The world is inhabited by many different types of butterflies, each of which has its own unique features and behavioral characteristics. One of the most amazing phenomena in the world of butterflies is their migration and reproduction. Every year, millions of butterflies make long flights, overcoming vast distances and obstacles, to find the perfect place to breed.
One of the key factors influencing butterfly migration is the availability of food. Traveling butterflies prefer to lay their eggs on rotten fruit, which is a food source for their caterpillars. Rotten fruits have a high sugar content, which is a necessary condition for the development of caterpillars and their subsequent transformation into pupae and butterflies.
Butterfly migration is also associated with changes in climate and seasonal changes. Already ancient people noticed that butterflies appear and disappear at certain times of the year. However, it was only with the advent of modern scientific methods that it was possible to establish that the migration of butterflies is associated with a change in the length of the day and the ambient temperature. Some species of butterflies migrate thousands of miles across mountains, rivers and oceans in search of ideal conditions for reproduction and survival.
However, butterfly migration has become threatened due to human intervention in natural ecosystems. The destruction of their natural habitat, air pollution and the use of pesticides lead to a decrease in the number and diversity of butterflies. It is important to preserve their migratory routes and provide conditions for their reproduction in order to preserve the amazing phenomenon of butterfly migration for future generations.
Traveler Butterflies and Rotten Fruit
The migration of traveling butterflies is a phenomenon that fascinates nature researchers. Every autumn, thousands of butterflies embark on a long journey south to escape the cold winter months. They seek warmer climates and abundant food for their offspring.
One of the main reasons for the migration of traveling butterflies is the lack of food. As autumn sets in, many of the plants that serve as a food source for butterflies begin to wither and die. Butterflies that remain in place face the problem of nutrient deficiencies, which can lead to their death.
However, not all butterflies leave their native places. Some of them find other food sources - rotten fruits. Rotten fruits, such as overripe apples or pears, contain a lot of sugars and other nutrients that are ideal food for butterflies. They can stay in place and satiate themselves with these fruits until spring comes and new plants begin to grow.
Interestingly, rotten fruits also play an important role in the reproduction of traveling butterflies. Female butterflies lay their eggs on rotten fruit, where they can safely develop and obtain the necessary nutrients. When the larvae hatch, they may feed on fruit for some time before turning into a chrysalis and then into a butterfly.
Thus, the migration of traveling butterflies and their use of rotten fruits as a source of food and a place for reproduction is an amazing phenomenon that allows these beautiful insects to survive and preserve their species.
Migration of traveling butterflies
Traveler butterfly migration is an amazing phenomenon that happens every year. They travel vast distances, flying over oceans and mountains to reach their destination. The main reason for migration is the search for suitable conditions for reproduction and feeding.
Journey starts from warm countrieswhere butterflies spend the winter. When spring arrives, they begin their long journey north in search of fresh greenery and suitable plants for laying eggs. Butterflies-travelers can travel huge distances, covering several thousand kilometers.
During their travels, butterflies use different strategies to overcome obstacles and find their way to their destination. One such strategy is to use thermal vents to help them climb to heights and cross mountains. They can also use the wind to get to their target faster.
The migration of traveling butterflies has not only practical, but also aesthetic value. Thousands of colorful butterflies flying together create a unique spectacle. In addition, they play an important ecological role by pollinating plants and participating in the food cycle of many animals.
Conservation of Traveling Butterfly Migration
However, migrating butterflies are becoming increasingly vulnerable due to habitat destruction and the use of pesticides. To save this amazing phenomenon, it is necessary to take measures to protect and restore their habitat.
One way is to create special reserves and parks where butterflies can find suitable conditions for breeding and feeding. It is also important to limit the use of pesticides and take steps to conserve vegetation, which is a food source for butterflies.
Migration of traveling butterflies is a unique and amazing natural phenomenon that needs to be protected and preserved for future generations. Only by working together can we ensure that their routes are preserved and that these colorful female travelers continue to delight us with their presence and fulfill their important ecological role.
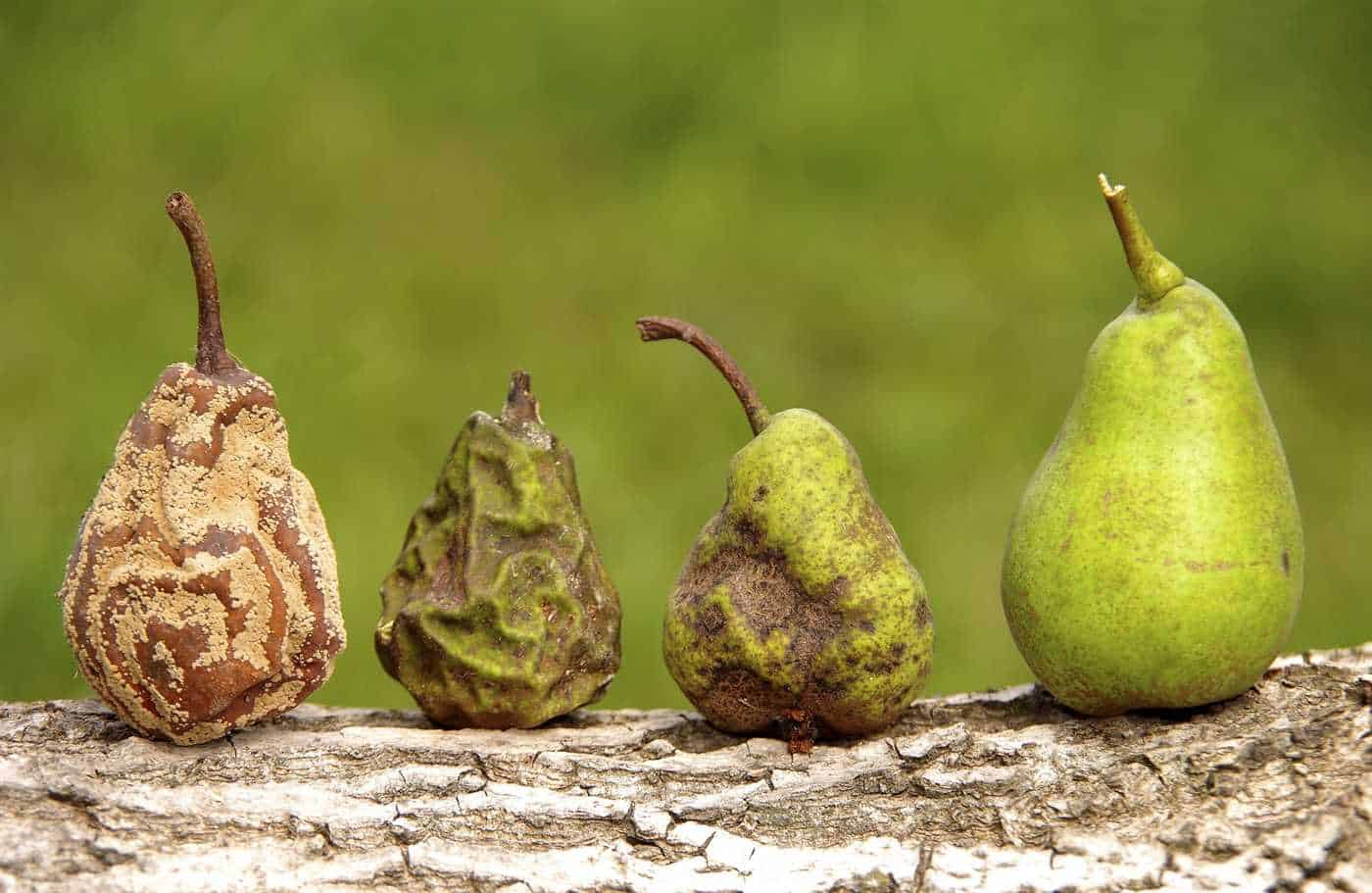
Rotten Fruit Breeding Secrets

The reproduction of rotten fruit is a complex process that requires certain conditions and factors. One of the main secrets of the successful reproduction of rotten fruit is the presence of special microorganisms that live on the surface of the fruit and participate in the decomposition of its pulp.
Power supply: Rotten fruits are an excellent food source for many types of microorganisms. They contain a large amount of sugars and other nutrients that promote the active reproduction of bacteria and fungi.
Spread of spores: Rotten fruits also play an important role in the spread of microbial spores. As the fruit begins to rot, the microorganisms on its surface release spores that can be carried by wind, insects, or birds to other fruits and plants.
Environmental conditions: Rotten fruit requires certain environmental conditions to successfully propagate. Humidity, temperature, and oxygen availability all affect the rate and efficiency of fruit decomposition and microbial growth.
Defense mechanisms: Some rotten fruits have defense mechanisms that help them survive and reproduce. For example, some types of fruit produce special chemicals that kill or retard the growth of microorganisms, preventing them from multiplying.
Interaction with animals: Some rotten fruits attract animals that help in their reproduction. For example, some types of fruit contain a sweet smell that attracts insects. Animals that feed on rotten fruit may inadvertently transfer microbial spores to other plants, allowing them to multiply.
Impact of migration on the population of traveling butterflies

Migration is one of the important components of the life cycle of traveling butterflies and has a significant impact on their population. Migration allows these insects to find new food sources and breeding sites, as well as avoid adverse environmental conditions.
During migration, traveling butterflies cover considerable distances, crossing oceans, mountains and deserts. They use various landmarks such as the sun, stars, and the earth's magnetic field to find their way. This allows them to find optimal environmental conditions for survival and reproduction.
Migration also contributes to the genetic diversity of the traveling butterfly population. Traveling long distances, they meet with individuals from other regions, which leads to interbreeding and the exchange of genetic material. This allows them to adapt to different environmental conditions and increases their chances of surviving in a changing climate.
However, migration can also pose a risk to the traveling butterfly population. Their path can be blocked by road construction, fences and other obstacles, which can lead to their death. Therefore, it is important to preserve and restore migratory routes and create reserves where traveling butterflies can migrate and breed freely.
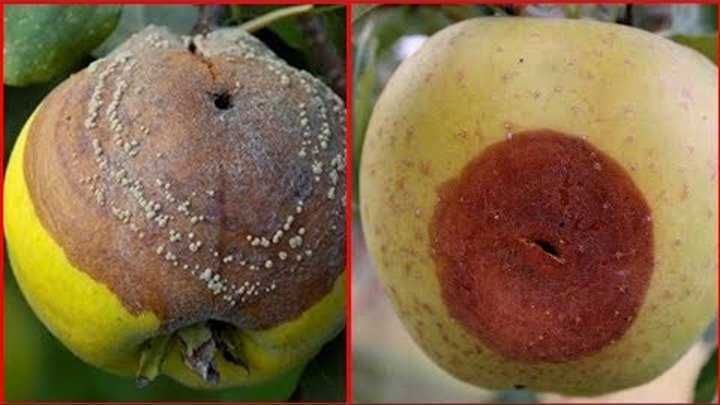
The role of rotten fruit in the life cycle of butterflies
Rotten fruits play an important role in the life cycle of butterflies. They become an attractive food source and breeding ground for many species of butterflies.
When fruits begin to rot, they give off a specific odor that attracts butterflies. This smell can only be felt by butterflies or other insects that are their predators. Butterflies use their sensitive antennae to detect this scent and locate the food source.
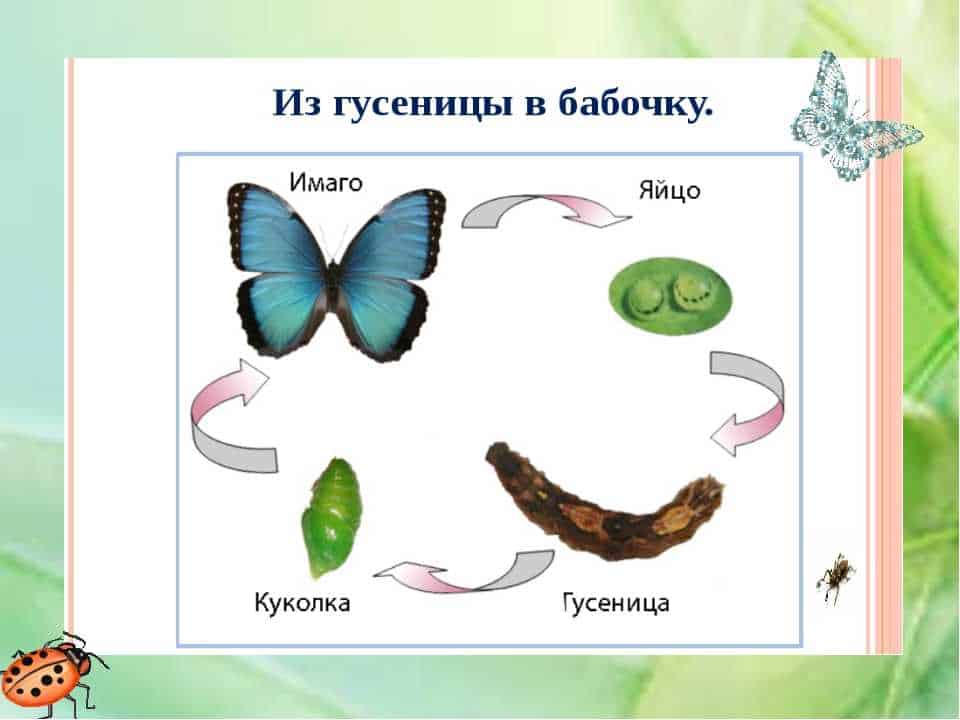
When a butterfly finds a rotten fruit, it can use it not only as food, but also as a place to lay its eggs. Rotten fruits provide ideal conditions for the development of butterfly larvae. They provide nutrients, moisture, and protection from predators.
After laying eggs on rotten fruits, butterfly larvae begin to develop. They feed on the pulp of fruits and gradually go through several stages of development, turning into pupae. The pupae usually attach themselves to or near the surface of rotten fruit, where they are less likely to be found and eaten by predators.
When the chrysalis is fully formed, it hatches into an adult butterfly. Adult moths usually stay close to a food source and breeding site to continue the breeding cycle. They can also carry pollen from one rotten fruit to another, aiding pollination and plant dispersal.
Adaptation of traveling butterflies to different climatic conditions
Traveler butterflies are species of butterflies that make long migrations in order to find sufficient food and suitable breeding conditions. They have unique adaptation mechanisms that allow them to survive in various climatic conditions.
1. Mechanisms of thermoregulation
Traveling butterflies have the ability to regulate their body temperature to survive in different climates. They use thermoregulatory mechanisms, such as solar panels on their wings, to get heat from the sun's rays and maintain the optimum temperature for their activity.
2. Adaptation to lack of food

Traveling butterflies migrate long distances to find enough food. They are able to adapt to the lack of food, allowing them to live in conditions where vegetation is limited. They may use various food sources, such as the juices of rotten fruits or the nectar from the flowers of various plants.
3. Ability to find suitable breeding sites

Traveling butterflies have an amazing ability to find suitable breeding sites. They are able to detect optimal conditions such as the presence of suitable food for caterpillars, the presence of protective hiding places, and the absence of predators. They can use various signals and marks in the environment to determine the appropriate place to lay their eggs.
Thus, traveler butterflies have unique adaptation mechanisms that allow them to survive and reproduce in various climatic conditions. Their ability to thermoregulate, adapt to food scarcity, and find suitable breeding sites make them successful travelers and survivors in a variety of environments.
Environmental impact on the reproduction of rotten fruit
The environment plays an important role in the reproduction of rotten fruit. As the fruit begins to rot, it becomes a source of nutrients for various organisms such as fungi, bacteria, and insects.
Fruit rot occurs due to the presence in the environment of certain microorganisms that decompose organic matter inside the fruit mass. These micro-organisms can enter the fruit through damaged skins or through small cracks on the surface.
Rotten fruit is an ideal breeding ground for fungi and bacteria. They provide the necessary moisture and nutrition for the development of these organisms. Mushrooms can form spores that spread in the environment and can infect other fruits.
Insects also play an important role in the propagation of rotten fruit. They can feed on rotten mass, as well as transfer fungal spores to other fruits. Some insects, such as flies and wasps, are pollinators and can help spread fungal spores.
So, the environment plays an important role in the reproduction cycle of rotten fruit. It provides the necessary conditions for the development of fungi, bacteria and insects that interact with each other, spreading and influencing other fruits. Understanding this process can help develop methods to control and prevent the growth of rotten fruit.
The Importance of Preserving Migratory Sites for Traveling Butterflies and Rotten Fruit
The migration of traveling butterflies and reproduction on rotten fruits are important processes in nature. Traveling butterflies act as pollinators for many plants, providing pollen distribution and plant diversity. Rotten fruits, in turn, are a source of food for many animal species, including birds, mammals, and insects. Therefore, the conservation of migratory habitats for traveling butterflies and rotten fruits plays an important role in maintaining biodiversity and ecosystem sustainability.
Traveling butterfly migration areas are unique ecosystems that provide favorable conditions for their reproduction and rest. In these places, butterflies find food and suitable conditions for laying eggs. They are also on the migration path of other animal species, making them even more important for biodiversity conservation. Therefore, the protection and protection of the migration sites of traveling butterflies is an integral part of nature conservation and maintaining ecological balance.
Rotten fruits, in turn, play an important role in the ecosystem, as they serve as a source of food for many animals. They attract insects that spread plant pollen and are food for other animals such as birds and mammals. Rotten fruits also serve as a breeding ground for some types of insects and eggs. Therefore, the conservation of rotten fruits and their habitats is of great importance for the maintenance of biodiversity and the functioning of ecosystems.