those individuals that looked more like dangerous or unpleasant species were more likely to survive and pass on their genes to the next generation.
Thus, the evolution of mimicry in butterflies is the result of a long selection process that allows them to survive in a harsh world. Mimicry helps butterflies deceive predators and protect themselves from them, providing them with a high probability of survival and reproduction.
Mimicry butterflies: who are they and how do they survive?
Mimicry butterflies are amazing creatures of nature that are able to imitate the appearance of other animals or objects to survive in a harsh world. They use various mimicry strategies to deceive predators and evade danger.
One of the most well-known forms of mimicry in butterflies is the imitation of poisonous species. They mimic the bright colors and patterns of poisonous butterflies to intimidate predators and protect themselves. Some mimicry butterflies even produce poison-like chemicals to enhance the illusion.
Another mimicry strategy is to imitate the environment. Some mimicry butterflies mimic leaves, tree bark, or flowers to blend in with their environment and become indistinguishable to predators. They may also mimic eyes or other patterns to draw the predator's attention away from their vulnerable body.
Some mimicry butterflies use mimicry to obtain food. They may imitate flowers or fruits to attract pollinating insects and use them as a food source. Thus, they deceive not only predators, but also their neighbors in the ecosystem.
Mimicry butterflies show amazing evolutionary adaptations and the ability to survive in a harsh world through trickery. Their diversity and beauty is amazing, and their mimicry is an important factor in their survival and success in nature.






