
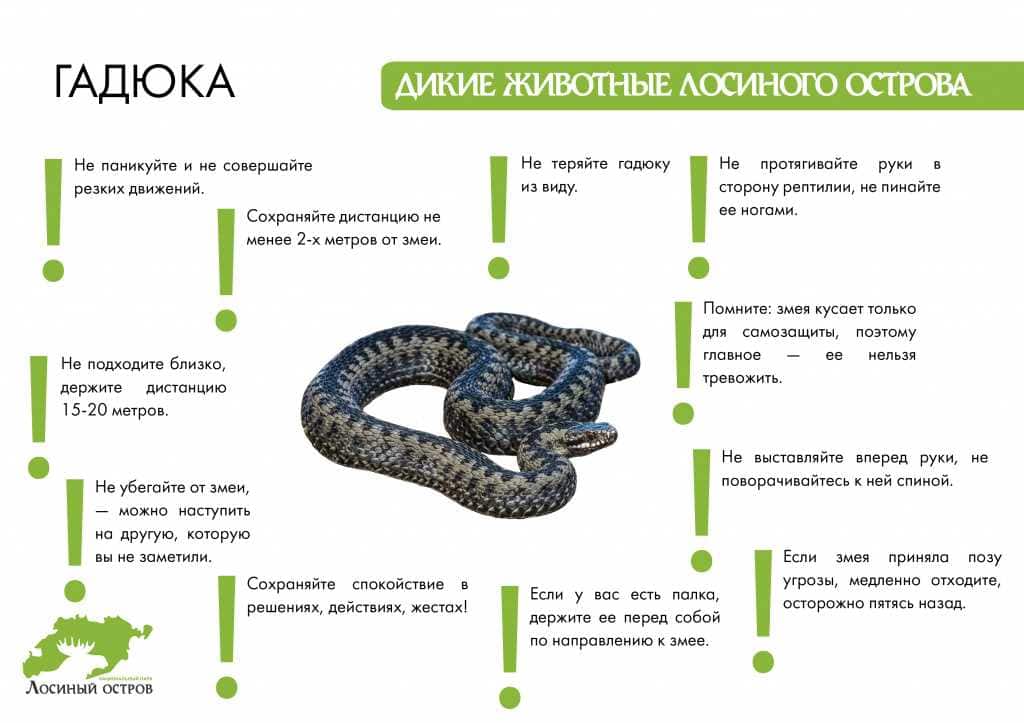
Poisonous butterflies — amazing creatures that attract attention with their beauty and exquisite patterns on their wings. But why do they need toxicity and what advantages does it give them? Research shows that toxicity in poisonous butterflies is a defense mechanism that helps them survive in harsh natural conditions.
The toxicity of poisonous butterflies is the result of an evolutionary process that allowed them to develop poison as a way of repelling and protecting themselves from predators. The poison contained in their body can be dangerous to other animals and even humans. This is a powerful signal for predators who, sensing the smell or taste of poison, understand that the butterfly is poisonous and should not be touched.
The benefits of poisonousness for poisonous butterflies are quite significant. Firstly, they can safely graze on plants without fear of being eaten by other insects or birds. Due to their toxicity, they become unsuitable for consumption and become "forbidden food" for predators. Thus, poisonous butterflies have a better chance of surviving and continuing their species.
In addition, toxicity is a kind of warning for other butterflies and insects. They see colorful patterns on the wings of poisonous butterflies and know that it is better not to approach them. Such "advertisement" of toxicity allows poisonous butterflies to protect themselves from potential enemies, without wasting extra energy on the struggle for survival.
Thus, toxicity for poisonous butterflies is not only a way of protection, but also an effective mechanism for survival and continuation of their species. Their beautiful but dangerous wings serve not only as a decoration of nature, but also as a signal for cautious creatures not to come too close to them.
Poisonous butterflies: why are they poisonous and what advantages does it give them?

Poisonous butterflies are one of the brightest and most beautiful representatives of insects. They possess a venom that serves several important functions in their lives. First, venom is a defense mechanism that helps butterflies avoid predators. Many species of poisonous butterflies have bright colors, which serve as a signal to predators that they are dangerous and inedible.
Poisonousness also helps poisonous butterflies in finding breeding partners. Some species of poisonous butterflies secrete pheromones that attract the opposite sex. At the same time, toxicity serves as a signal to partners that the butterfly is healthy and capable of reproduction.
In addition, the poisonousness of poisonous butterflies is a means of protection against diseases and parasites. The venom contains substances that can kill or repel microorganisms or parasites that could harm the butterfly.
Thus, toxicity in poisonous butterflies is an integral part of their survival and reproduction. It helps them avoid predators, attract mates, and protect themselves from diseases and parasites. Beautiful coloring and poisonousness make these butterflies unique and protected creatures that attract attention and surprise people.
What are poisonous butterflies and what do they look like?
Poisonous butterflies - These are species of butterflies that have a toxic substance that serves them as protection from predators. They belong to the Nymphalidae family and number about 600 species. Poisonous butterflies live in tropical and subtropical regions of South America, Africa and Asia.
The appearance of poisonous butterflies can vary significantly depending on the species. However, they share some common features. The body of poisonous butterflies is usually small, painted in bright and rich colors such as orange, red, yellow or blue. This is a kind of warning to predators about their toxicity.
One of the most famous poisonous butterflies is the monarch. Her wings are bright orange with black veins and white dots on the edges. Another popular species is the heliconia, which is distinguished by its long and narrow wings with floral patterns. Another interesting poisonous butterfly is the blue-winged snakehead, whose wings are greenish-blue with black stripes and spots.
Thus, poisonous butterflies attract attention with their colorful colors and variety of shapes. They exemplify evolutionary adaptations that allow them to survive and protect themselves from predators.
Why do poisonous butterflies need poisonousness?

Poisonous butterflies secrete special toxic substances that help them protect themselves from predators and ensure their survival in unpleasant conditions. Venom is a unique adaptation of these butterflies that helps them survive in harsh natural environments.
The toxicity of poisonous butterflies provides them with reliable protection from predators. When a predator tries to eat a poisonous butterfly, he feels the bitter taste of the poison and experiences unpleasant sensations. This forces the predator to give up trying to eat the poisonous butterfly, which contributes to its survival.
Poisonousness also helps poisonous butterflies establish their territory and defend it from competitors. They can use toxic substances to emit a specific odor that alerts other butterflies to the presence of danger and indicates their presence.
In addition, the toxicity of poisonous butterflies plays an important role in their reproduction. The males of these butterflies can pass venom on to their offspring, which helps them strengthen their defenses and increase their chances of survival. This transfer of poison is a kind of hereditary mechanism that contributes to the preservation and development of the population of poisonous butterflies.
To summarize, venom is an important protective adaptation for poisonous butterflies that helps them survive in harsh natural environments. It provides them with protection from predators, helps establish territory, and is involved in reproduction. The toxicity of poisonous butterflies is a unique and effective mechanism that helps them adapt to life in the environment.
What poisons are used in poisonous butterflies?

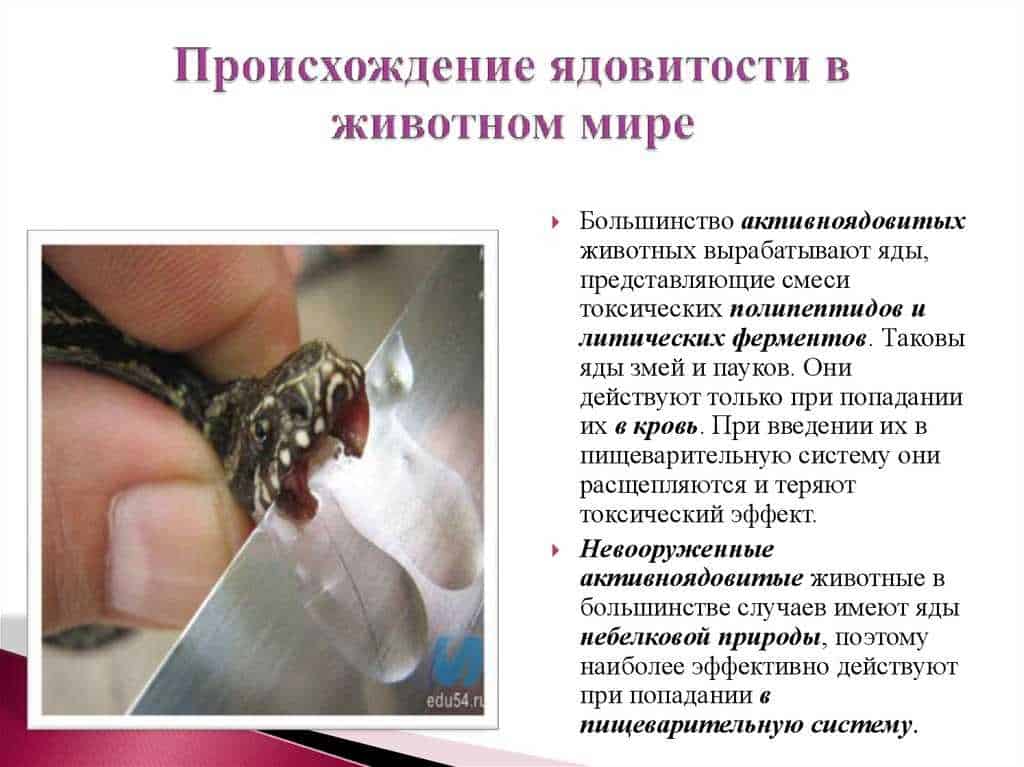
Poisonous butterflies known for their ability to use various poisons for self-defense. They produce toxic substances that can repel predators or even kill them. As a rule, the poisons of poisonous butterflies are a mixture of various toxic compounds.
One of the most famous poisons used by poisonous butterflies is called cyanide. This is a very strong toxic compound that can cause serious disruptions in the functioning of the body. Cyanide is contained in the plants that these butterflies feed on, and they are able to accumulate it in their tissues.
In addition to cyanide, poisonous butterflies can use other toxic substances. For example, they may contain compounds in their tissues called alkaloids. Alkaloids are very powerful poisons that can cause paralysis or even death in predators.
Some species of poisonous butterflies may also use poisonous compounds that they obtain from sources other than plants. For example, they can collect poisons from the fruits of rotten trees or the waste of other insects. This allows them to expand their arsenal of poisons and be more effective in fighting predators.
How poisonous butterflies protect themselves with poisonousness
Poisonous butterflies are one of the most dangerous insects on the planet. They protect themselves, as well as their territories and offspring, with poisonous substances that have various benefits.
One of the main ways that poisonous butterflies protect themselves is through a kind of “danger signal” that they transmit through their bright colors. Bright colors such as bright red, orange or yellow are a warning to potential predators. This color indicates the presence of toxic substances in the butterfly’s body, and forces predators to leave it alone.
Another method of self-defense of poisonous butterflies is mimicry. Some species of poisonous butterflies have very similar colors to other, non-poisonous species of butterflies. Thus, they disguise themselves as harmless fellows, and predators familiar with poisonous species are careful not to attack even non-poisonous individuals, so as not to risk eating a poisonous butterfly.
Also, the poisonousness of butterflies can be used to protect offspring. Some species of poisonous butterflies lay their eggs on certain plants that contain toxic substances. When a poisonous caterpillar eats such a plant, it becomes poisonous. In this way, the caterpillars and their pupae also receive protection from predators.
In general, venom is an effective self-defense strategy for butterflies. She helps them stay alive and continue to exist, despite the presence of numerous predators in their environment.
Advantages of poisonousness in poisonous butterflies

Poisonous butterflies have bright colors and a variety of patterns on their wings. This is one of the main advantages of venomousness in these butterflies. The bright coloring serves as a warning to potential predators, indicating that they are dangerous and not suitable for consumption.
In addition, the toxicity of poisonous butterflies protects them from attacks by their relatives. This is due to territorial behavior and competition for resources. Poisonous butterflies can scare away and attack competitors, giving themselves an advantage in the fight for territory and food.
In addition, toxic substances contained in the body of poisonous butterflies can be used to protect their offspring. Eggs and caterpillars may also have poisonous properties, which warns predators of possible dangers and promotes the survival of young individuals.
It is interesting that the toxicity of poisonous butterflies can vary among different species. This allows them to adapt to different conditions and habitats. Some poisoners may have bright red markings on their wings that serve as a warning that they are poisonous, while other species may have hidden coloration that allows them to remain undetected and pretend to be harmless.
In general, venom in poisonous butterflies plays an important role in their survival and protection from predators. It helps them avoid attacks, compete for resources and ensure the continuation of their lineage over generations.
The influence of toxicity on the behavior and interaction of poisonous butterflies

Toxicity is one of the key adaptive properties of poisonous butterflies and plays an important role in their behavior and interaction with the environment. The main purpose of toxicity in these butterflies is protection from predators and ensuring survival in the wild.
The poisonous substances contained in the body of poisonous butterflies have a repulsive effect on predators. When a predator tries to attack a butterfly, it experiences unpleasant sensations, such as nausea or stomach pain, and associates these sensations with a certain external feature - the coloring or pattern on the butterfly's wings.
Thus, toxicity becomes a kind of "protective suit" for poisonous butterflies, providing them with protection from predators. However, to effectively use toxicity, butterflies also need to have certain behaviors and strategies for interacting with the environment.
Poisonous butterflies often display bright colors and patterns on their wings, which serves as a signal to predators that poison is present. This type of coloration is called aposematic coloration and helps warn a potential predator of the possible negative consequences of attacking the butterfly.
An important part of the behavior of poisonous butterflies is also mimicry - the ability to imitate other species that carry poison. Some poisonous butterflies imitate the appearance and coloring of other, in fact, poisonous butterfly species. This allows them to deceive predators, making them believe that they are also poisonous and do not pose a threat.
Thus, toxicity in poisonous butterflies plays an important role in their behavior and interaction with the environment. It helps them avoid predators and ensure survival in the wild, and also allows them to use various strategies, such as aposematic coloration and mimicry, to deceive potential threats.






